Summary
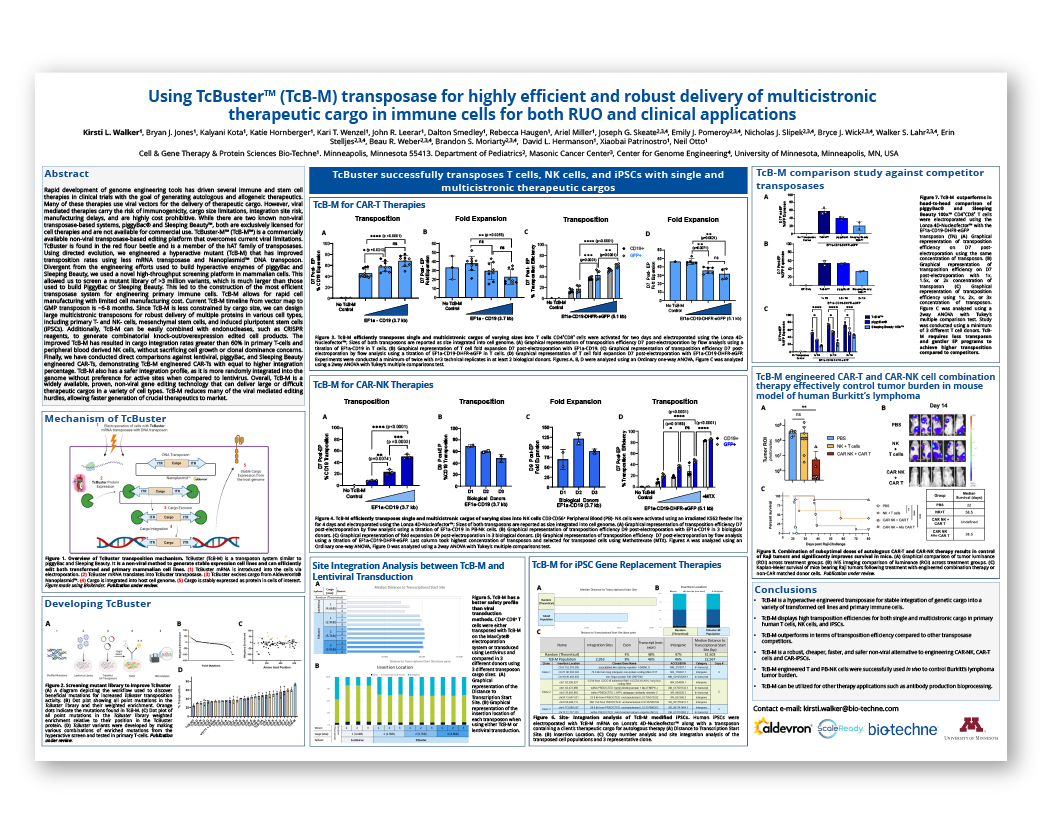
The rapid evolution of genome engineering tools has fueled the development of immune and stem cell therapies, as both autologous and allogeneic therapeutics. However, viral-mediated therapies present challenges such as immunogenicity, cargo size limits, integration risks, manufacturing delays, and high costs.
This study explores how TcBuster-M (TcB-M), a commercially available non-viral transposase-based editing platform, addresses viral limitations to allow for faster generation of therapeutics to market.
Download this TcBuster scientific poster to gain insights into:
- The utilization of screening mutant libraries (containing >3 million variants) to generate a hyperactive mutant (TcB-M) with enhanced transposition rates
- TcB-M’s performance in transposing T cells, NK cells, and iPSCs with single and multicistronic cargos of varying sizes
- The comparative performance of TcB-M and other competitor transposases
- The efficacy of TcB-M engineered CAR-T and CAR-NK cell combination therapy in controlling tumor burden in a mouse model of human Burkitt’s lymphoma
Request Literature
To access this literature content please fill out the form below.