Summary
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer among women worldwide. Notably, 1 in 8 women will develop invasive breast cancer during their lifetime. Continued research of the biology underlying breast cancer is essential to the development of novel therapeutics and biomarker detection methods.
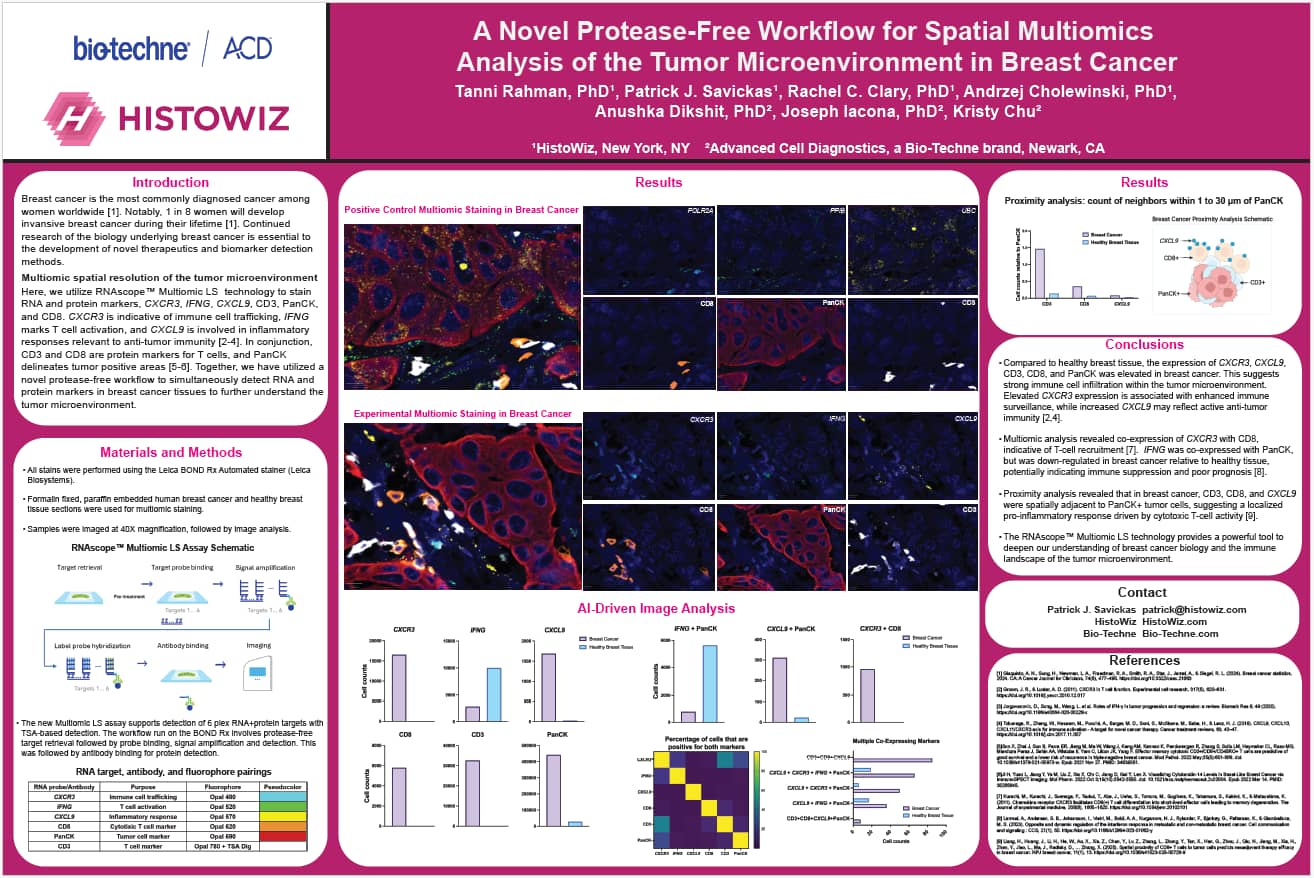
Here, we utilize RNAscope™ Multiomic LS technology to stain RNA and protein markers, CXCR3, IFNG, CXCL9, CD3, PanCK, and CD8. CXCR3 is indicative of immune cell trafficking, IFNG marks T cell activation, and CXCL9 is involved in inflammatory responses relevant to anti-tumor immunity. In conjunction, CD3 and CD8 are protein markers for T cells, and PanCK delineates tumor positive areas. Together, we have utilized a novel protease-free workflow to simultaneously detect RNA and protein markers in breast cancer tissues to further understand the tumor microenvironment.
- Multiomic analysis revealed co-expression of CXCR3 with CD8, indicative of T-cell recruitment. IFNG was co-expressed with PanCK, but was down-regulated in breast cancer relative to healthy tissue, potentially indicating immune suppression and poor prognosis.
- Proximity analysis revealed that in breast cancer, CD3, CD8, and CXCL9 were spatially adjacent to PanCK+ tumor cells, suggesting a localized pro-inflammatory response driven by cytotoxic T-cell activity.
- The RNAscope™ Multiomic LS technology provides a powerful tool to deepen our understanding of breast cancer biology and the immune landscape of the tumor microenvironment.
This poster was presented at the AACR 2025 meeting.
Request Literature
To access this literature content please fill out the form below.