Recombinant Human IFN-gamma R2 His-tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 11576-GR

Key Product Details
- R&D Systems CHO-derived Recombinant Human IFN-gamma R2 His-tag Protein (11576-GR)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
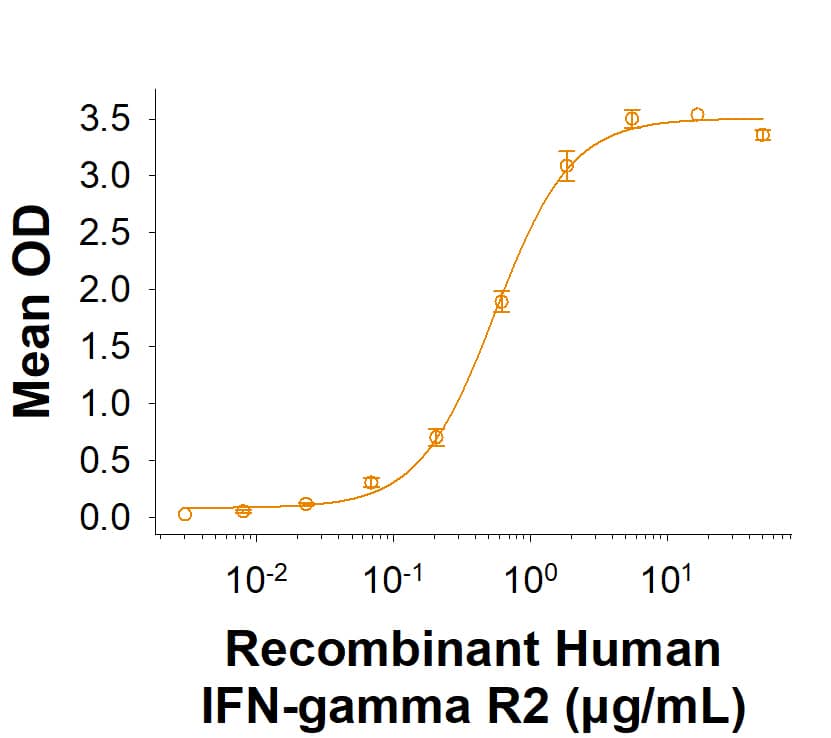
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human IFN-gamma R2 His-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human IFN-gamma R2 His-tag Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human IFN-gamma R2 His-tag Protein (Catalog # 11576-GR) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 38-42 kDa, under reducing conditions.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
11576-GR
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Store the unopened product at -20 to -70 °C. Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Do not use past expiration date. |
Background: IFN-gamma R2
IFN‑ gamma R2 (Interferon gamma receptor 2; also called IFN‑ gamma R beta IFN‑ gamma RII, or AF1) is a 60‑64 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is a member of the class II cytokine receptor family of molecules (1). It is widely expressed as part of a preassembled cell surface multimeric complex. In the absence of IFN‑ gamma, the complex contains two each of IFN‑ gamma R1, R2 and Jak1 molecules (2). Binding of IFN‑ gamma to IFN‑ gamma R1 recruits Jak2 to IFN‑ gamma R2 and initiates phosphorylation, STAT1 binding, conformational changes, and transcriptional regulation, which mainly inhibits proliferation and/or promotes apoptosis (2, 3). Within the ECD, human IFN‑ gamma R2 shares 56% aa sequence identity with mouse IFN‑ gamma R2. IFN‑ gamma R1 and R2 must be from the same species for receptor complexes to be active, and human IFN‑ gamma is not active on the mouse IFN‑ gamma receptor complex (1, 2). IFN‑ gamma R1 is essential for ligand binding and is more constitutively expressed, while IFN‑ gamma R2 is essential for signaling, and its more limited expression controls cell response to IFN‑ gamma (2, 3). For example, mouse T cell IFN‑ gamma R2 is down‑regulated during differentiation to subtypes such as Th1 which produce IFN‑ gamma. (3, 4) This allows expansion of activated cells without growth arrest due to paracrine response to IFN‑ gamma. Following expansion, IFN‑ gamma R2 is re‑expressed to limit the immune reaction (5). IFN‑ gamma signaling mediates control of intracellular pathogens such as mycobacteria (3, 4, 6). In humans, deficiency of IFN‑ gamma R2 or other IFN‑ gamma pathway molecules causes the MSMD (mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial diseases) syndrome (6‑8).
References
- Hemmi, S. et al. (1994) Cell 76:803.
- Krause, C.D. et al. (2006) Cell Res. 16:55.
- Haring, J. S. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 174:6791.
- Tau, G.Z. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Med. 192:977.
- Foulds, K.E. et al. (2008) J. Immunol. 180:842.
- Rosenzweig, S.D. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:4000.
- Filipe-Santos. O. et al. (2006) Semin. Immunol. 18:347.
- Zhang, S-Y. et al. (2008) Immunol. Rev. 226:29.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional IFN-gamma R2 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human IFN-gamma R2 His-tag Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human IFN-gamma R2 His-tag Protein, CF
For research use only