Mouse IKK beta Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB7155

Conjugate
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Mouse
Cited:
Mouse
Applications
Validated:
Western Blot
Cited:
Western Blot
Label
Unconjugated
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Rat IgG2A Clone # 725818
Product Specifications
Immunogen
E. coli-derived recombinant mouse IKK beta
Val530-Asp757
Accession # O88351
Val530-Asp757
Accession # O88351
Specificity
Detects mouse IKK beta in direct ELISAs and Western blots.
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Rat
Isotype
IgG2A
Scientific Data Images for Mouse IKK beta Antibody
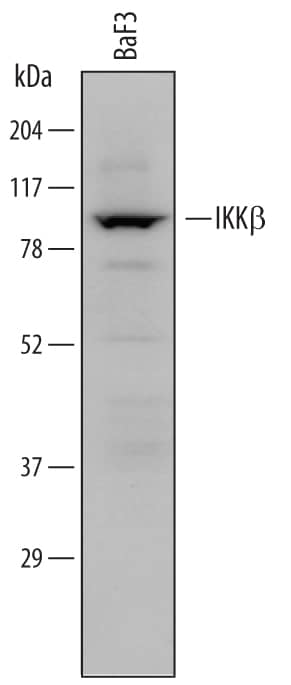
Detection of Mouse IKK beta by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Rat Anti-Mouse IKK beta Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB7155) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Rat IgG Secondary Antibody. A specific band was detected for IKK beta at approximately 87 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot
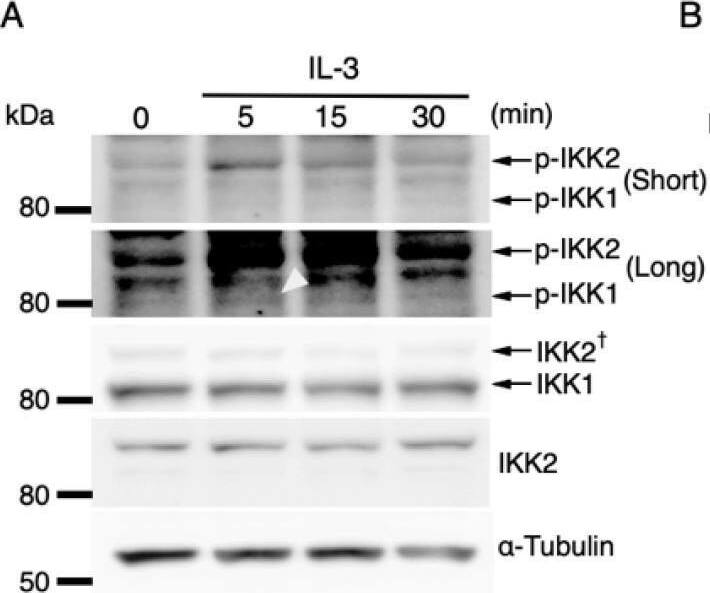
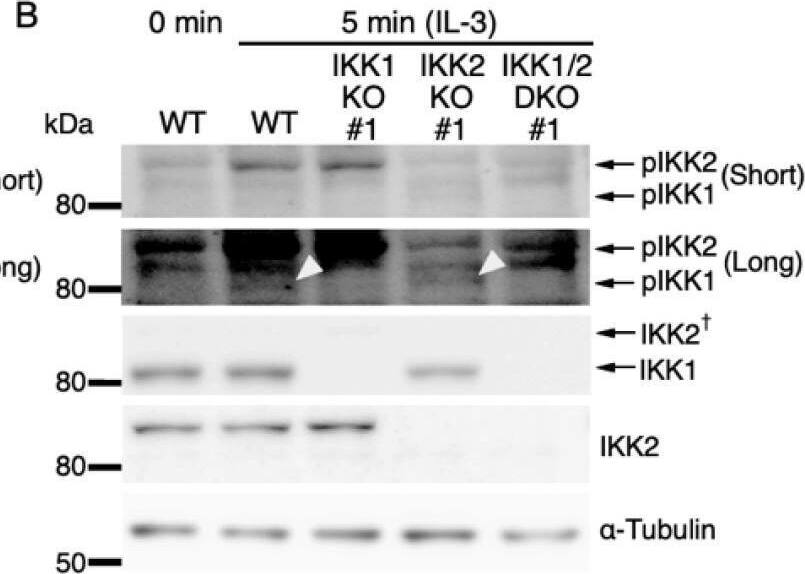
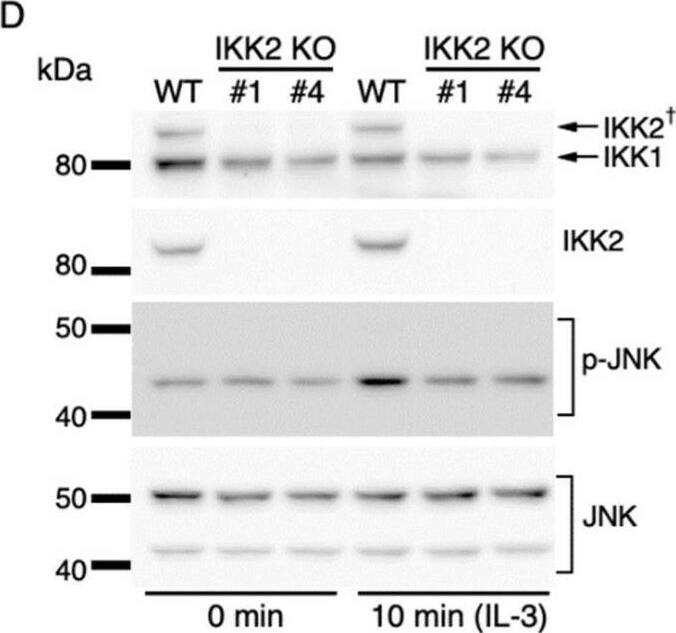
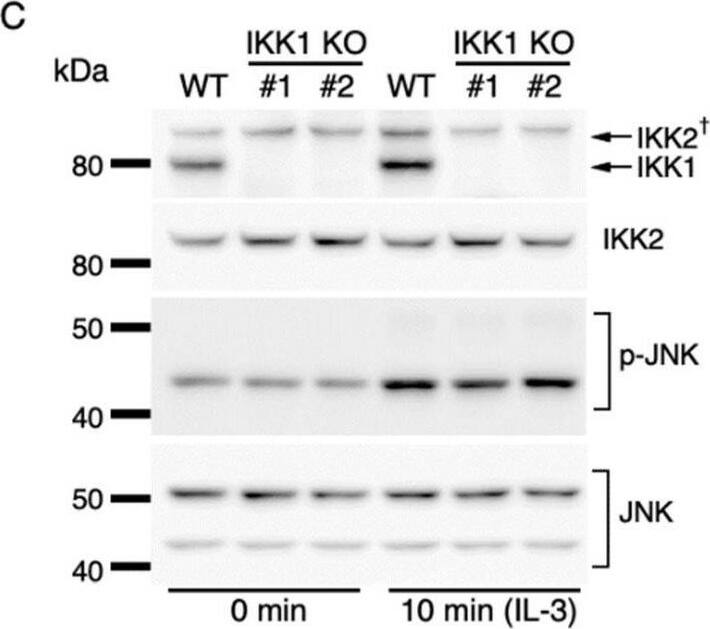
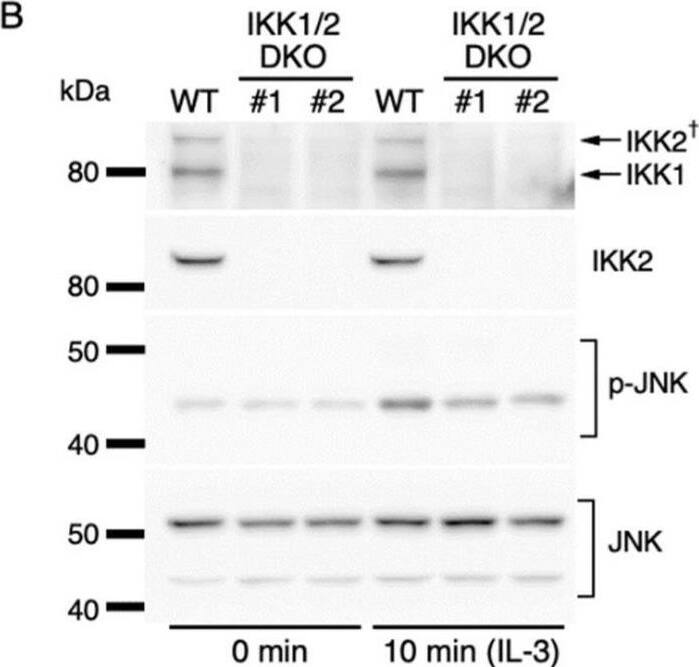
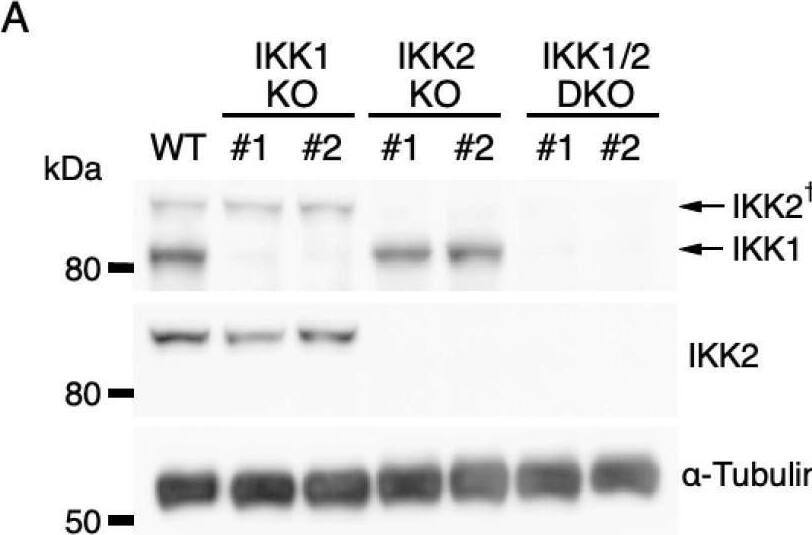
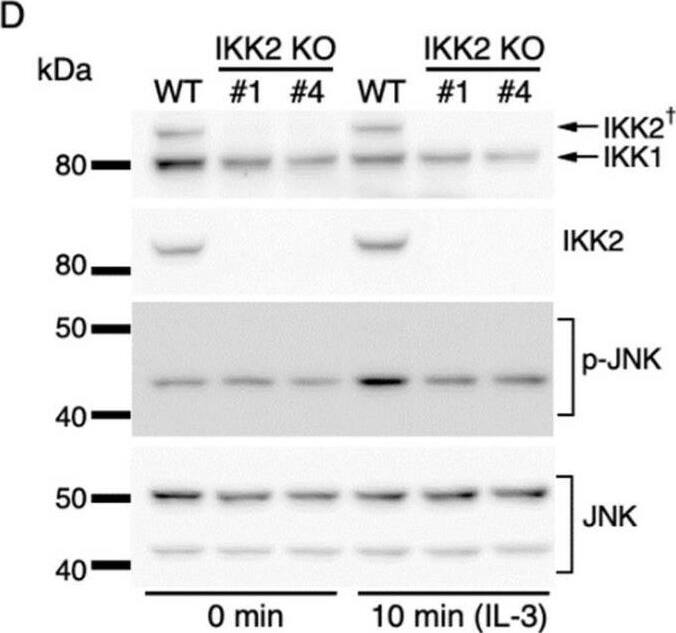
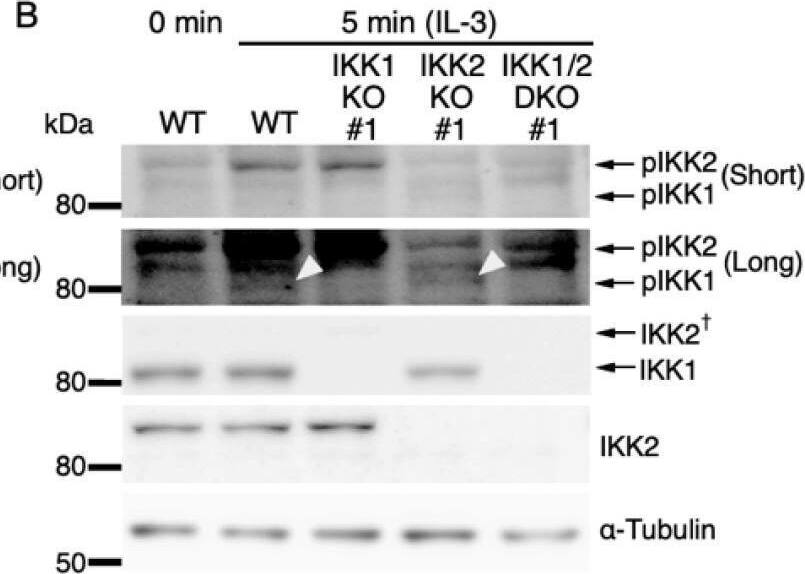
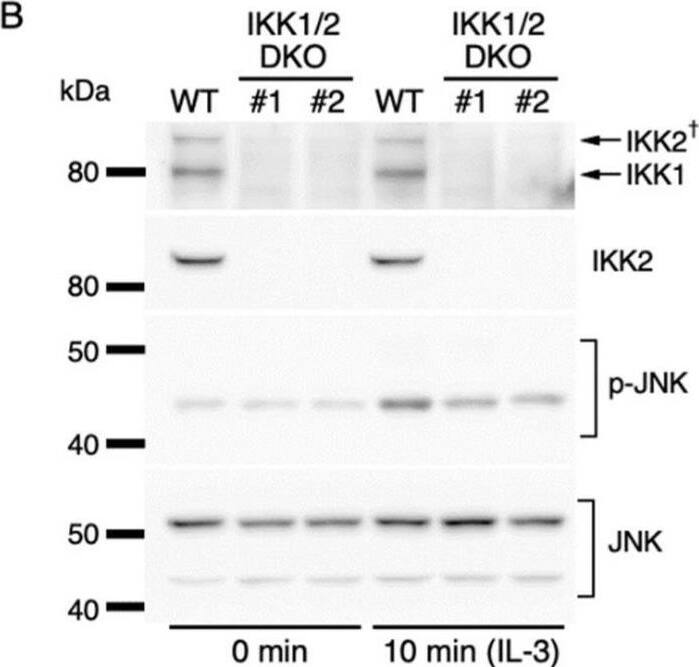
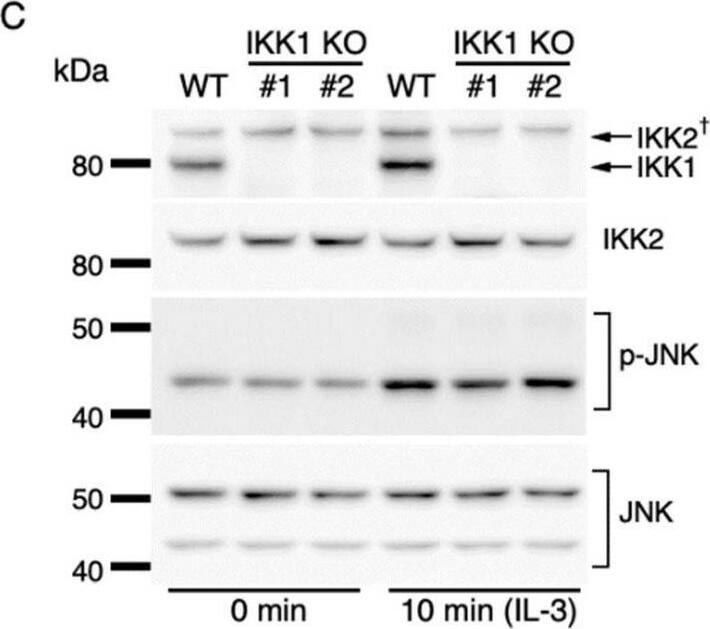
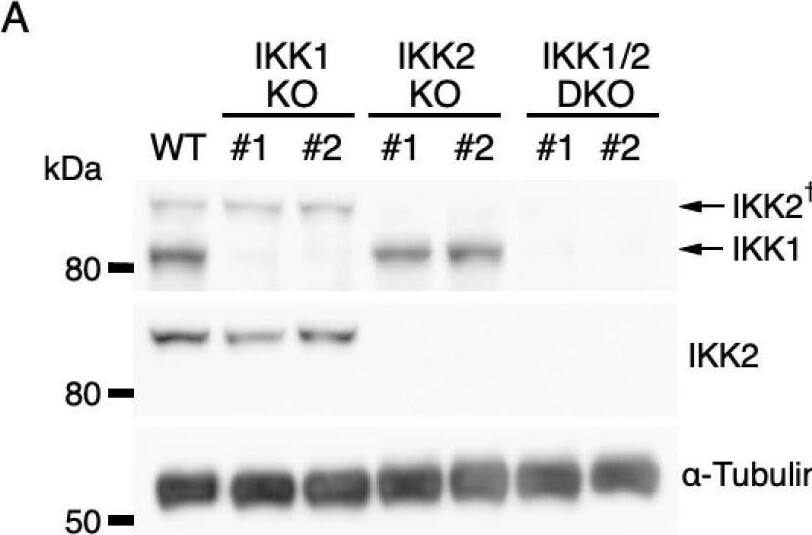
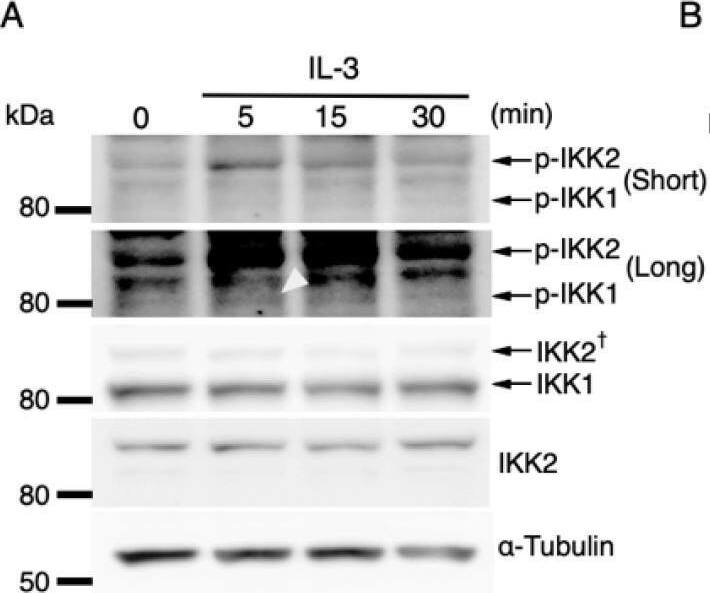
IL-3-induced IKK activation was not associated with the degradation of I kappaB-alpha followed by nuclear translocation of p65. (A) Phosphorylation of IKKs after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. Long and short exposures to detect phosphorylated IKK1 and IKK2 are shown. An arrowhead indicates the band corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1 at 5 min after IL-3 stimulation. A dagger denotes the detection of IKK2 by potential cross-reactivity of the anti-IKK1 Ab. (B) Phosphorylation of IKKs in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 for 5 min. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. Arrowheads indicate the bands corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1. (C) Degradation of I kappaB-alpha by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. (D) Induction of nuclear translocation of p65 by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated times and immunoblotted with Abs to the cytosol marker alpha-tubulin and the nuclear marker fibrillarin. Long and short exposures to detect p65 are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of IKK beta by Western Blot
IL-3-induced IKK activation was not associated with the degradation of I kappaB-alpha followed by nuclear translocation of p65. (A) Phosphorylation of IKKs after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 for the indicated times, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. Long and short exposures to detect phosphorylated IKK1 and IKK2 are shown. An arrowhead indicates the band corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1 at 5 min after IL-3 stimulation. A dagger denotes the detection of IKK2 by potential cross-reactivity of the anti-IKK1 Ab. (B) Phosphorylation of IKKs in IKK KO cells after IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 parental (WT), IKK1 KO, IKK2 KO, and IKK1/2 DKO cells were stimulated with IL-3 for 5 min. Immunoblot analysis was performed with whole-cell lysates using the indicated Abs. Arrowheads indicate the bands corresponding to phosphorylated IKK1. (C) Degradation of I kappaB-alpha by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated durations, and whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted using the indicated Abs. (D) Induction of nuclear translocation of p65 by TNF-alpha but not by IL-3 stimulation. Following IL-3 deprivation for 6 h, Ba/F3 cells were stimulated with IL-3 or TNF-alpha for the indicated times and immunoblotted with Abs to the cytosol marker alpha-tubulin and the nuclear marker fibrillarin. Long and short exposures to detect p65 are shown. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35563758), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse IKK beta Antibody
Application
Recommended Usage
Western Blot
0.5 µg/mL
Sample: BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line
Sample: BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein A or G purified from hybridoma culture supernatant
Reconstitution
Sterile PBS to a final concentration of 0.5 mg/mL. For liquid material, refer to CoA for concentration.
Formulation
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. *Small pack size (SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Shipping
Lyophilized product is shipped at ambient temperature. Liquid small pack size (-SP) is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: IKK beta
Long Name
IkB Kinase beta
Alternate Names
IkBKB, IKK2, NFKBIKB
Gene Symbol
IKBKB
UniProt
Additional IKK beta Products
Product Documents for Mouse IKK beta Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse IKK beta Antibody
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...