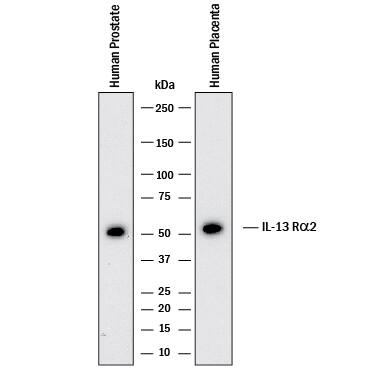
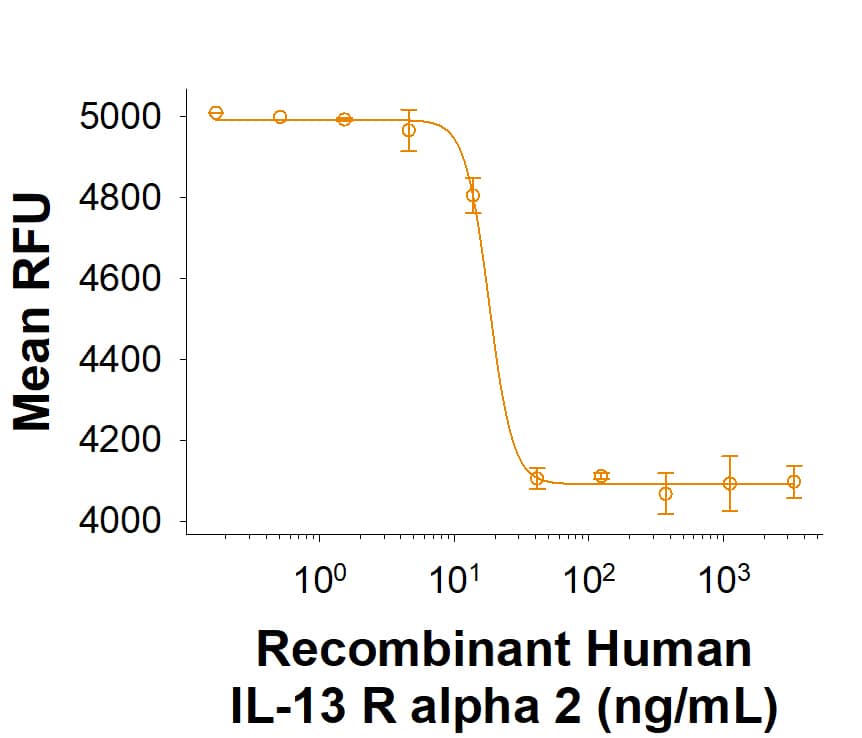
IL-13 R alpha 2 Products
Two members of the type 5 subfamily of type I cytokine receptors can serve as receptors for IL-13. IL-13 can bind to IL-13 R alpha 1 (CD213a1; previously designated IL-13 R alpha or NR4) with low affinity, then recruits the IL-4 R alpha chain to form a high affinity receptor, causing downstream STAT6 activation. Alternately, IL-13 can bind IL-13 R alpha 2 (CD213a2) with high affinity; this interaction does not cause activation of STAT6, but does induce TGF-beta production. IL-13 R alpha 1 and IL-13 R alpha 2 each have three extracellular fibronectin type III domains, two cytokine receptor homology modules and a WSXWS motif typical of the class I cytokine receptor family, but IL-13 R alpha 2 has a much shorter cytoplasmic tail. IL-13 R subunits can be expressed on monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, human B cells, basophils, eosinophils, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells.
235 results for "IL-13 R alpha 2" in Products
235 results for "IL-13 R alpha 2" in Products
IL-13 R alpha 2 Products
Two members of the type 5 subfamily of type I cytokine receptors can serve as receptors for IL-13. IL-13 can bind to IL-13 R alpha 1 (CD213a1; previously designated IL-13 R alpha or NR4) with low affinity, then recruits the IL-4 R alpha chain to form a high affinity receptor, causing downstream STAT6 activation. Alternately, IL-13 can bind IL-13 R alpha 2 (CD213a2) with high affinity; this interaction does not cause activation of STAT6, but does induce TGF-beta production. IL-13 R alpha 1 and IL-13 R alpha 2 each have three extracellular fibronectin type III domains, two cytokine receptor homology modules and a WSXWS motif typical of the class I cytokine receptor family, but IL-13 R alpha 2 has a much shorter cytoplasmic tail. IL-13 R subunits can be expressed on monocytes, macrophages, fibroblasts, human B cells, basophils, eosinophils, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells.
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC, ICC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Simple Western, Flow, IHC, Block, +1 More |
| Sensitivity: | 5.6 pg/mL |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Assay Range: | 39 - 2,500 pg/mL |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | O88786 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #83834 |
| Applications: | WB |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | NP_000631.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Assay Range: | 0.312 - 20 ng/mL |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #83807 |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody.
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #2725C |
| Applications: | WB, Simple Western |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Accession #: | Q14627.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready |
| Assay Range: | 31.2 - 2,000 pg/mL |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC, ICC |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC, ICC |