TNF-alpha: Proteins and Enzymes
TNF-alpha (Tumor necrosis factor alpha) plays a central role in inflammation, immune system development, apoptosis, and lipid metabolism. TNF-alpha was first identified as a cytotoxic factor produced by macrophages capable of killing mouse tumor cells. It is the prototypic ligand and along with Lymphotoxin-alpha, were identified as the first members of the TNF superfamily. Active TNF-alpha and other members of the TNF superfamily exist as a homotrimer with high structural homology. Receptor binding occurs at the interface of two TNF-alpha monomers. And receptor activation occurs when all three monomer interfaces are engaged with a receptor. For TNF-alpha, receptor binding and activation occurs through TNF R1 or TNF RII, and subsequently leads to activation of NF-kB or MAPK signaling pathways. Another pathway that TNF-alpha can activate utilizes the death domain of TNF RI to induce apoptosis. TNF-alpha promotes the inflammatory response largely through NF-kB signaling, and inhibition of TNF-alpha has proven successful in treating many autoimmune disorders. TNF-alpha is also present on the cell surface as membrane-bound TNF-alpha can induce the lysis of neighboring tumor cells and virus infected cells. TNF-alpha protein is translated as a type II transmembrane protein containing an N-terminal transmembrane domain. The soluble cytokine is released from its cell-anchoring TM domain by proteolytic processing by metalloproteases.
30 results for "TNF-alpha Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
30 results for "TNF-alpha Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
TNF-alpha: Proteins and Enzymes
TNF-alpha (Tumor necrosis factor alpha) plays a central role in inflammation, immune system development, apoptosis, and lipid metabolism. TNF-alpha was first identified as a cytotoxic factor produced by macrophages capable of killing mouse tumor cells. It is the prototypic ligand and along with Lymphotoxin-alpha, were identified as the first members of the TNF superfamily. Active TNF-alpha and other members of the TNF superfamily exist as a homotrimer with high structural homology. Receptor binding occurs at the interface of two TNF-alpha monomers. And receptor activation occurs when all three monomer interfaces are engaged with a receptor. For TNF-alpha, receptor binding and activation occurs through TNF R1 or TNF RII, and subsequently leads to activation of NF-kB or MAPK signaling pathways. Another pathway that TNF-alpha can activate utilizes the death domain of TNF RI to induce apoptosis. TNF-alpha promotes the inflammatory response largely through NF-kB signaling, and inhibition of TNF-alpha has proven successful in treating many autoimmune disorders. TNF-alpha is also present on the cell surface as membrane-bound TNF-alpha can induce the lysis of neighboring tumor cells and virus infected cells. TNF-alpha protein is translated as a type II transmembrane protein containing an N-terminal transmembrane domain. The soluble cytokine is released from its cell-anchoring TM domain by proteolytic processing by metalloproteases.
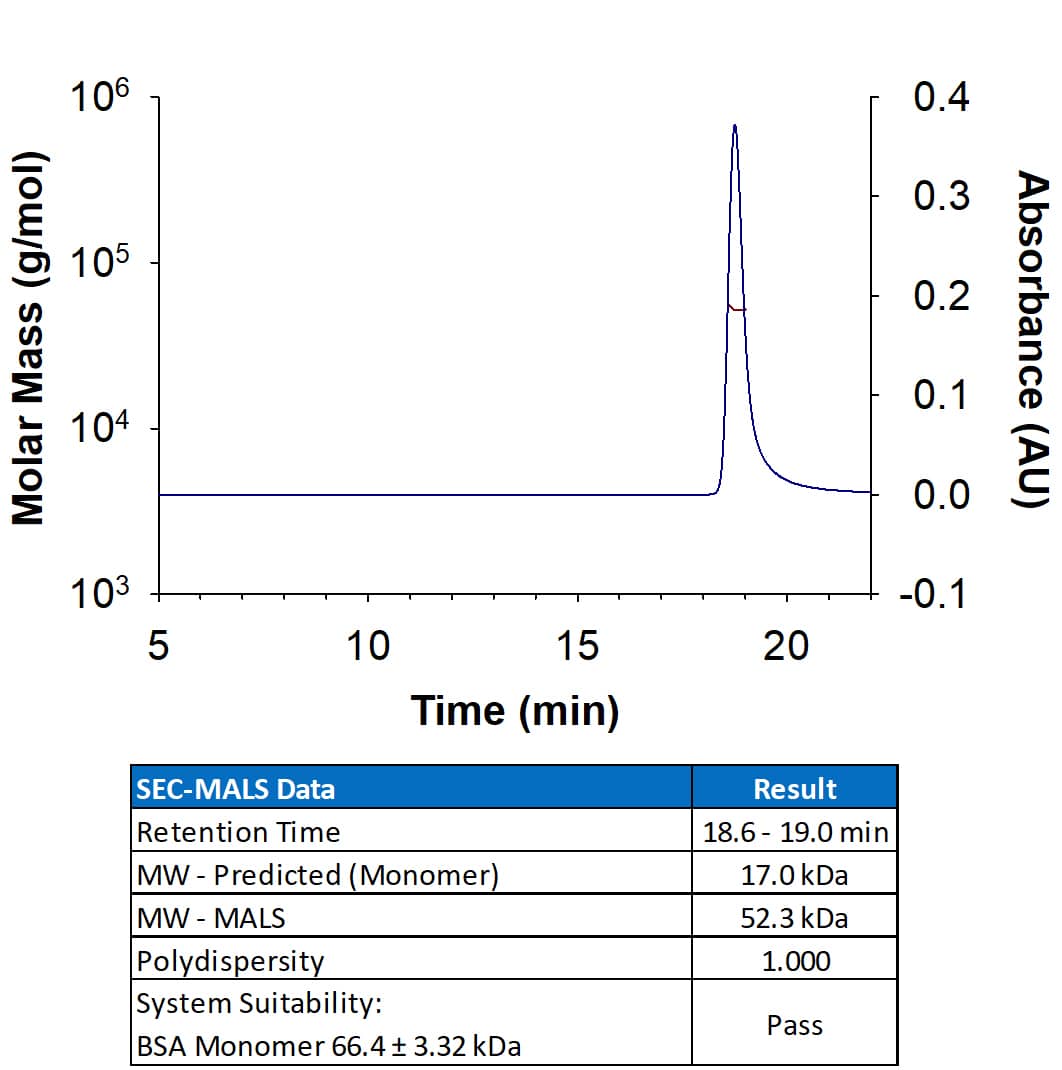
Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P06804 |
| Applications: | BA |
Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | P01375 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P16599 |
| Applications: | BA |
Animal-Free.
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P01375.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | NP_001075732 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P01375 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | Q06599 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | CAA64403 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P23563 |
| Applications: | BA |
Intended for preclinical researchers who may transition to GMP TNF-alpha for their clinical work
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P01375.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated, Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | P01375.1 |
| Applications: | BA, BA, GelChrom |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | NP_001075288 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P06804 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P48094 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Applications: | PAGE, Bioactivity |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | NP_001272206.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Mutant form with approximately 5-fold greater activity
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P01375 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | AAL18818 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P01375 |
| Applications: | EnzAct |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P19101 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P51435 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Applications: | AC |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA |
| Applications: | PAGE |
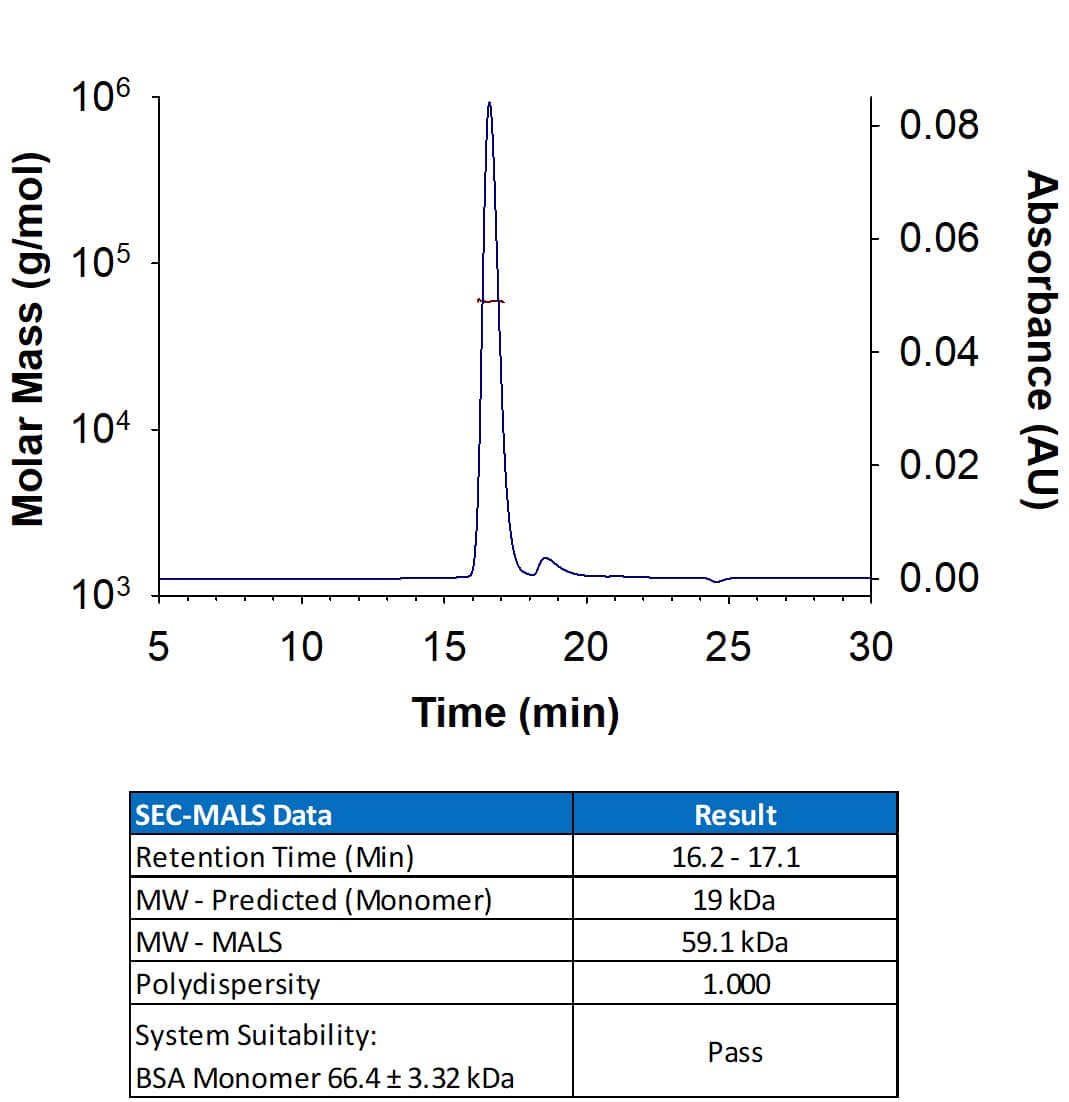
Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | E. coli |
| Accession #: | P01375 |
| Applications: | BA |







![SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Human TNF-alpha Protein [NBC1-18460] SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Human TNF-alpha Protein [NBC1-18460]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Recombinant-Human-TNF-alpha-Protein-SDS-Page-NBC1-18460-img0002.jpg)
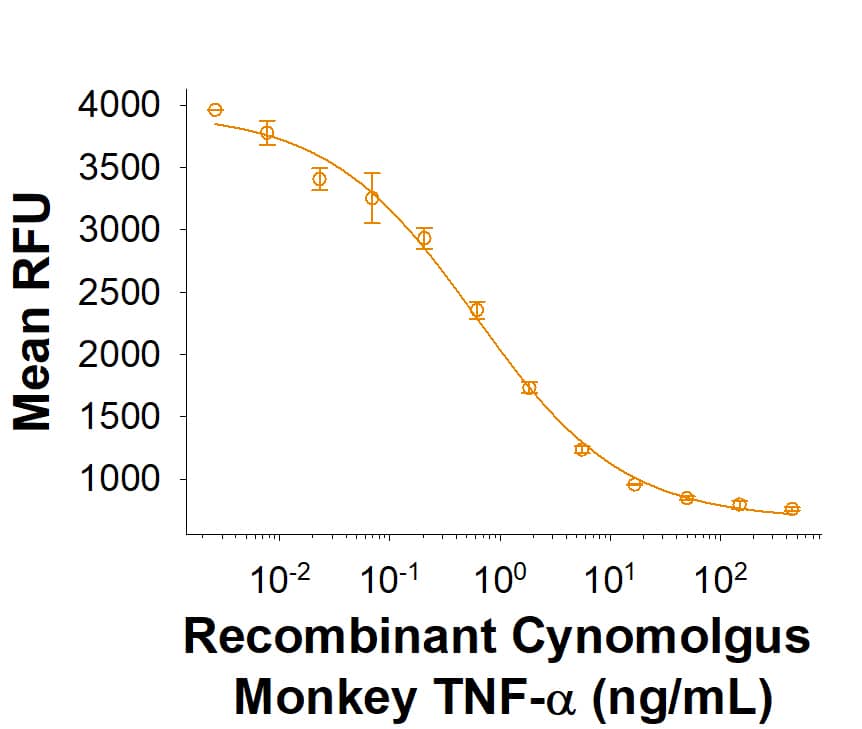

![ELISA: Recombinant Sheep TNF-alpha Protein [NBP3-11067] ELISA: Recombinant Sheep TNF-alpha Protein [NBP3-11067]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Recombinant-Sheep-TNF-alpha-Protein-ELISA-NBP3-11067-img0001.jpg)
![SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Rat TNF-alpha His Protein [NBP2-52131] SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Rat TNF-alpha His Protein [NBP2-52131]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Recombinant-Rat-TNF-alpha-Protein-SDS-Page-NBP2-52131-img0002.jpg)
