Human Pentraxin 2/SAP Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB19481

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
His20-Val233
Accession # P02743
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human Pentraxin 2/SAP Antibody
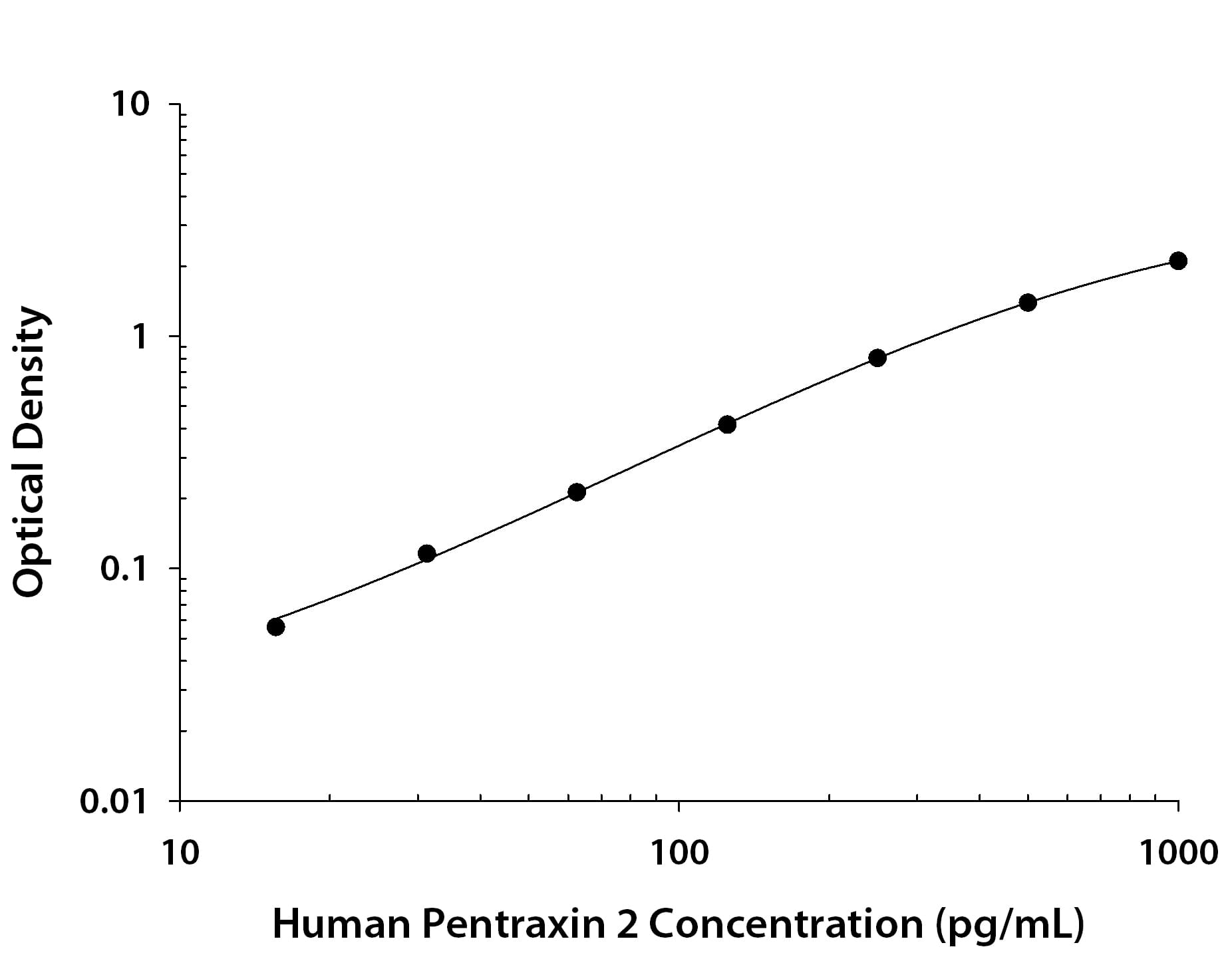
Human Pentraxin 2/SAP ELISA Standard Curve.
Recombinant Human Pentraxin 2/SAP protein was serially diluted 2-fold and captured by Mouse Anti-Human Pentraxin 2/SAP Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB19481) coated on a Clear Polystyrene Microplate (Catalog # DY990). Mouse Anti-Human Pentraxin 2/SAP Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB19483) was biotinylated and incubated with the protein captured on the plate. Detection of the standard curve was achieved by incubating Streptavidin-HRP (Catalog # DY998) followed by Substrate Solution (Catalog # DY999) and stopping the enzymatic reaction with Stop Solution (Catalog # DY994).Applications for Human Pentraxin 2/SAP Antibody
ELISA
This antibody functions as an ELISA capture antibody when paired with Mouse Anti-Human Pentraxin 2/SAP Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB19483).
This product is intended for assay development on various assay platforms requiring antibody pairs. We recommend the Human Pentraxin 2/SAP DuoSet ELISA Kit (Catalog # DY1948-05) for convenient development of a sandwich ELISA.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Pentraxin 2/SAP
Pentraxin 2 (PTX2), also known as Serum Amyoid P Component (SAP), is a secreted serum glycoprotein that is a universal non-fibrillar component of amyloid deposits. These extracellular deposits of insoluble protein fibrils are the result of protein misfolding and can lead to tissue damage and disease (1, 2). PTX2 belongs to the pentraxin (pentaxin) superfamily, whose members have the characteristic pentagonal discoid arrangement of five non-covalently bound subunits. Pentraxins bind to a variety of molecules in a calcium-dependent lectin-like manner through a pattern-recognition-binding site (1, 4, 5). There are two known subfamilies of pentraxins, the classical or short pentraxin subfamily that includes the serum C-reactive Protein (CRP) and PTX2, and the fusion or long pentraxin subfamily whose members contain pentraxin-related carboxyl-terminal halves (1).
PTX2 and CRP share approximately 50% amino acid sequence identity (2, 5). They are produced and secreted by liver hepatocytes and circulates in plasma. Mouse PTX2 is a major acute-phase protein whose plasma concentrations increase dramatically during an acute phase response (2). In human where CRP is the major acute-phase protein, the plasma concentration of human PTX2 remains relatively constant in response to tissue-damage (2, 5).
PTX2 associates ubiquitously with all amyloid deposits that are implicated in a diverse range of diseases including Alzheimer’s and prion diseases, type 2 diabetes and various systemic amyloidoses (3, 6, 7). As a non-fibrillar component, PTX2 regulates the solubility of amyloid fibrils and protects them from degradation by proteolytic enzymes and phagocytic cells. In addition to its role in the pathogenesis of amyloidoses, PTX2 also has an important physiological function in innate immunity (8).
References
- Goodman, A. et al. (1996) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 7:191.
- Steel, D. and A. Whitehead (1994) Immunol. Today 15:81.
- Hirschfield, G.M. and P.N. Hawkins (2003) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 35:1608.
- Emsley, J. et al. (1994) Nature 367:338.
- Mantzouranis, E. et al. (1985) J. Biol. Chem. 260:7752.
- Botto, M. et al. (1997) Nature Medicine 3:855.
- Pepys, M. et al. (2002) Nature 417:254.
- Bharadwaj, D. et al. (2001) J. Immunol. 166:6735.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Pentraxin 2/SAP Products
Product Documents for Human Pentraxin 2/SAP Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Pentraxin 2/SAP Antibody
For research use only