Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot
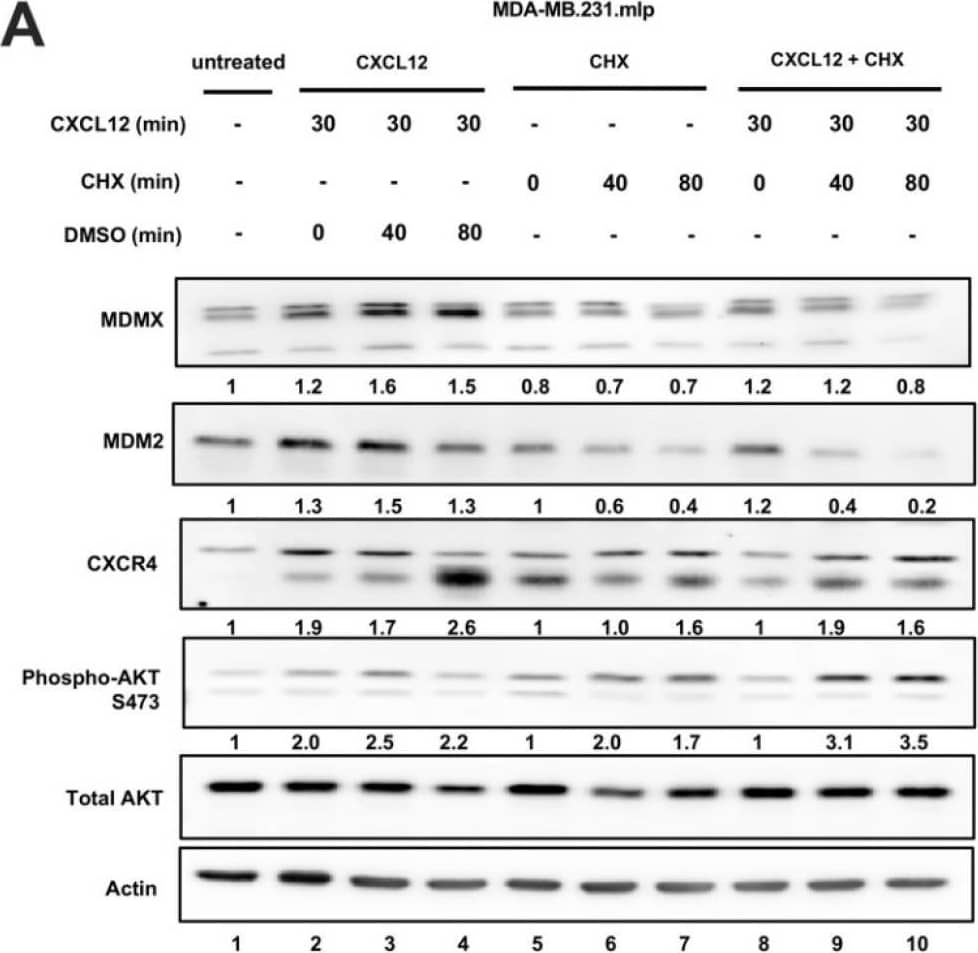
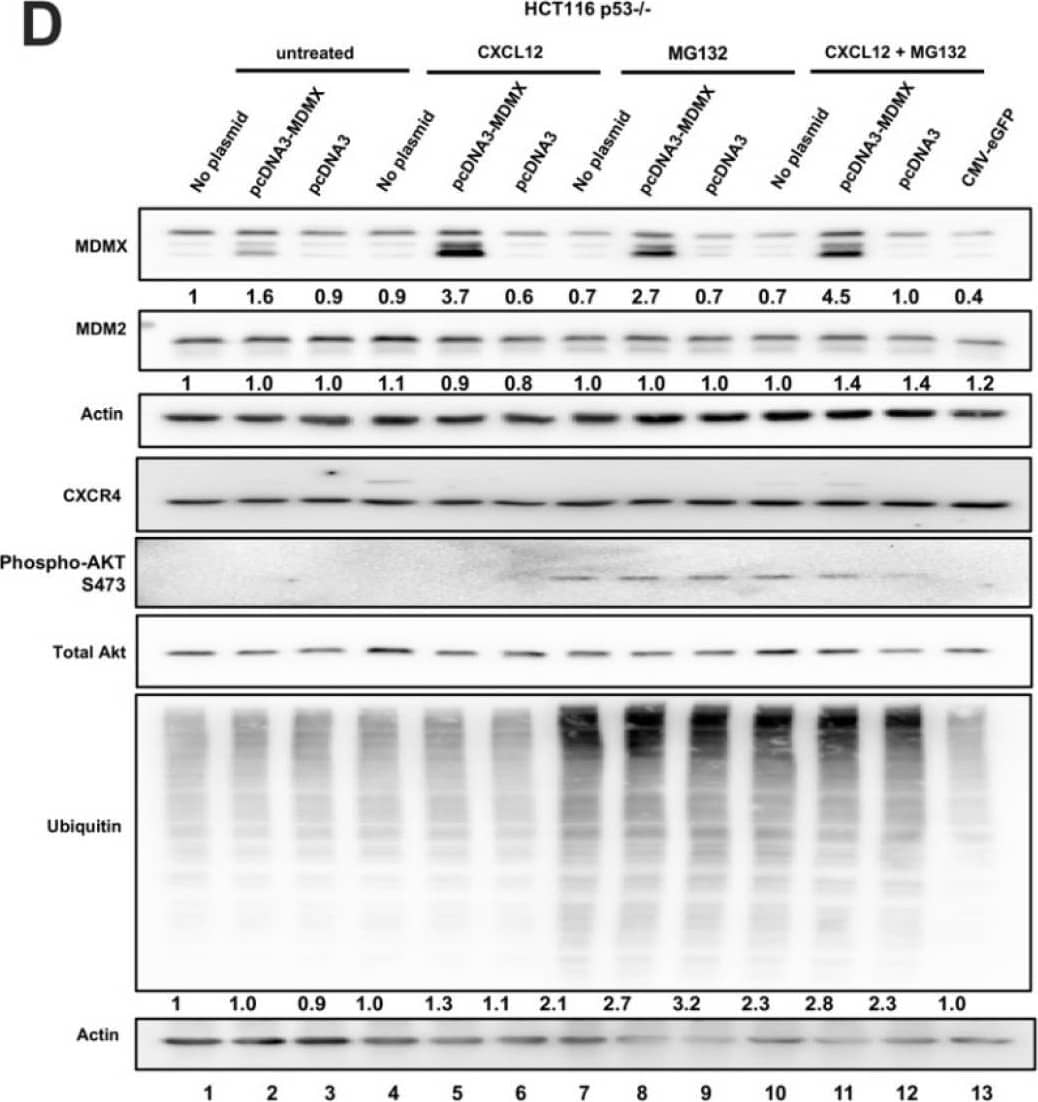
CXCL12 addition does not increase MDMX protein half-life following cycloheximide or MG132 treatment. (A) Immunoblot analysis of lysates from MDA-MB-231 cells treated with CXCL12 (50 ng/mL) for 30 min followed by cycloheximide (CHX) or DMSO for 40 or 80 min. Cells were harvested and lysed in CHAPS lysis buffer and subjected to immunoblotting to probe for MDM2 and MDMX. Actin was probed as a loading control. (B,C) Evaluation of Western blot band density was carried out using ImageJ and Prism software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant. (D) HCT116 p53-/- cells were transfected with pcDNA3-MDMX for 24 h and then treated with CXCL12 (50 ng/mL) for 30 min followed by MG132 or DMSO for 40 or 80 min. Cells were harvested and lysed in CHAPS lysis buffer and subjected to immunoblotting to probe for MDM2, MDMX, and Ubiquitin. Actin was probed as a loading control. (E,F) Evaluation of Western blot band density was carried out using ImageJ and Prism 10 software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot
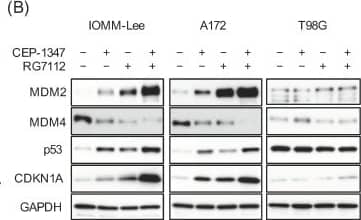
The MDM2 antagonist RG7112 concomitant with CEP-1347 effectively activates p53 and inhibits the growth of malignant brain tumor cells expressing wild-type p53. (A) IMR90 normal human fibroblasts, IOMM-Lee cells, and A172 cells treated with the indicated drugs (CEP-1347, 250 nM; RG7112, 500 nM) for 3 days were subjected to the trypan blue dye exclusion assay. (B) IOMM-Lee, A172, and T98G cells treated with the indicated drugs (CEP-1347, 250 nM; RG7112, 500 nM) for 2 days were subjected to a Western blot analysis. (C) Cells treated with the indicated drugs (CEP-1347, 250 nM; RG7112, 500 nM) for 3 days were cultured for another 5 days in the absence of any drugs for the colony formation assay. Representative images (left panels) and the number of colonies (right graphs) are shown. Values represent means + SD from triplicate samples of a representative experiment. * p < 0.05. † p < 0.05 vs. cells treated without any drugs. Similar results were obtained from more than two independent biological replicates. Original blot images can be found in Figure S4. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37686602), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot
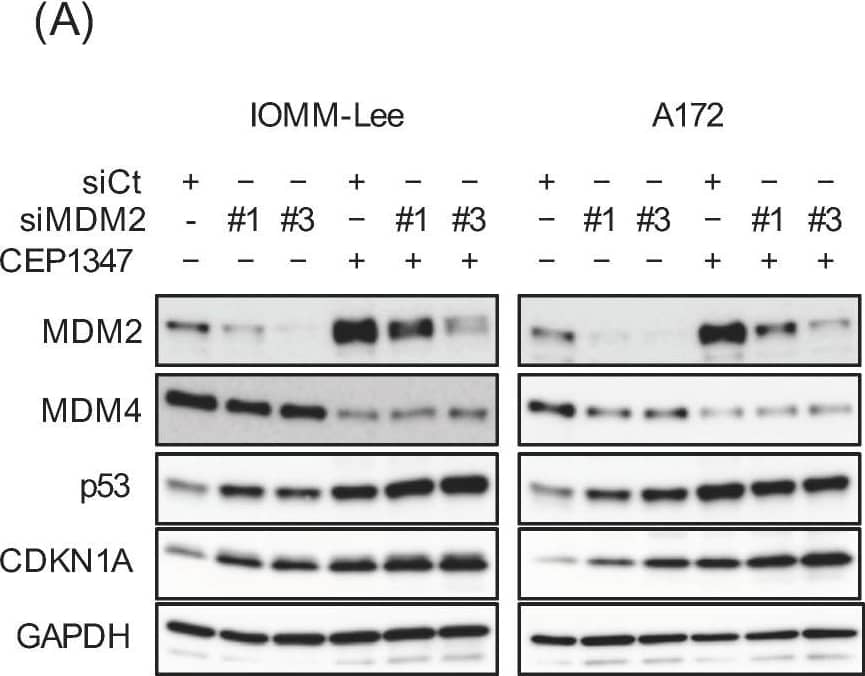
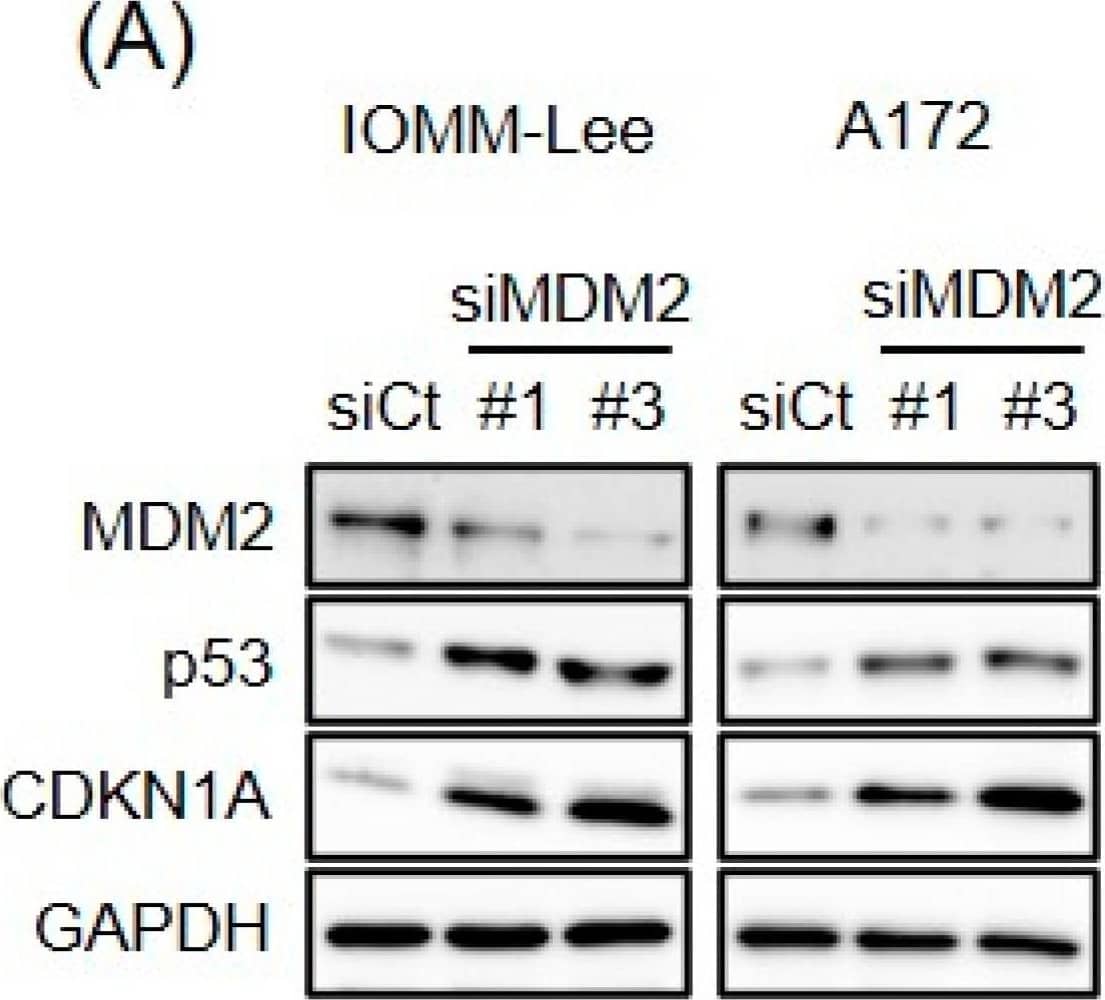
CEP-1347-induced MDM2 overexpression counteracts the CEP-1347-induced activation of p53. IOMM-Lee and A172 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated siRNA against MDM2 (#1 and #3) or with control siRNA (siCt). After being cultured for 1 day, cells treated without or with 250 nM CEP-1347 for 2 and 3 additional days were subjected to a Western blot analysis (A) and the trypan blue dye exclusion assay (B), respectively. Values represent the means + SD of triplicate samples of a representative experiment. * p < 0.05. † p < 0.05 vs. siCt-transfected cells treated without CEP-1347. Similar results were obtained from more than three independent biological replicates. Original blot images can be found in Figure S3. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37686602), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot
Endogenous expression of MDM2 contributes to p53 inactivation. (A) IOMM-Lee and A172 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated siRNA against MDM2 (#1 and #3) or with control siRNA (siCt). After being cultured for 3 days, cells were subjected to a Western blot analysis. (B) Cells were transiently transfected as in (A). After 3 days, transfected cells were subjected to the trypan blue dye exclusion assay to measure the number of viable cells. Values represent means + SD from triplicate samples of a representative experiment. * p < 0.05 vs. siCt-transfected cells. Similar results were obtained from more than two independent biological replicates. Original blot images can be found in Figure S2. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37686602), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot
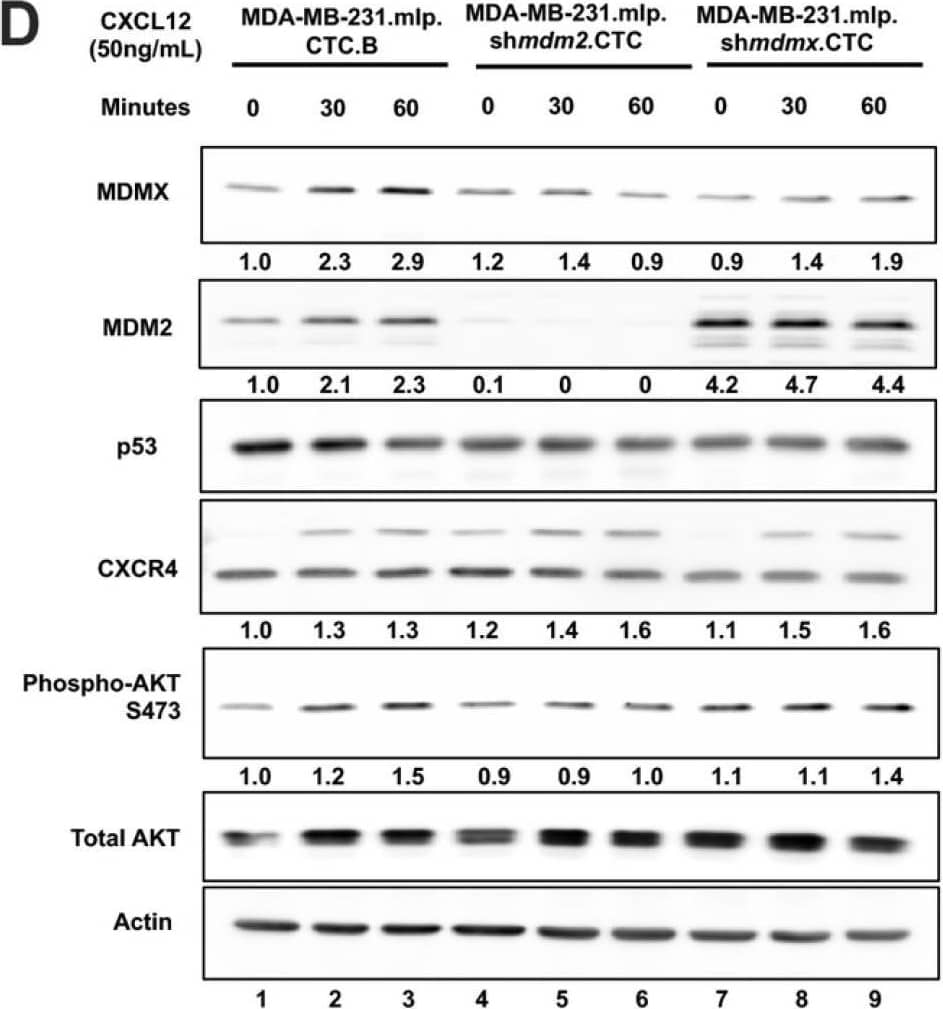
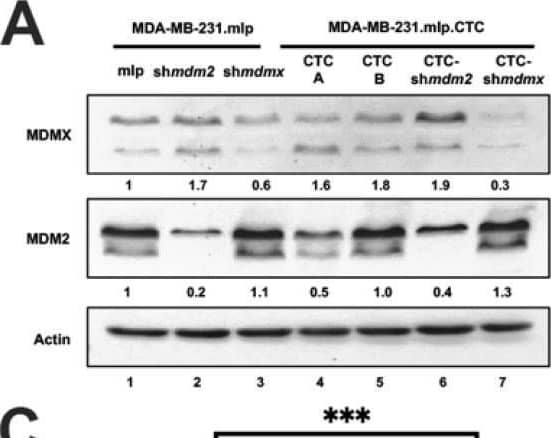
MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC lines compared to MDA-MB-231.shmdm2.CTC and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx.CTC maintain increased migratory compacity but have reduced response to CXCL12. (A) Immunoblot of whole cell lysates from MDA-MB-231.mlp, MDA-MB-231.shmdm2, and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx (lanes 1–3) and MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC A and B (lanes 4 and 5), MDA-MB-231.shmdm2.CTC (lane 6), and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx.CTC (lane 7) cell lines probed for MDMX (top) and MDM2 (middle). The loading control was actin (bottom) (B) Representative images of MDA-MB-231-derived CTC lines in wound healing assay. Black lines denote the borders of the scratch made. (C) Graph of % wound closure at 12 h time point. Error bars represent SD. *** p < 0.001, NS = nonsignificant. The p value was calculated using two-tailed unpaired t tests on Prism software (D) Immunoblot of whole cell lysates from MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC lines treated with CXCL12 at a final concentration of 50 ng/mL for 30 and 60 min. (E) MDMX and MDM2 protein expression was compared using ImageJ quantitation relative to actin, respectively, as a loading control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot
MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC lines compared to MDA-MB-231.shmdm2.CTC and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx.CTC maintain increased migratory compacity but have reduced response to CXCL12. (A) Immunoblot of whole cell lysates from MDA-MB-231.mlp, MDA-MB-231.shmdm2, and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx (lanes 1–3) and MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC A and B (lanes 4 and 5), MDA-MB-231.shmdm2.CTC (lane 6), and MDA-MB-231.shmdmx.CTC (lane 7) cell lines probed for MDMX (top) and MDM2 (middle). The loading control was actin (bottom) (B) Representative images of MDA-MB-231-derived CTC lines in wound healing assay. Black lines denote the borders of the scratch made. (C) Graph of % wound closure at 12 h time point. Error bars represent SD. *** p < 0.001, NS = nonsignificant. The p value was calculated using two-tailed unpaired t tests on Prism software (D) Immunoblot of whole cell lysates from MDA-MB-231.mlp.CTC lines treated with CXCL12 at a final concentration of 50 ng/mL for 30 and 60 min. (E) MDMX and MDM2 protein expression was compared using ImageJ quantitation relative to actin, respectively, as a loading control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot
CXCL12 addition does not increase MDMX protein half-life following cycloheximide or MG132 treatment. (A) Immunoblot analysis of lysates from MDA-MB-231 cells treated with CXCL12 (50 ng/mL) for 30 min followed by cycloheximide (CHX) or DMSO for 40 or 80 min. Cells were harvested and lysed in CHAPS lysis buffer and subjected to immunoblotting to probe for MDM2 and MDMX. Actin was probed as a loading control. (B,C) Evaluation of Western blot band density was carried out using ImageJ and Prism software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant. (D) HCT116 p53-/- cells were transfected with pcDNA3-MDMX for 24 h and then treated with CXCL12 (50 ng/mL) for 30 min followed by MG132 or DMSO for 40 or 80 min. Cells were harvested and lysed in CHAPS lysis buffer and subjected to immunoblotting to probe for MDM2, MDMX, and Ubiquitin. Actin was probed as a loading control. (E,F) Evaluation of Western blot band density was carried out using ImageJ and Prism 10 software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot
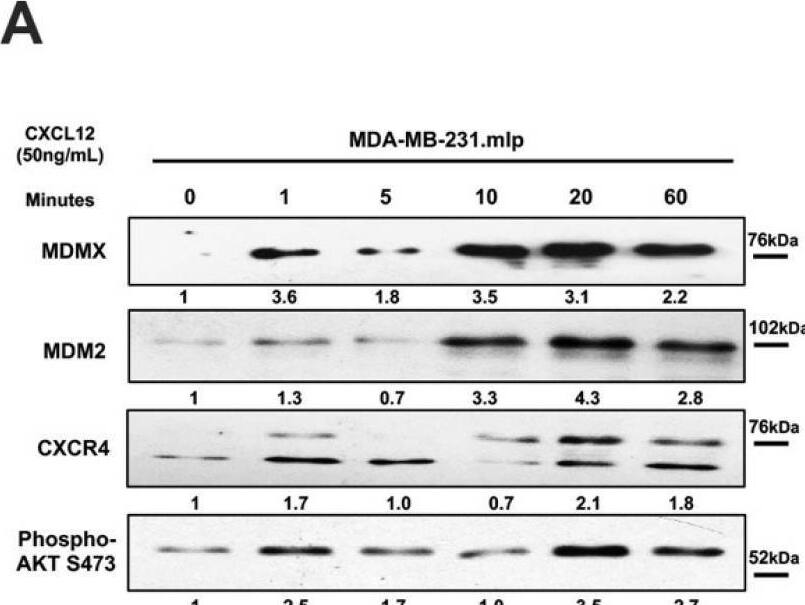
Chemokine CXCL12 addition to cell culture increases CXCR4, activates PI3K/AKT, and MDMX and MDM2 protein levels. (A) Panels show immunoblot analysis for MDMX, MDM2, CXCR4, and phospho-AKT S473, total AKT, and actin in MDA-MB-231.mlp cells after treatment for up to 60 min with CXCL12 at 50 ng/mL for 0, 1, 5, 10, 20, and 60 min, lanes 1–6. Total AKT and actin were used as loading controls. The proteins were derived from the same samples run on different gels/membranes at the same time and their molecular weights are shown. (B) Untreated cells and those following the 20 min treatments were compared for the MDMX and MDM2 protein levels evaluated (using actin as a normalizer control for loading) using ImageJ and graphs were created with Prism 10 software, with the untreated value set as 1 and the ratio reported for CXCL12-treated samples (20 min) used to report the fold change. (C) Untreated and 20 min treatments were compared for CXCR4 and phospho-AKT S473 protein levels quantified via ImageJ relative to total AKT as a loading control with the untreated value set as 1 and the ratio reported for CXCL12-treated samples (20 min) used to report the fold change. Images were analyzed using ImageJ and graphs were created with Prism software. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, NS = non-significant (N = 4 biological replicates). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of MDM2/HDM2 by Western Blot
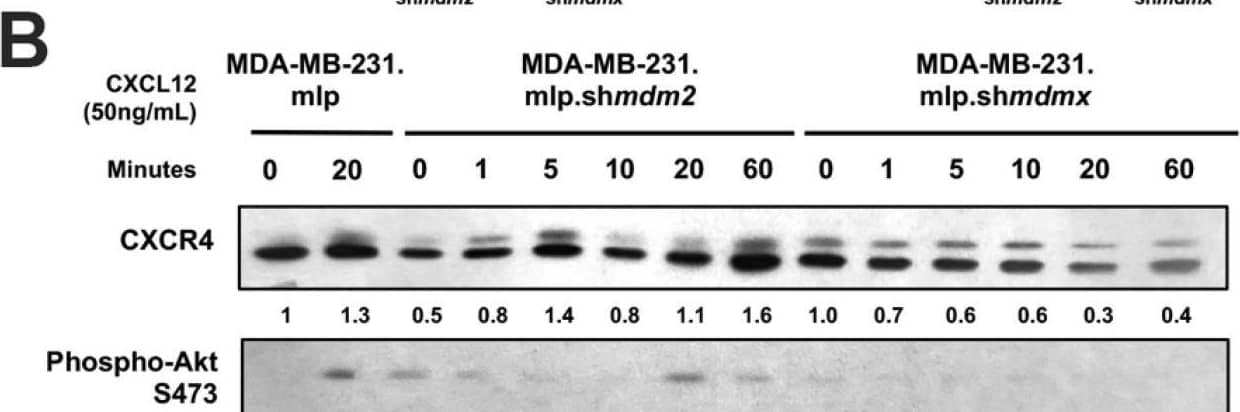
Knockdown of MDMX in MDA-MB-231 cells disrupts CXCL12 signaling to upregulate CXCR4, MDM2, and AKT activation. MDA-MB-231.mlp, MDA-MB-231.mlp.shmdm2, and MDA-MB-231.mlp.shmdmx cells treated in cell culture with the addition of CXCL12 at a final concentration of 50 ng/mL in cell culture for up to 60 min. (A) CXCR4 and phospho-AKT S473 protein levels were semi-quantified at 20 min via ImageJ relative to actin as a loading control. Protein level analysis was carried out using Western blot results using Image J and Prism software and densitometries were measured as a ratio relative to the actin band density. Fold change was calculated relative to protein levels in the untreated 231.mlp vector control cells. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant (N = 3 biological replicates). (B) Immunoblot analysis for CXCR4, phospho-AKT, MDMX, and MDM2 protein levels in MDA-MB-231 or knockdown cells after the addition of CXCL12. (C) MDMX and MDM2 protein levels were semi-quantified at 20 min post addition of CXCL12 to the cell culture. Protein levels were normalized to actin and fold change was calculated relative to untreated 231.mlp vector control cells. MDM2 or MDMX knockdown were confirmed for each respective cell line. Protein level analysis was carried out from Western blot results using Image J and Prism software and expression scores were normalized to actin. Error bars represent SD. * p < 0.05, NS = non-significant (N = 3 biological replicates). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39766093), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.