Recombinant Human BTK His-tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 11750-BK

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Spodoptera frugiperda, Sf 21 (baculovirus)-derived human BTK protein
| Met | 6-His tag | Sumo-tag (mutated, uncleavable) |
3c Protease site | Human BTK (Ala2-Ser659) Accession # Q06187.3 |
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Protein identity confirmed by mass spectrometry.
Predicted Molecular Mass
89 kDa
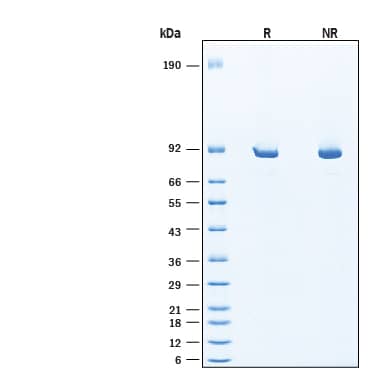
SDS-PAGE
82-90 kDa, under reducing conditions
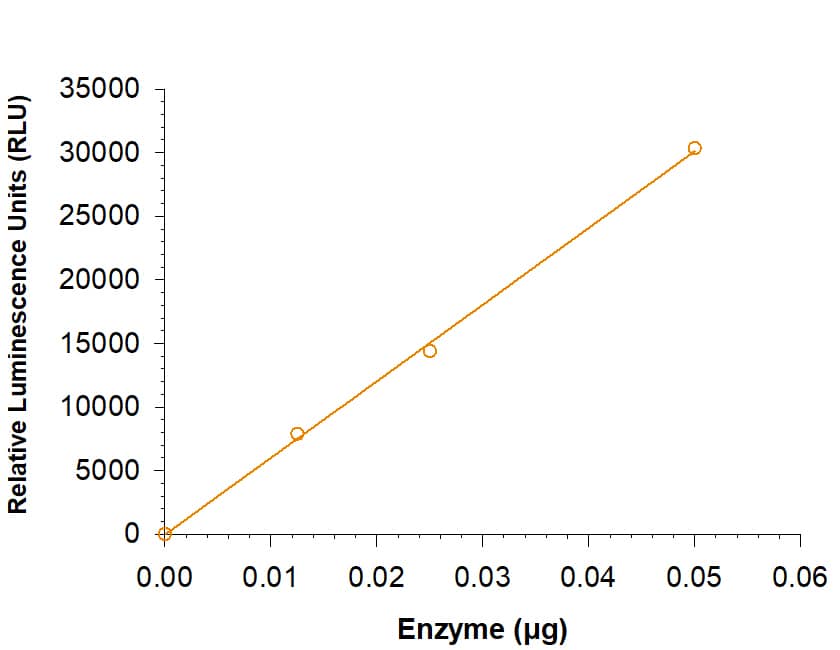
Activity
Measured by its ability to transfer phosphate from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to a synthetic peptide substrate.
The specific activity is >80 pmol/min/μg, as measured under the described conditions.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human BTK His-tag Protein, CF
Recombinant Human BTK His-tag Enzyme Activity.
Recombinant Human BTK His-tag (Catalog # 11750-BK) is measured by its ability to transfer phosphate from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to a synthetic peptide substrate.Recombinant Human BTK His-tag SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human BTK His-tag Protein (Catalog # 11750-BK) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 82-90 kDa, under reducing conditions.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
11750-BK
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris, NaCl, DTT and Glycerol. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: BTK
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK), also known as Agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase (ATK) and B-cell progenitor kinase (BPK), is one of five members of the tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (TEC) family of cytoplasmic non-receptor tyrosine kinases (1,2) that is primarily expressed in B-lymphocytes. BTK, like others in this family, contains a characteristic N-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain as well as a TEC homology domain with three regions including a Btk homology region and two proline-rich regions. In addition, BTK contains two Src homology domains that mediate binding events and a C-terminal kinase domain (1) with a conserved catalytic domain with an ATP binding site within the cleft of two lobes at the N-terminal and C-terminal regions (1,2). BTK is activated by phosphorylation by SYK or SRC family kinases and then subsequent autophosphorylation after recruitment to the membrane through its interaction with PIP3 production resulting from B cell antigen receptor activation (2). Mutations in the human btk gene were found to cause X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA), a male immune deficiency disorder characterized by a lack of mature, immunoglobulin-producing, peripheral B cells (3,4). Its activation is known to be involved in signal transduction pathways regulating survival, activation, proliferation, and also differentiation of B lineage lymphoid cells (1, 3-5). Consequently BTK is critical for the survival of leukemic cells in various B cell malignancies including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)(2,6,7). Inhibition of BTK is a promising target for therapeutics for B-cell malignancies given initial small-molecule inhibitors showed excellent anti-tumor activity in clinical studies (8) and their success in therapeutic application for CLL and small lymphocytic leukemia (SLL)(9). Significant interest remains in the development of higher specificity BTK inhibitors with less off-target activity (10,11) as well as combination inhibitors targeting other kinases or other proteins targets (2,12-14) in addition to BTK in B-cell malignancy. In addition, ectopic expression of BTK has been observed in various solid tumors making BTK a therapeutic target of interest in a broader context for the role the kinase may play in the tumor microenvironment (2,15).
References
- Mao, C. et. al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:41435.
- Singh, S.P. et. al. (2018) Mol. Cancer 17:57.
- Tsukada, S. et. al. (1993) Cell. 72:279.
- Vetrie, D. et. al. (1993) Nature. 361:226.
- Kurosaki, T. and M. Kurosaki (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:15595.
- Herman, S.E. et. al. (2011) Blood. 117:6287.
- Chang, B.Y. et. al. (2013) Blood 122:2412.
- Byrd, J.C. et. al. (2013) N. Engl. J. Med. 369:32.
- Burger, J.A. et. al. (2015) N. Engl. J. Med. 373:2425.
- Wu, J. et. al. (2016) J. Hematol. Oncol. 9:80.
- Tan, S. et. al. (2025) Cancer. 131:e70083.
- Sagiv-Barfi, I. et. al. (2015) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112:E966.
- Yahiaoui, A. et. al. (2017) PLoS One. 12:e0171221.
- Secchiero, P. et. al. (2017) Oncotarget. 8:59235.
- Grassilli, E. et. al. (2022) Front. Oncol. 12:944538.
Long Name
Bruton Agammaglobulinemia Tyrosine Kinase
Alternate Names
AGMX1, IMD1, PSCTK1, XLA
Entrez Gene IDs
695 (Human)
Gene Symbol
BTK
UniProt
Additional BTK Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human BTK His-tag Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human BTK His-tag Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...