Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein, Animal-Free
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # BT-SHH-AFL
Widely used for both human and mouse cell culture.

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
E. coli-derived mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh protein
Cys25-Gly198 (Cys25Ile-Ile) with an N-terminal Met
Produced using non-animal reagents in an animal-free laboratory.
Cys25-Gly198 (Cys25Ile-Ile) with an N-terminal Met
Produced using non-animal reagents in an animal-free laboratory.
Purity
>97%, by SDS-PAGE with quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Met
Predicted Molecular Mass
19.8 kDa
SDS-PAGE
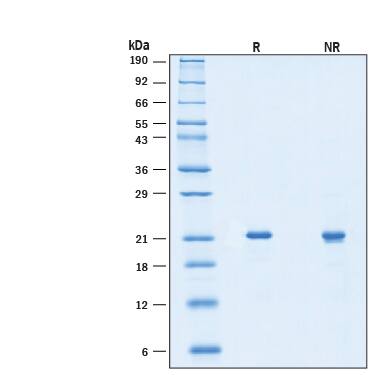
21 kDa, under reducing conditions.
Activity
Measured by its ability to induce alkaline phosphatase production by C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. Nakamura, T. et al. (1997) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 237:465.
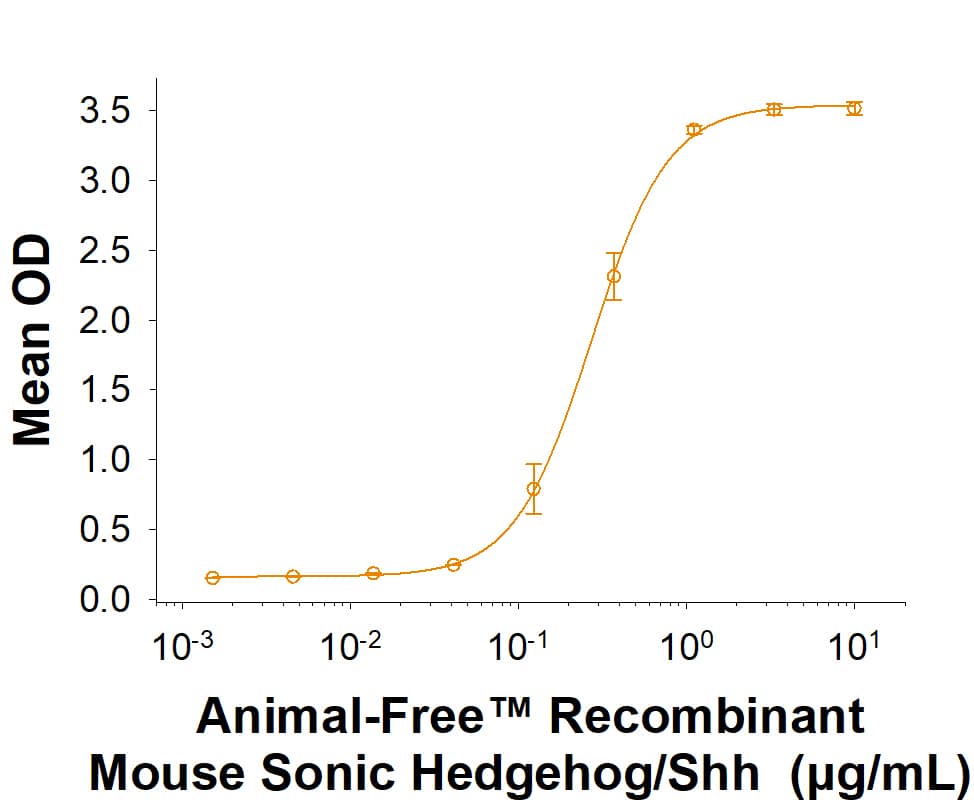
The ED50 for this effect is 0.0500-0.600 μg/mL.
The ED50 for this effect is 0.0500-0.600 μg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein, Animal-Free
Equivalent Bioactivity of GMP, Animal-Free, and RUO grades of Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh.
Equivalent bioactivity of GMP (BT-SHH-GMP), Animal-Free (Catalog # BT-SHH-AFL) and RUO grades of Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh as measured in the alkaline phosphatase production using C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells (orange, green, red, respectively).Animal-Free™ Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein Bioactivity.
Animal-Free™ Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein (Catalog # BT-SHH-AFL) induces alkaline phosphatase production by the C3H10T1/2 mouse embryonic fibroblast cell line. The ED50 for this effect is 0.0500-0.600 μg/mL.Animal-Free™ Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Animal-Free™ Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein (Catalog # BT-SHH-AFL) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing a band at 21 kDa under reducing conditions.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
BT-SHH-AFL
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Sodium Phosphate, NaCl and DTT with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in water. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Sonic Hedgehog/Shh
N-terminal cysteine and modified by cholesterol addition at its C-terminus (6). These modifications contribute to the membrane tethering of Shh as well as its assembly into various sized multimers (6-9). Lipid modification and multimerization greatly increase Shh-N receptor binding affinity and signaling potency (5, 6, 8, 9). Monomeric and multimeric Shh can be released from the plasma membrane by the cooperative action of DISP1, SCUBE2, and TACE/ADAM17 (10-12). Modifications also extend the effective range of Shh functionality and are required for the development of protein gradients important in tissue morphogenesis (9, 13). Canonical signaling of Shh is mediated by a multicomponent receptor complex that includes Patched (PTCH1, PTCH2) and Smoothened (SMO) (14). The binding of Shh to PTCH releases the basal repression of SMO by PTCH. Shh activity can also be regulated through interactions with heparin, glypicans, and membrane-associated Hip (hedgehog interacting protein) (13, 15, 16).
References
- Briscoe, J. and P.P. Therond (2013) Mol. Cell. Biol. 14:416.
- Aviles, E.C. et al. (2013) Front. Cell. Neurosci. 7:86.
- Xie, J. et al. (2013) OncoTargets Ther. 6:1425.
- Echelard, Y. et al. (1993) Cell 75:1417.
- Zeng, X. et al. (2001) Nature 411:716.
- Feng, J. et al. (2004) Development 131:4357.
- Goetz, J.A. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:4087.
- Pepinsky, R.B. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273:14037.
- Chen, M.-H. et al. (2004) Genes Dev. 18:641.
- Etheridge, L.A. et al. (2010) Development 137:133.
- Jakobs, P. et al. (2014) J. Cell Sci. 127:1726.
- Dierker, T. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284:8013.
- Lewis, P.M. et al. (2001) Cell 105:599.
- Carpenter, D. et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:13630.
- Filmus, J. and M. Capurro (2014) Matrix Biol. 35:248.
- Chuang, P.-T. and A.P. McMahon (1999) Nature 397:617.
Alternate Names
HHG1, HLP3, HPE3, MCOPCB5, Shh, ShhNC, SMMCI, TPTPS
Gene Symbol
SHH
UniProt
Additional Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein, Animal-Free
Manufacturing Specifications
Animal-Free Manufacturing ConditionsOur dedicated controlled-access animal-free laboratories ensure that at no point in production are the products exposed to potential contamination by animal components or byproducts. Every stage of manufacturing is conducted in compliance with R&D Systems' stringent Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). Production and purification procedures use equipment and media that are confirmed animal-free.
Production
- All molecular biology procedures use animal-free media and dedicated labware.
- Dedicated fermentors are utilized in committed animal-free areas.
Purification
- Protein purification columns are animal-free.
- Bulk proteins are filtered using animal-free filters.
- Purified proteins are stored in animal-free containers in a dedicated cold storage room.
- Low Endotoxin Level.
- No impairment of biological activity.
- High quality product obtained under stringent conditions.
- For ex vivo research or bioproduction, additional documentation can be provided.
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Mouse Sonic Hedgehog/Shh Protein, Animal-Free
For research use or further manufacturing only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...