Mouse Osteoactivin/GPNMB Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB2330

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Lys23-Asn502
Accession # NP_444340
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Osteoactivin/GPNMB Antibody
Detection of Osteoactivin/GPNMB by Immunohistochemistry
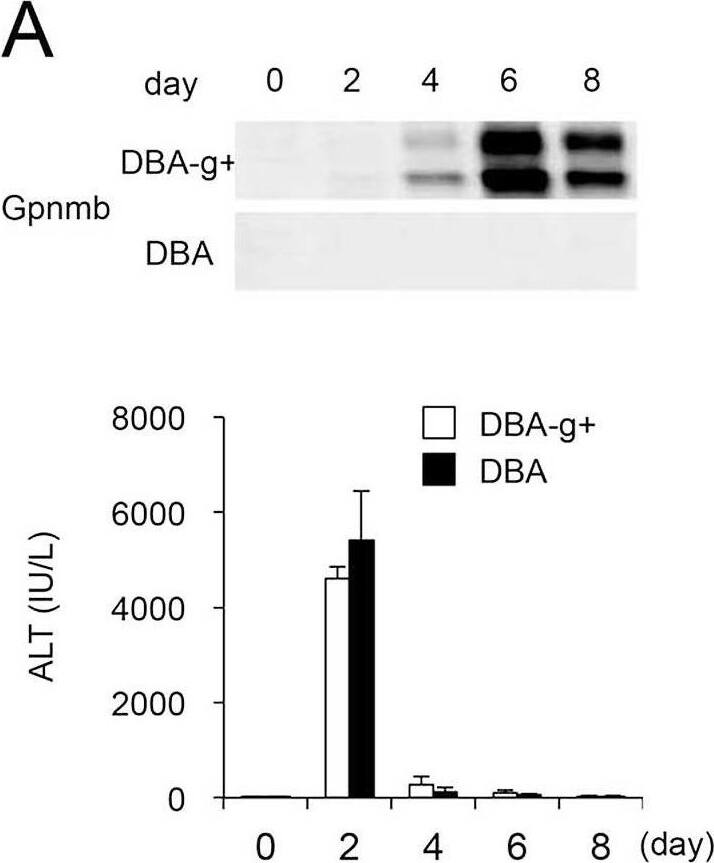
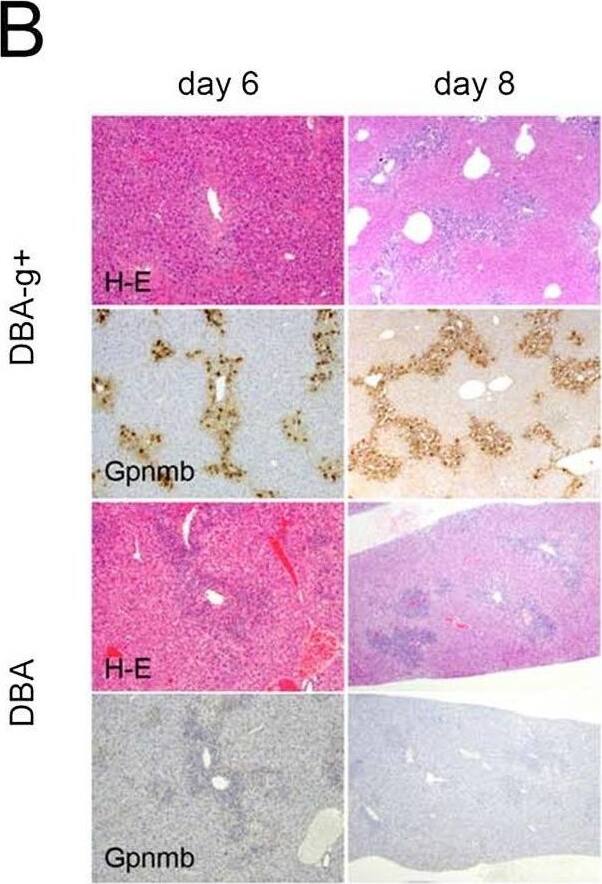
Features of DBA-g+ and DBA mice.(A) Expression of Gpnmb is observed in DBA-g+ but not DBA mice following a single injection of CCl4. However, (B) sequential changes in serum ALT levels and the degree of liver injury are not affected by the lack of Gpnmb-positive macrophages (original magnification, x100). Conversely, (C) the areas of fibrosis and (D) the number of alpha-SMA-positive cells are significantly decreased in the liver tissues of DBA mice compared to DBA-g+ mice (original magnification, x200). Additionally, (E) although lack of Gpnmb-positive macrophages does not affect expression of TGF-beta or Col1 alpha1, expression of MMP-9, MMP-13, and TIMP-1 are significantly decreased in mice lacking Gpnmb expression at six or eight days after single injection of CCl4. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4). * P < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26599547), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Osteoactivin/GPNMB by Western Blot
Features of DBA-g+ and DBA mice.(A) Expression of Gpnmb is observed in DBA-g+ but not DBA mice following a single injection of CCl4. However, (B) sequential changes in serum ALT levels and the degree of liver injury are not affected by the lack of Gpnmb-positive macrophages (original magnification, x100). Conversely, (C) the areas of fibrosis and (D) the number of alpha-SMA-positive cells are significantly decreased in the liver tissues of DBA mice compared to DBA-g+ mice (original magnification, x200). Additionally, (E) although lack of Gpnmb-positive macrophages does not affect expression of TGF-beta or Col1 alpha1, expression of MMP-9, MMP-13, and TIMP-1 are significantly decreased in mice lacking Gpnmb expression at six or eight days after single injection of CCl4. Values are mean ± SEM (n = 4). * P < 0.05 (Mann-Whitney U test). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26599547), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Osteoactivin/GPNMB by Immunohistochemistry
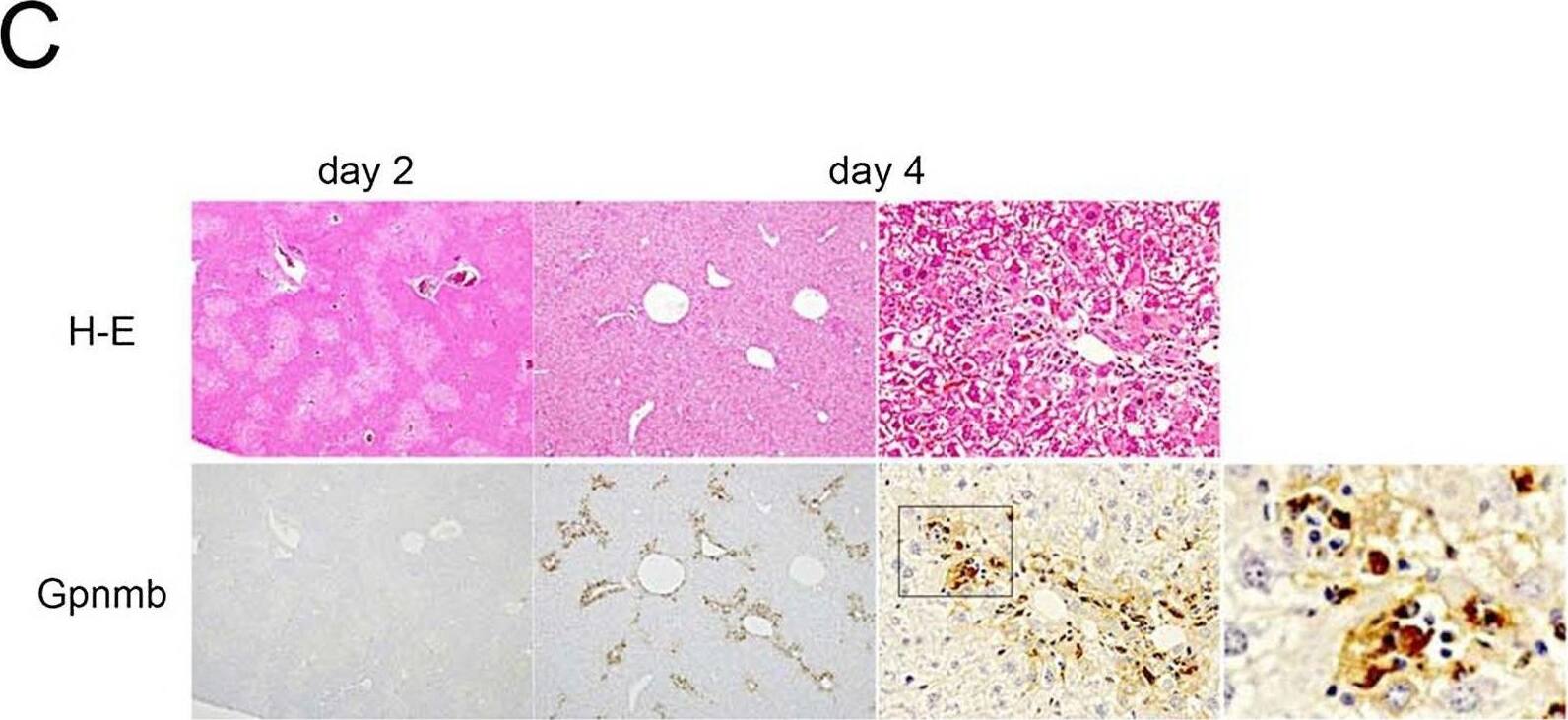
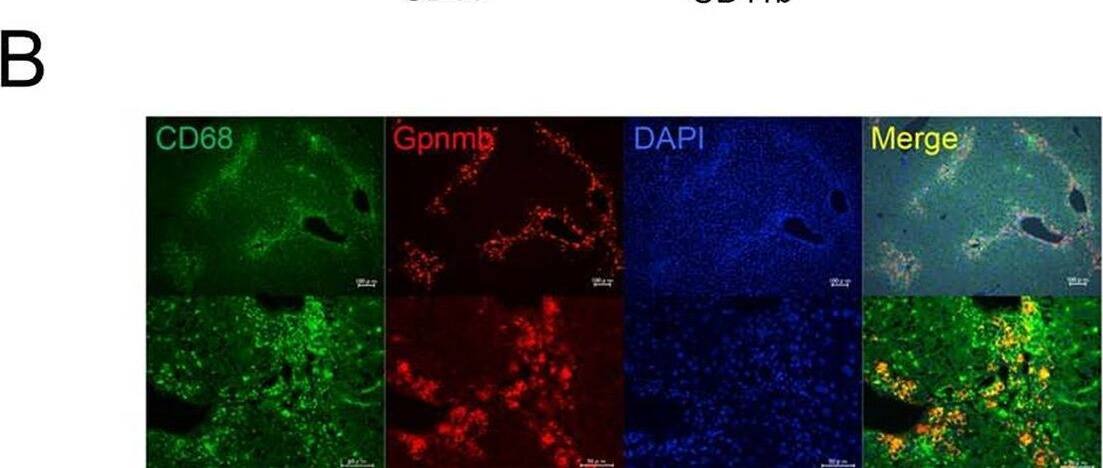
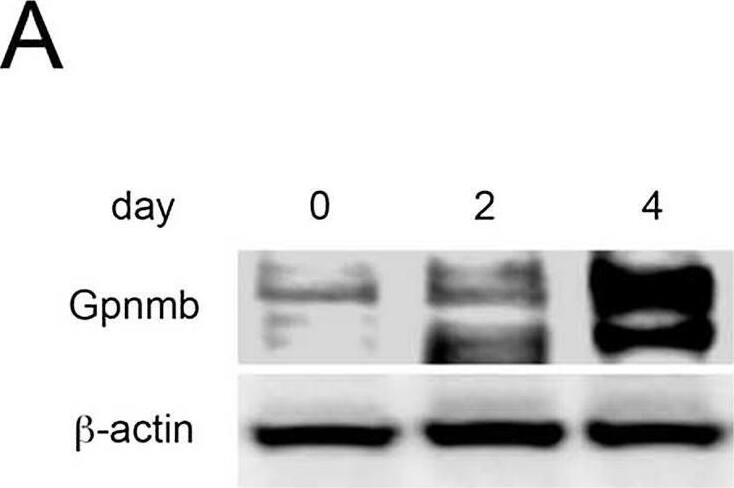
Sequential changes in and localization of Gpnmb expression. Gpnmb expression is enhanced in the recovery phase (A) in whole liver as determined by Western blotting and (B) in isolated hepatic macrophages as determined by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (n = 5 at each day). (C) Moreover, Gpnmb expression is observed immunohistochemically around injured lesions in a pattern similar to that in F4/80-positive macrophages, and Gpnmb-positive cells exhibit partial phagocytosis. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26599547), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse Osteoactivin/GPNMB Antibody
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse Osteoactivin/GPNMB Fc Chimera (Catalog # 2330-AC)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Osteoactivin/GPNMB
Osteoactivin (also named GPNMB and DC-HIL) is a 125 kDa, intracellular glycoprotein that is associated with cell endosomal/lysosomal compartments (1, 2). Mouse osteoactivin is synthesized as a type I, transmembrane, 574 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 22 aa signal sequence, a 478 aa luminal/extracellular domain, a 23 aa transmembrane segment and a 51 aa cytoplasmic tail. The luminal region contains an N-terminal heparin-binding motif, multiple glycosylation sites, an RGD motif and a 130 aa PKD domain. The intracellular tail also has an RGD motif, plus an ITAM (Y-x-x-I) and lysosomal targeting (L-L) motif. The extracellular/luminal region is 89% and 74% aa identical to the equivalent regions in rat and human, respectively. Cells known to express osteoactivin include osteoblasts, dendritic cells, and melanocytes, plus fetal chondrocytes and stratum basale keratinocytes (2, 3). Osteoactivin is reported to bind to heparan sulfate-proteoglycan, possibly on the surface of fibroblasts and endothelial cells (2). It may also interact with integrins.
References
- Bachner, D. et al. (2002) Gene Exp. Patterns 1:159.
- Shikano, S. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:8125.
- Owen, T.A. et al. (2003) Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 13:205.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Osteoactivin/GPNMB Products
Product Documents for Mouse Osteoactivin/GPNMB Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Osteoactivin/GPNMB Antibody
For research use only