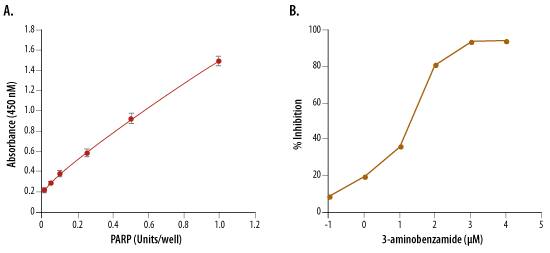
PARP: Activity Assays
PARP [Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase], also known as ADPRT and PPOL, is a 118-kDa enzyme that uses NAD as a substrate to catalyze the covalent transfer of ADP-ribose to a variety of nuclear protein acceptors. ADP ribosyltransferase is required for cellular repair, and PARP expression is induced by single-strand breaks in DNA. PARP is proteolytically cleaved by Caspase-3 into two fragments of 89- and 24-kDa in one of the hallmark events of apoptosis.
11 results for "PARP Activity Assays" in Products
11 results for "PARP Activity Assays" in Products
PARP: Activity Assays
PARP [Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase], also known as ADPRT and PPOL, is a 118-kDa enzyme that uses NAD as a substrate to catalyze the covalent transfer of ADP-ribose to a variety of nuclear protein acceptors. ADP ribosyltransferase is required for cellular repair, and PARP expression is induced by single-strand breaks in DNA. PARP is proteolytically cleaved by Caspase-3 into two fragments of 89- and 24-kDa in one of the hallmark events of apoptosis.
Biotinylated-NAD+; substrate for ADP-ribosylation
| Chemical Name: | β-Nicotinamide-N6-[2-[[6-[biotinyl]amino]hexyl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]adenine dinucleotide |
For the in vitro screening of candidate PARP-1 inhibitors
For the measurment of PARP-1 activity in cell extracts
For the quantitation of PAR in tissue culture cells and tumor lysates.
For the measurment of PARP-1 activity in cell extracts