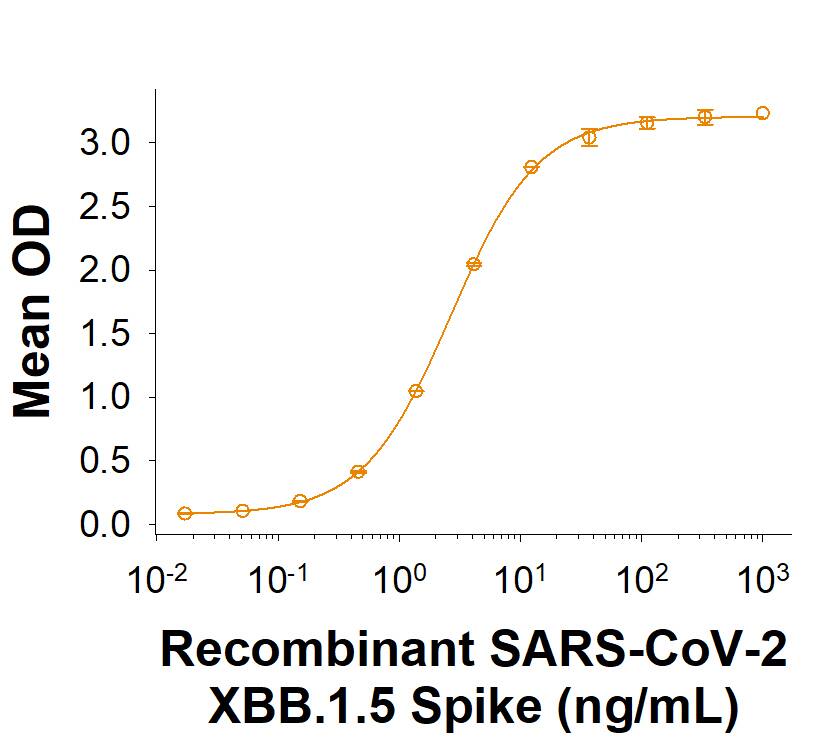
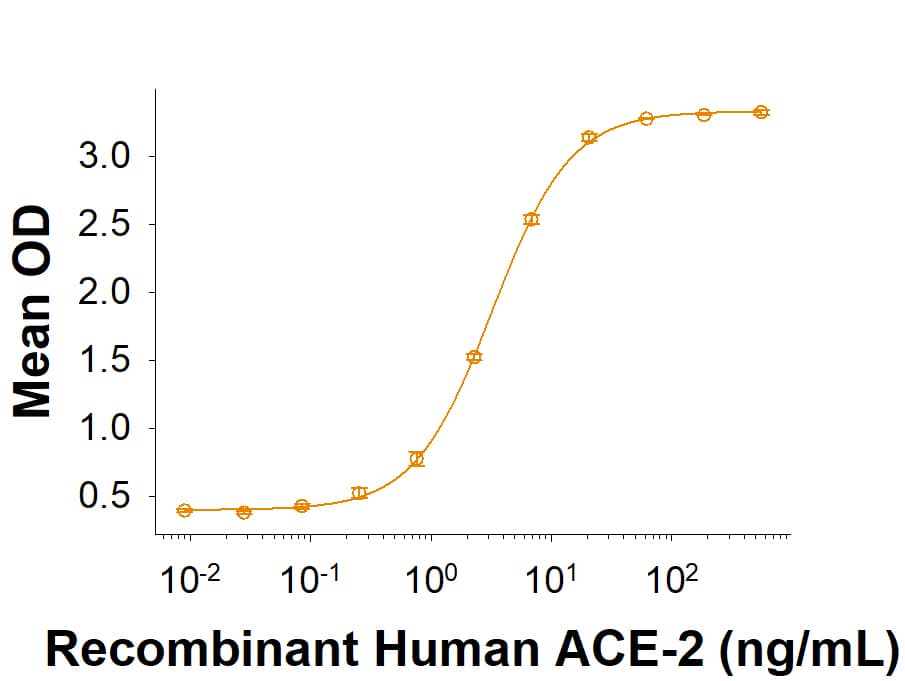
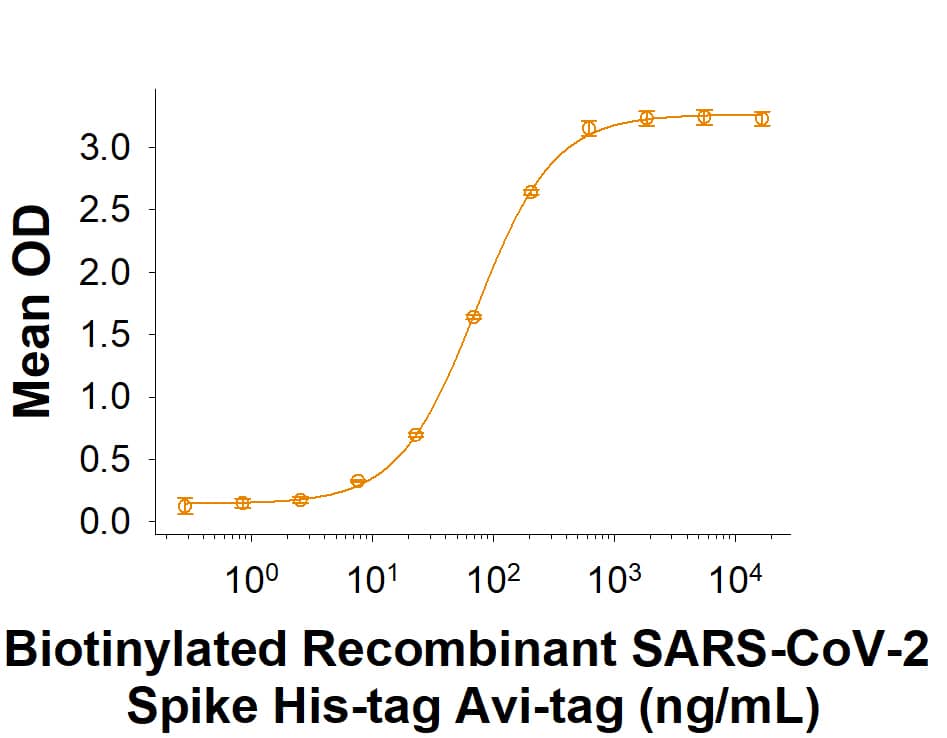
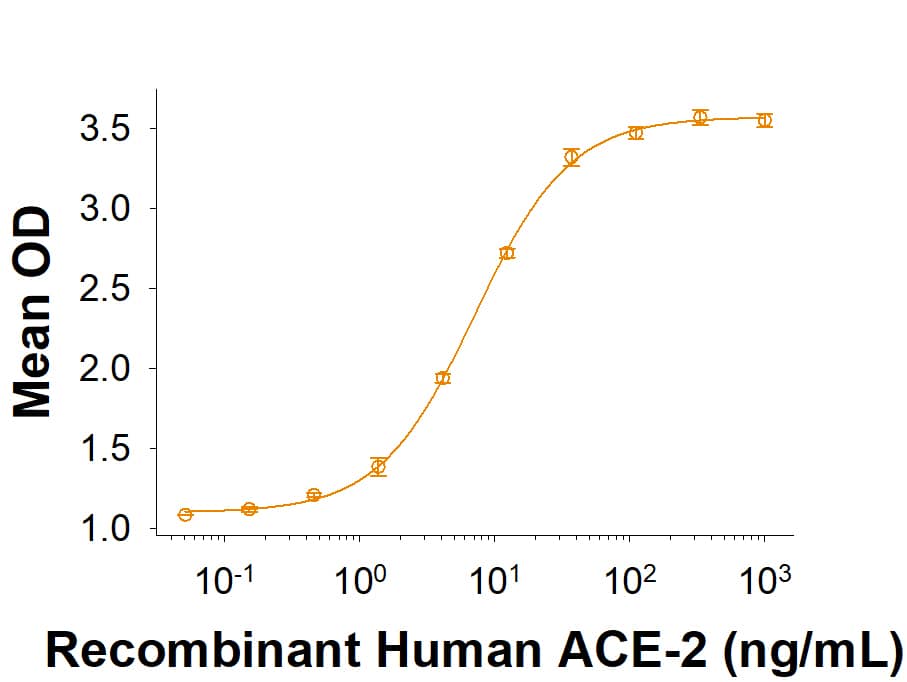
Spike: Proteins and Enzymes
The Coronavirus Spike protein (S Protein) is one of four major structural proteins (S, M, E, N) present in each viral particle. Spike proteins are abundantly expressed on the surface forming its characteristic crown-like halo structure. The Spike protein is a highly glycosylated, type I transmembrane protein that plays a critical role in receptor recognition and host cell entry. There are two subunits, S1 and S2, that divide the protein roughly in half.
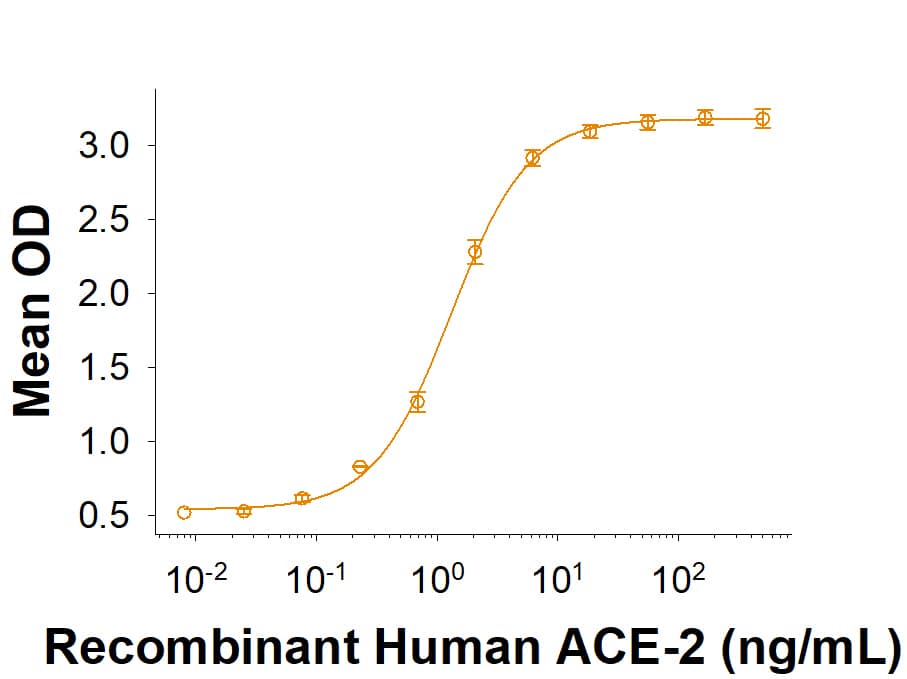
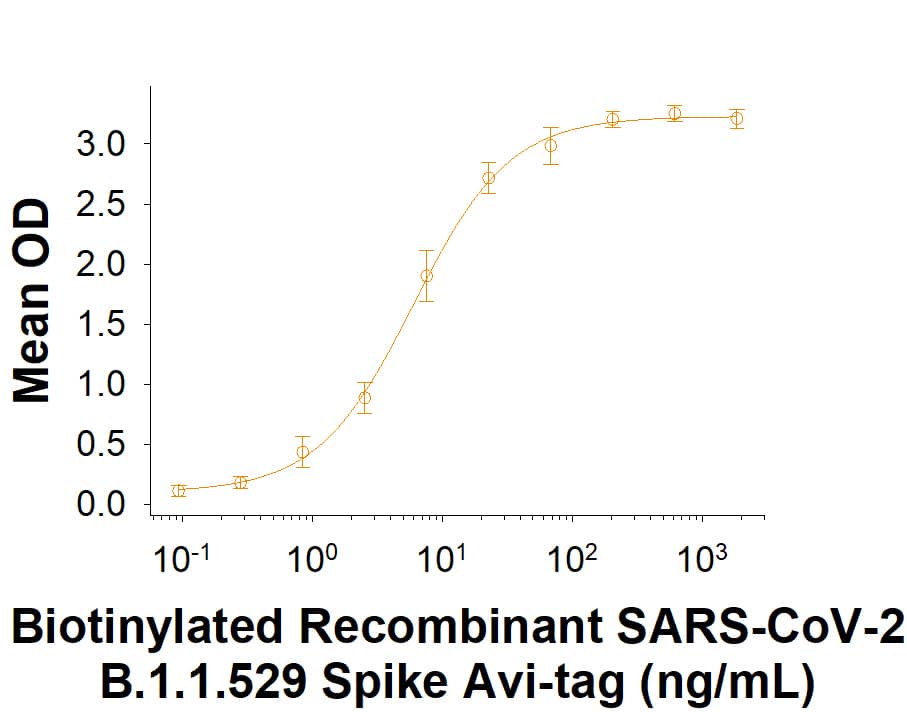
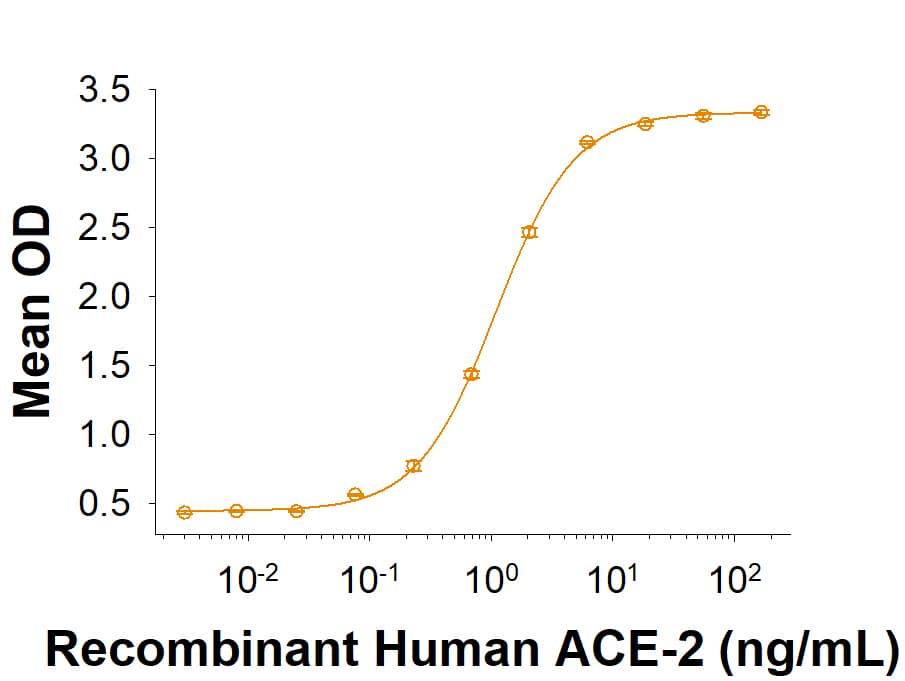
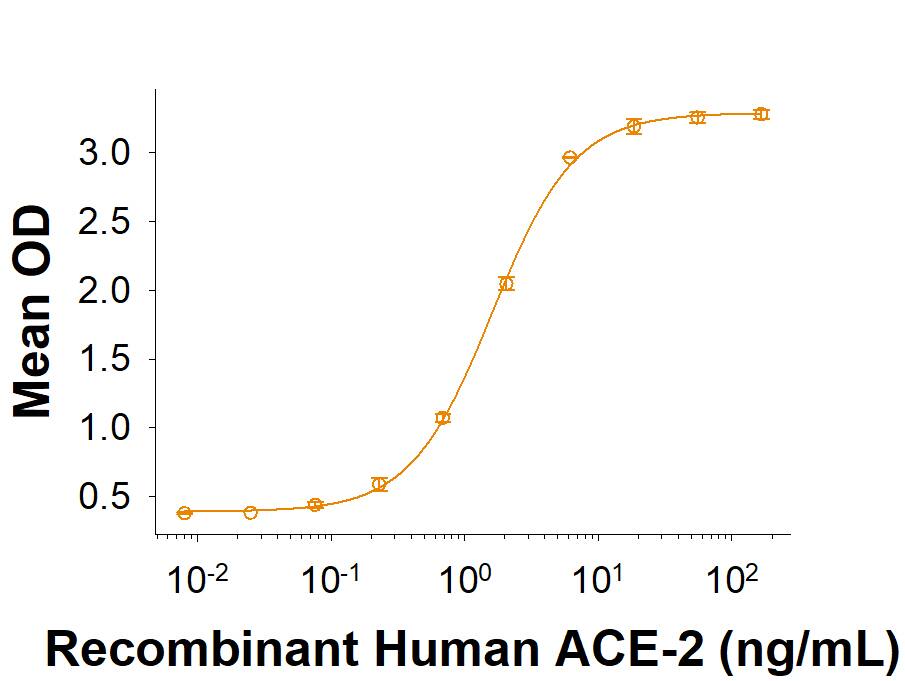
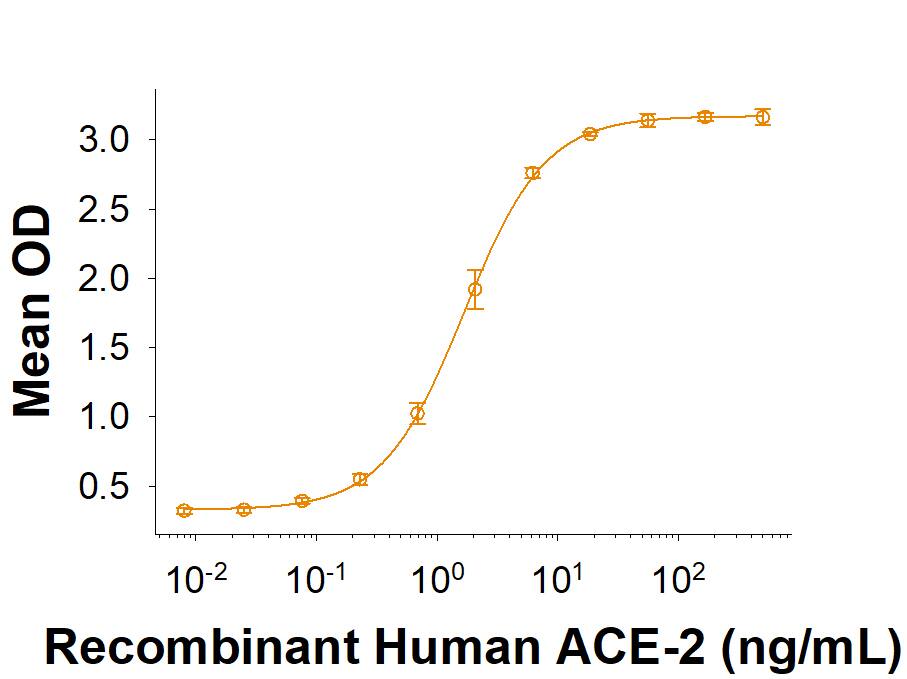
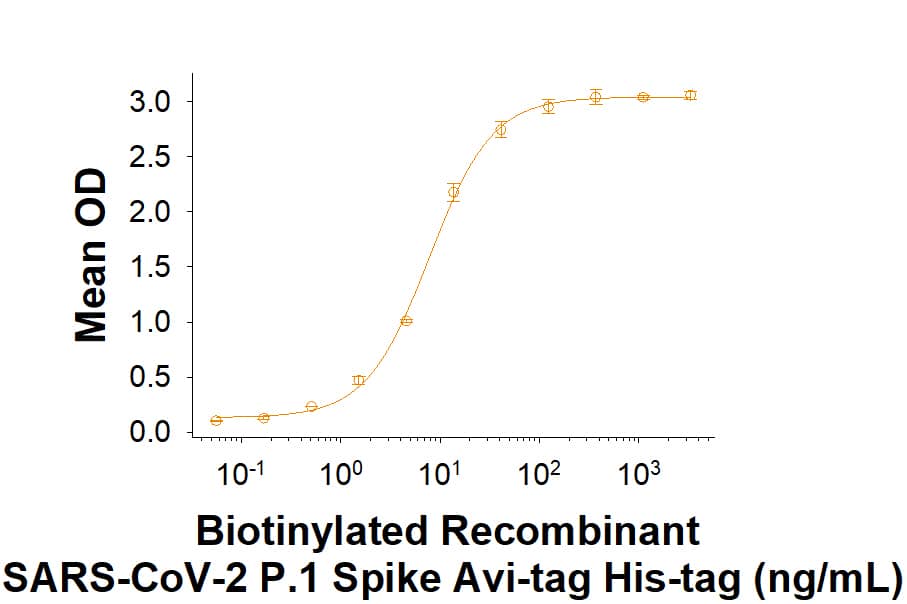
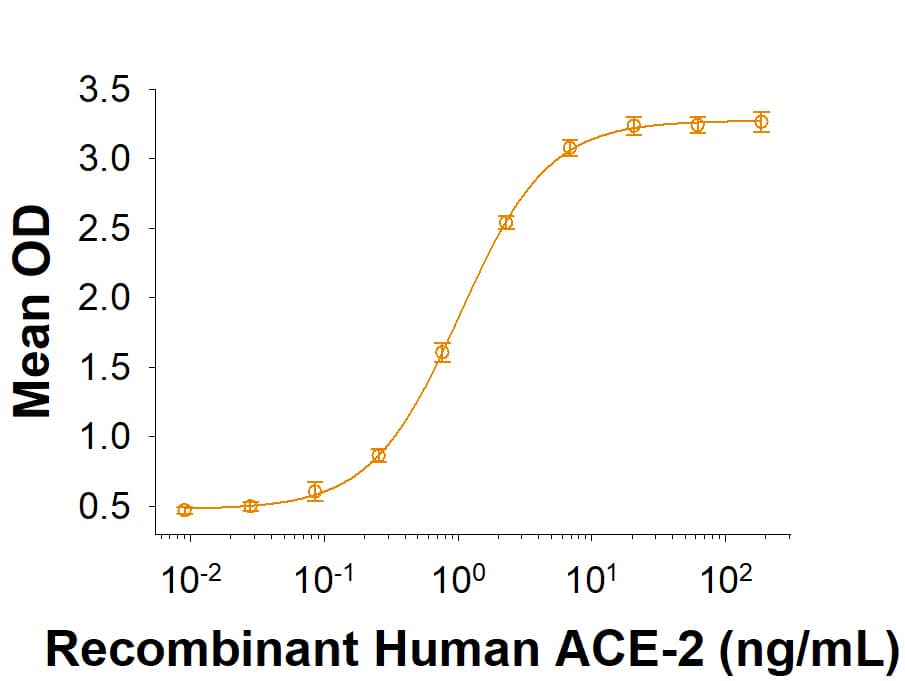
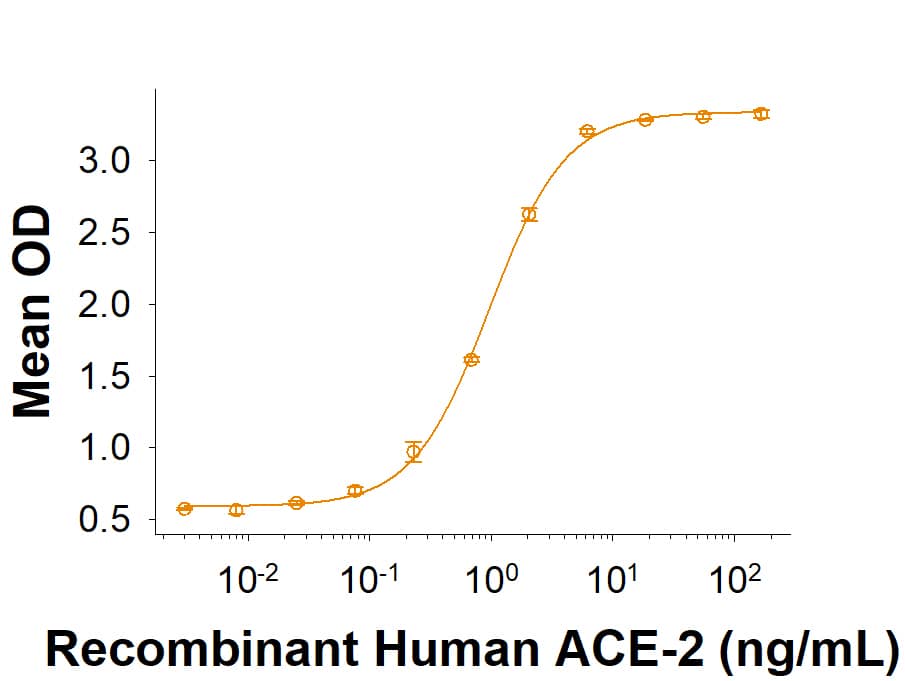
Within the N-terminal S1 subunit is the N-terminal domain and receptor binding domain (Spike RBD protein). The Spike RBD binds to the host cell and undergoes several conformational changes and proteolysis leading to fusion of the virus particle to the host cell membrane allowing transfer of the nucleocapsid into the host cell cytoplasm. For SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, the Spike RBD tightly associates with human ACE-2. Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 proteins and antibodies that recognize these proteins are essential for studying the molecular mechanisms of the coronavirus life cycle.
Products:
114 results for "Spike Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
114 results for "Spike Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
Spike: Proteins and Enzymes
The Coronavirus Spike protein (S Protein) is one of four major structural proteins (S, M, E, N) present in each viral particle. Spike proteins are abundantly expressed on the surface forming its characteristic crown-like halo structure. The Spike protein is a highly glycosylated, type I transmembrane protein that plays a critical role in receptor recognition and host cell entry. There are two subunits, S1 and S2, that divide the protein roughly in half.
Within the N-terminal S1 subunit is the N-terminal domain and receptor binding domain (Spike RBD protein). The Spike RBD binds to the host cell and undergoes several conformational changes and proteolysis leading to fusion of the virus particle to the host cell membrane allowing transfer of the nucleocapsid into the host cell cytoplasm. For SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, the Spike RBD tightly associates with human ACE-2. Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 proteins and antibodies that recognize these proteins are essential for studying the molecular mechanisms of the coronavirus life cycle.
Products:
Ectodomain, Stabilized Prefusion Conformation, Resistant to Furin Cleavage
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
His-tag
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Omicron variant
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Omnicron Variant
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Delta Variant (India) His-tag
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated via Amines
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
(1-1273 4x aa mut.)
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
L452R T478K Delta Variant (India)
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
GCN4-IZ trimerization domain, Stabilized Prefusion Conformation, Resistant to Furin Cleavage
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | P59594.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Omicron Variant Biotinylated His-tag
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Alpha Variant (UK)
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Gamma Variant (Brazil)
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Beta Variant (South Africa)
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Omicron Variant His-tag
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
CHO expressed. GCN4-IZ trimerization domain. Prefusion Conformation. High ACE-2 binding
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009825051.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Y144 del, A222V, Delta Variant (Vietnam) His-tag
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Lambda Variant
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
His-tag Biotinylated Gamma Variant (Brazil)
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
His-tag Kappa Variant (India)
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Alpha Variant (UK) Resistant to Furin & Stabilized Prefusion Conformation
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA, BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |