Mouse Galectin-3 Biotinylated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # BAF1197

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ala2-Ile264
Accession # NP_034835
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Galectin-3 Biotinylated Antibody
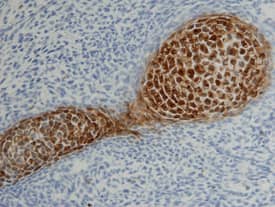
Galectin-3 in Mouse Cartilage.
Galectin-3 was detected in immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse cartilage using 15 µg/mL Goat Anti-Mouse Galectin-3 Biotinylated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # BAF1197) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.Applications for Mouse Galectin-3 Biotinylated Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed frozen sections of mouse cartilage
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse Galectin-3 (Catalog # 1197-GA)
Mouse Galectin-3 Sandwich Immunoassay
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Galectin-3
The galectins constitute a large family of carbohydrate-binding proteins with specificity for N-acetyl-lactosamine-containing glycoproteins. At least 14 mammalian galectins, which share structural similarities in their carbohydrate recognition domains (CRD), have been identified. The galectins have been classified into the prototype galectins (-1, -2, -5, -7, -10, -11, -13, -14), which contain one CRD and exist either as a monomer or a noncovalent homodimer; the chimera galectins (Galectin-3) containing one CRD linked to a nonlectin domain; and the tandem-repeat galectins (-4, -6, -8, -9, -12) consisting of two CRDs joined by a linker peptide. Galectins lack a classical signal peptide and can be localized to the cytosolic compartments where they have intracellular functions. However, via one or more as yet unidentified non-classical secretory pathways, galectins can also be secreted to function extracellularly. Individual members of the galectin family have different tissue distribution profiles and exhibit subtle differences in their carbohydrate-binding specificities. Each family member may preferentially bind to a unique subset of cell-surface glycoproteins (1-4). Galectin-3, also known as Mac-2, L29, CBP35, and epsilonBP, is a chimera galectin that has a tendency to dimerize. Besides the soluble protein, alternatively spliced forms of chicken Galectin-3 containing a transmembrane-spanning domain and a leucine zipper motif have been reported. Galectin-3 is expressed in tumor cells, macrophages, activated T cells, osteoclasts, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts. It binds various matrix glycoproteins including laminin, fibronectin, LAMPS, 90K/Mac-2BP, MP20, and CEA. Galectin-3 promotes cell growth and proliferation for many cell types. Galectin-3 acts intracellularly to prevent apoptosis. Depending on the cell types, Galectin-3 exhibits pro- or anti-adhesive properties. Galectin-3 has proinflammatory activities in vitro and in vivo. It induces pro-inflammatory and inhibits Th2 type cytokine production. Galectin-3 chemoattracts monocytes and macrophages. It activates and degranulates basophils and mast cells. Elevated circulating levels of Galectin-3 has been show to correlate with the malignant potential of several types of cancer, suggesting that Galectin-3 is also involved in tumor growth and metastasis. Human and mouse Galectin-3 shares approximately 80% amino acid sequence similarity (1-5).
References
- Rabinovich, A. et al. (2002) Trends in Immunol. 23:313.
- Rabinovich, A. et al. (2002) J. Leukocyte Biology 71:741.
- Hughes, R.C. (2001) Biochimie 83:667.
- R&D Systems Cytokine Bulletin; Summer 2002.
- Gorski, J.P. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:18840.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Galectin-3 Products
Product Documents for Mouse Galectin-3 Biotinylated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Galectin-3 Biotinylated Antibody
For research use only