eIF4E: Small Molecules and Peptides
Eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) are heterotrimeric initiation complexes that form on the ribosome during protein synthesis. Each eIF serves a distinct function during protein synthesis to help attach, assemble, and drive the ribosome along the mRNA. eIF4E interacts with the 7-methyl-GTP cap structure to facilitate the initiation and rate of translation of mRNA. Together with eIF4G and eIF4A, it forms the eIF4F complex. eIF4E activity has been shown to play a role in cell cycle progression, tumorigenesis, embryonic development, nuclear export and synaptic plasticity.
3 results for "eIF4E Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
3 results for "eIF4E Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
eIF4E: Small Molecules and Peptides
Eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) are heterotrimeric initiation complexes that form on the ribosome during protein synthesis. Each eIF serves a distinct function during protein synthesis to help attach, assemble, and drive the ribosome along the mRNA. eIF4E interacts with the 7-methyl-GTP cap structure to facilitate the initiation and rate of translation of mRNA. Together with eIF4G and eIF4A, it forms the eIF4F complex. eIF4E activity has been shown to play a role in cell cycle progression, tumorigenesis, embryonic development, nuclear export and synaptic plasticity.
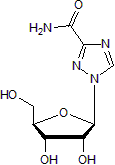
Blocks eIF4E activity; antiviral guanosine analog
| Chemical Name: | 1-β-D-Ribofuranosyl-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
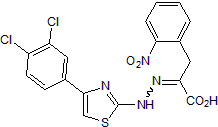
Inhibits eIF4E:eIF4G subunit interaction
| Chemical Name: | α-[2-[4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-2-thiazolyl]hydrazinylidene]-2-nitro-benzenepropanoic acid |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Inhibitor of protein synthesis; antileukemic agent
| Chemical Name: | Cephalotaxine 4-methyl (2R)-2-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-4-methylpentyl)butanedioate |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |