TNF-alpha: Small Molecules and Peptides
TNF-alpha (Tumor necrosis factor alpha) plays a central role in inflammation, immune system development, apoptosis, and lipid metabolism. TNF-alpha was first identified as a cytotoxic factor produced by macrophages capable of killing mouse tumor cells. It is the prototypic ligand and along with Lymphotoxin-alpha, were identified as the first members of the TNF superfamily. Active TNF-alpha and other members of the TNF superfamily exist as a homotrimer with high structural homology. Receptor binding occurs at the interface of two TNF-alpha monomers. And receptor activation occurs when all three monomer interfaces are engaged with a receptor. For TNF-alpha, receptor binding and activation occurs through TNF R1 or TNF RII, and subsequently leads to activation of NF-kB or MAPK signaling pathways. Another pathway that TNF-alpha can activate utilizes the death domain of TNF RI to induce apoptosis. TNF-alpha promotes the inflammatory response largely through NF-kB signaling, and inhibition of TNF-alpha has proven successful in treating many autoimmune disorders. TNF-alpha is also present on the cell surface as membrane-bound TNF-alpha can induce the lysis of neighboring tumor cells and virus infected cells. TNF-alpha protein is translated as a type II transmembrane protein containing an N-terminal transmembrane domain. The soluble cytokine is released from its cell-anchoring TM domain by proteolytic processing by metalloproteases.
11 results for "TNF-alpha Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
11 results for "TNF-alpha Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
TNF-alpha: Small Molecules and Peptides
TNF-alpha (Tumor necrosis factor alpha) plays a central role in inflammation, immune system development, apoptosis, and lipid metabolism. TNF-alpha was first identified as a cytotoxic factor produced by macrophages capable of killing mouse tumor cells. It is the prototypic ligand and along with Lymphotoxin-alpha, were identified as the first members of the TNF superfamily. Active TNF-alpha and other members of the TNF superfamily exist as a homotrimer with high structural homology. Receptor binding occurs at the interface of two TNF-alpha monomers. And receptor activation occurs when all three monomer interfaces are engaged with a receptor. For TNF-alpha, receptor binding and activation occurs through TNF R1 or TNF RII, and subsequently leads to activation of NF-kB or MAPK signaling pathways. Another pathway that TNF-alpha can activate utilizes the death domain of TNF RI to induce apoptosis. TNF-alpha promotes the inflammatory response largely through NF-kB signaling, and inhibition of TNF-alpha has proven successful in treating many autoimmune disorders. TNF-alpha is also present on the cell surface as membrane-bound TNF-alpha can induce the lysis of neighboring tumor cells and virus infected cells. TNF-alpha protein is translated as a type II transmembrane protein containing an N-terminal transmembrane domain. The soluble cytokine is released from its cell-anchoring TM domain by proteolytic processing by metalloproteases.
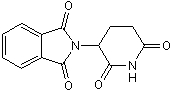
Binds cereblon; also TNF-α synthesis inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | N-(2,6-dioxo-3-piperidinyl)phthalimide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
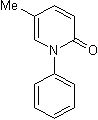
Antifibrotic agent; regulates cytokine levels in vivo
| Chemical Name: | 5-methyl-1-phenyl-2(1H)-pyridinone |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
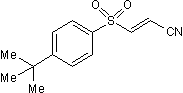
Irreversible inhibitor of TNF-α-induced IκBα phosphorylation
| Alternate Names: | Bay 11-7083 |
| Chemical Name: | (2E)-3-[[4-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)phenyl]sulfonyl]-2-propenenitrile |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
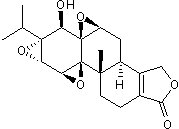
Inhibits RNAPII-mediated transcription; antitumor, anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive
| Chemical Name: | (3bS,4aS,5aS,6R,6aR,7aS,7bS,8aS,8bS)-3b,4,4a,6,6a,7a,7b,8b,9,10-Decahydro-6-hydroxy-8b-methyl-6a-(1-methylethyl)trisoxireno[4b,5:6,7:8a,9]phenanthro[1,2-c]furan-1(3H)-one |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
E2 ubiquitin (Ub) conjugating enzymes inhibitor
| Alternate Names: | Bay 11-7082 |
| Chemical Name: | (2E)-3-[(4-Methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-2-propenenitrile |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Cereblon binder; also TNF-α inhibitor and antiangiogenic
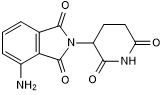
| Chemical Name: | 4-Amino-2-(2,6-dioxo-3-piperidinyl)-1H-isoindole-1,3(2H)-dione |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Active metabolite binds CPSF3; Pro-drug
| Alternate Names: | TO-207 |
| Chemical Name: | N-[3,5-Dichloro-2-hydroxy-4-[2-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)ethoxy]benzoyl]-L-phenylalanine ethyl ester dihydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
IGF-1 synthetic analogue
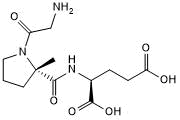
| Chemical Name: | Glycyl-2-methyl-L-prolyl-L-glutamic acid |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation
| Chemical Name: | (9β,13α,14β,20α)-3-Hydroxy-9,13-dimethyl-2-oxo-24,25,26-trinoroleana-1(10),3,5,7-tetraen-29-oic acid |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Potent and selective RIPK3 inhibitor; also blocks activation of necroptosis
| Chemical Name: | 3-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)-1-methyl-7-[[3-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)phenyl]amino]-1,6-naphthyridin-2(1H)-one dihydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Potent and selective Tpl2 (MAP3K8) inhibitor
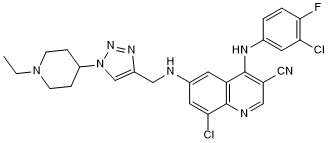
| Chemical Name: | 8-Chloro-4-[(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)amino]-6-[[[1-(1-ethyl-4-piperidinyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl]methyl]amino]-3-quinolinecarbonitrile |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |