Activin A: Small Molecules and Peptides
Activin A is an important member of the TGF-beta superfamily that is produced by many different cell types and is essential for proper development. Bioactive Activin A exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer that recognizes and binds to four Activin receptors, Activin RIA and RIB, and Activin RIIA and RIIB. This ligand-receptor binding event triggers activation of SMAD signaling pathways ultimately regulating a wide variety of functions including stem cell maintenance, self-renewal, and differentiation, B-cell differentiation and proliferation, wound healing, metabolism, and gonadal development.
Activin A is first produced as a precursor protein containing a propeptide that gets proteolytically cleaved off leaving the mature A chain. Two A chains assemble by disulfide bond formation creating the bioactive homodimer. The bioavailability of Activin A is regulated by cell-associated decoy molecules (BAMBI, Betaglycan, Cripto), secreted proteins (a2-Macroglobulin, Follistatin, FLRG), and intracellular incorporation of the beta A subunit into Activin AC or Inhibin A. Experimentally, recombinant Activin A is commonly used to maintain the proliferative potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells and to promote differentiation of embryonic stem cells into endoderm and pancreatic B cells.
Products:
3 results for "Activin A Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
3 results for "Activin A Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
Activin A: Small Molecules and Peptides
Activin A is an important member of the TGF-beta superfamily that is produced by many different cell types and is essential for proper development. Bioactive Activin A exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer that recognizes and binds to four Activin receptors, Activin RIA and RIB, and Activin RIIA and RIIB. This ligand-receptor binding event triggers activation of SMAD signaling pathways ultimately regulating a wide variety of functions including stem cell maintenance, self-renewal, and differentiation, B-cell differentiation and proliferation, wound healing, metabolism, and gonadal development.
Activin A is first produced as a precursor protein containing a propeptide that gets proteolytically cleaved off leaving the mature A chain. Two A chains assemble by disulfide bond formation creating the bioactive homodimer. The bioavailability of Activin A is regulated by cell-associated decoy molecules (BAMBI, Betaglycan, Cripto), secreted proteins (a2-Macroglobulin, Follistatin, FLRG), and intracellular incorporation of the beta A subunit into Activin AC or Inhibin A. Experimentally, recombinant Activin A is commonly used to maintain the proliferative potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells and to promote differentiation of embryonic stem cells into endoderm and pancreatic B cells.
Products:
mTOR inhibitor; immunosuppressant
| Chemical Name: | (3S,6R,7E,9R,10R,12R,14S,15E,17E,19E,21S,23S,26R,27R,34aS)-9,10,12,13,14,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,32,33,34,34a-Hexadecahydro-9,27-dihydroxy-3-[(1R)-2-[(1S,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethyl]-10,21-dimethoxy-6,8,12,14,20,26-hexamethyl-23,27-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclohentriacontine-1,5,11,28,29(4H,6H,31H)-pentone |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Pan-histone deacetylase inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | (2E)-N-Hydroxy-3-[4-[[[2-(2-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]amino]methyl]phenyl]-2-propenamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Negative control for 1S,3R-RSL3 (Cat. No. 6118)
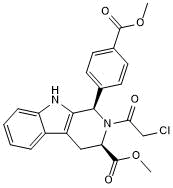
| Chemical Name: | (1R,3R)-Methyl 2-(2-chloroacetyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1-[4-(methoxycarbonyl)phenyl]-1H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylate |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |