FEN-1: Small Molecules and Peptides
The FEN-1 enzyme is active in base excision repair (BER) pathways. Once the DNA glycosylase removes the desired nucleotide stretch, a DNA polymerase synthesizes the complementary nucleotides for replacement. To complete the DNA repair, the FEN-1 enzyme removes the extra flap of nucleotides and DNA ligase finishes the repair.
3 results for "FEN-1 Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
3 results for "FEN-1 Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
FEN-1: Small Molecules and Peptides
The FEN-1 enzyme is active in base excision repair (BER) pathways. Once the DNA glycosylase removes the desired nucleotide stretch, a DNA polymerase synthesizes the complementary nucleotides for replacement. To complete the DNA repair, the FEN-1 enzyme removes the extra flap of nucleotides and DNA ligase finishes the repair.
Inhibitor of protein synthesis
| Chemical Name: | 4-[2-(3,5-Dimethyl-2-oxo-cyclohexyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]-2,6-piperidinedione |
| Purity: | ≥97% (HPLC) |
Endogenous, non-selective glutamate receptor agonist
| Chemical Name: | (S)-1-Aminopropane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid |
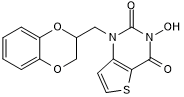
Potent flap endonuclease 1 (FEN1) inhibitor; induces DNA damage response
| Chemical Name: | 1-[(2,3-Dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-2-yl)methyl]-3-hydroxythieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |