Compounds for Stem Cell Differentiation Products
Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into specialized cell subtypes depending upon their level of potency. For instance, embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells can give rise to cells of all three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Adult stem cells are generally considered to have limited potency and differentiate into a restricted number of cell types. In order to generate populations of specialized cell types for regenerative medicine, drug screening, or disease and development models, researchers must control and direct the differentiation of stem cells. Cell fate decisions can be directed by natural or chemically synthesized small molecules. For instance, a specific inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta can induce neuronal differentiation in pluripotent stem cells. Combinations of specific cytokines and sodium butyrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, have been shown to direct the differentiation of stem cells into hepatocytes. Tocris provides a complete range of bioactive small molecules to control the differentiation of stem cells into defined derivatives.
52 results for "Compounds for Stem Cell Differentiation" in Products
52 results for "Compounds for Stem Cell Differentiation" in Products
Compounds for Stem Cell Differentiation Products
Stem cells have the ability to differentiate into specialized cell subtypes depending upon their level of potency. For instance, embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells can give rise to cells of all three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. Adult stem cells are generally considered to have limited potency and differentiate into a restricted number of cell types. In order to generate populations of specialized cell types for regenerative medicine, drug screening, or disease and development models, researchers must control and direct the differentiation of stem cells. Cell fate decisions can be directed by natural or chemically synthesized small molecules. For instance, a specific inhibitor of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta can induce neuronal differentiation in pluripotent stem cells. Combinations of specific cytokines and sodium butyrate, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, have been shown to direct the differentiation of stem cells into hepatocytes. Tocris provides a complete range of bioactive small molecules to control the differentiation of stem cells into defined derivatives.
γ-secretase inhibitor; induces neuronal differentiation; blocks Notch signaling
| Chemical Name: | (2S)-N-[(3,5-Difluorophenyl)acetyl]-L-alanyl-2-phenyl]glycine 1,1-dimethylethyl ester |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
Adenylyl cyclase activator
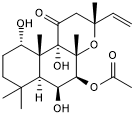
| Chemical Name: | (3R,4aR,5S,6S,6aS,10S,10aR,10bS)-5-(Acetyloxy)-3-ethenyldodecahydro-6,10,10b-trihydroxy-3,4a,7,7,10a-pentamethyl-1H-naphtho[2,1-b]pyran-1-one |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Potent and selective ALK2 and ALK3 inhibitor; inhibits BMP4 signaling; promotes neural induction of hPSCs
| Chemical Name: | 4-[6-[4-(1-Piperazinyl)phenyl]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl]quinoline dihydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Potent AMPK inhibitor; also BMP type I receptor inhibitor
| Alternate Names: | Compound C,BML-275 |
| Chemical Name: | 6-[4-[2-(1-Piperidinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]-3-(4-pyridinyl)-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine dihydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
DMSO, sterile filtered, wide ranging applications in cell culture, cryopreservation and organic chemistry. Solvent for polar and nonpolar compounds
| Alternate Names: | Methyl sulfoxide |
| Chemical Name: | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Purity: | ≥99.9% |
Selective ALK2 inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | 4-[6-[4-(1-Methylethoxy)phenyl]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl]-quinoline |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Endogenous retinoic acid receptor agonist
| Alternate Names: | Tretinoin,ATRA |
| Chemical Name: | 3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2E,4E,6E,8E,-nonatetraenoic acid |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Intracellular cryoprotective agent
| Chemical Name: | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| Purity: | ≥99.9% |
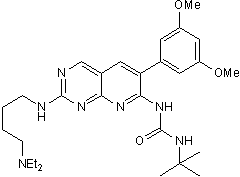
FGFR1 and -3 inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | N-[2-[[4-(Diethylamino)butyl]amino]-6-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-yl]-N'-(1,1-dimethylethyl)urea |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid
| Chemical Name: | (11β,16α)-9-Fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methyl-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Glutathione (GSH) precursor; maintains stem cell function in culture.
| Chemical Name: | (2R)-2-Acetamido-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Endogenous agonist of LPA1 and LPA2
| Chemical Name: | 1-O-9Z-Octadecenoyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphoric acid sodium salt |
LDN 193189 synthesized to cGMP guidelines
| Chemical Name: | 4-[6-[4-(1-Piperazinyl)phenyl]pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl]quinoline dihydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥99% |
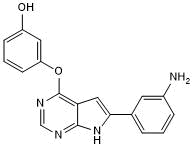
Potent GSK3 inhibitor; induces neuronal and CD8(+) T cell differentiation
| Chemical Name: | 3-[[6-(3-Aminophenyl)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]oxy]phenol |
| Purity: | ≥97% (HPLC) |
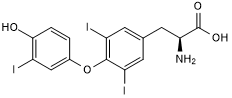
Thyroid hormone; also promotes differentiation of oligodendroglial precursor cells
| Chemical Name: | O-(4-Hydroxy-3-iodophenyl-3,5-diiodo-L-tyrosine |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
AMPK activator
| Chemical Name: | N1-(β-D-Ribofuranosyl)-5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
Selective JNK inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | Anthra[1-9-cd]pyrazol-6(2H)-one |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Smo receptor agonist
| Chemical Name: | 9-Cyclohexyl-N-[4-(4-morpholinyl)phenyl]-2-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-9H-purin-6-amine |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
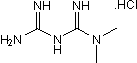
Activator of LKB1/AMPK; antidiabetic agent
| Chemical Name: | N,N-Dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide hydrochloride |
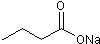
Histone deacetylase inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | Butanoic acid sodium salt |
DAPT synthesized to Ancillary Material Grade
| Chemical Name: | (2S)-N-[(3,5-Difluorophenyl)acetyl]-L-alanyl-2-phenylglycine 1,1-dimethylethyl ester |
| Purity: | ≥99% |
PDE inhibitor (non-selective)
| Chemical Name: | 3,7-Dihydro-1-methyl-3-(2-methylpropyl)-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Ascorbic acid derivative; maintains differentiation potential in bone marrow-derived MSCs
| Chemical Name: | 2-(Dihydrogen phosphate)-L-ascorbic acid sodium salt |
| Purity: | ≥95% (HPLC) |
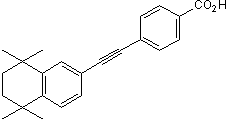
Synthetic retinoid; induces differentiation of stem cells
| Chemical Name: | 4-[2-(5,6,7,8-Tetrahydro-5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-2-naphthalenyl)ethynyl)-benzoic acid |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
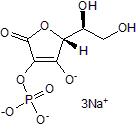
Promotes ESCs/iPSCs differentiation into pancreatic endocrine islet cells
| Chemical Name: | 5,5'-[(2-Hydroxy-1,3-propanediyl)bis(oxy)]bis[4-oxo-4H-1-benzopyran-2-carboxylic acid] disodium salt |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |