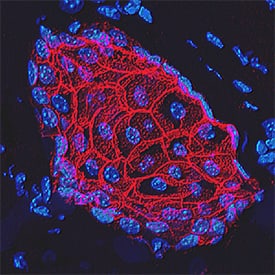
E‑Cadherin in Mouse Intestinal Organoids.
E-Cadherin was detected in immersion fixed mouse intestinal organoids using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E-Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF748) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (green; Catalog #
NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Magnification shown at 100X (upper panel) and 40X (lower panel). Specific staining was localized to cell surfaces. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
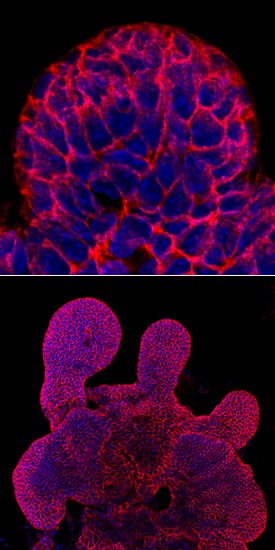
E‑Cadherin in Mouse Intestinal Organoids.
E-Cadherin was detected in immersion fixed mouse intestinal organoids using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E-Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF748) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 493-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (green; Catalog #
NL003) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell surfaces. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.
E‑Cadherin in Mouse Spinal Cord.
E-Cadherin was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse spinal cord using Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E-Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF748) at 1.7 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog #
CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to dorsal horn. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.
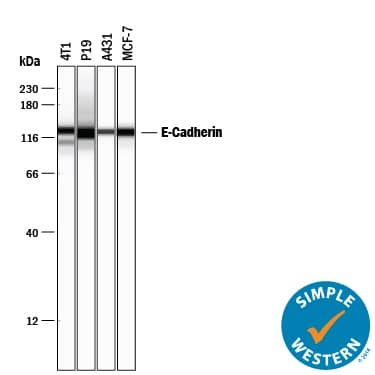
Detection of Human and Mouse E‑Cadherin by Simple WesternTM.
Simple Western lane view shows lysates of 4T1 mouse breast cancer cell line, P19 mouse embryonal carcinoma cell line, A431 human epithelial carcinoma cell line, and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for E-Cadherin at approximately 128 kDa (as indicated) using 5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E-Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF748) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog #
HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.
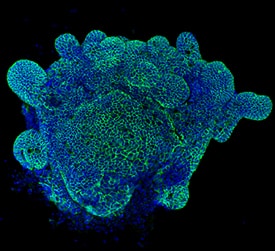
Detection of Mouse E-Cadherin by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
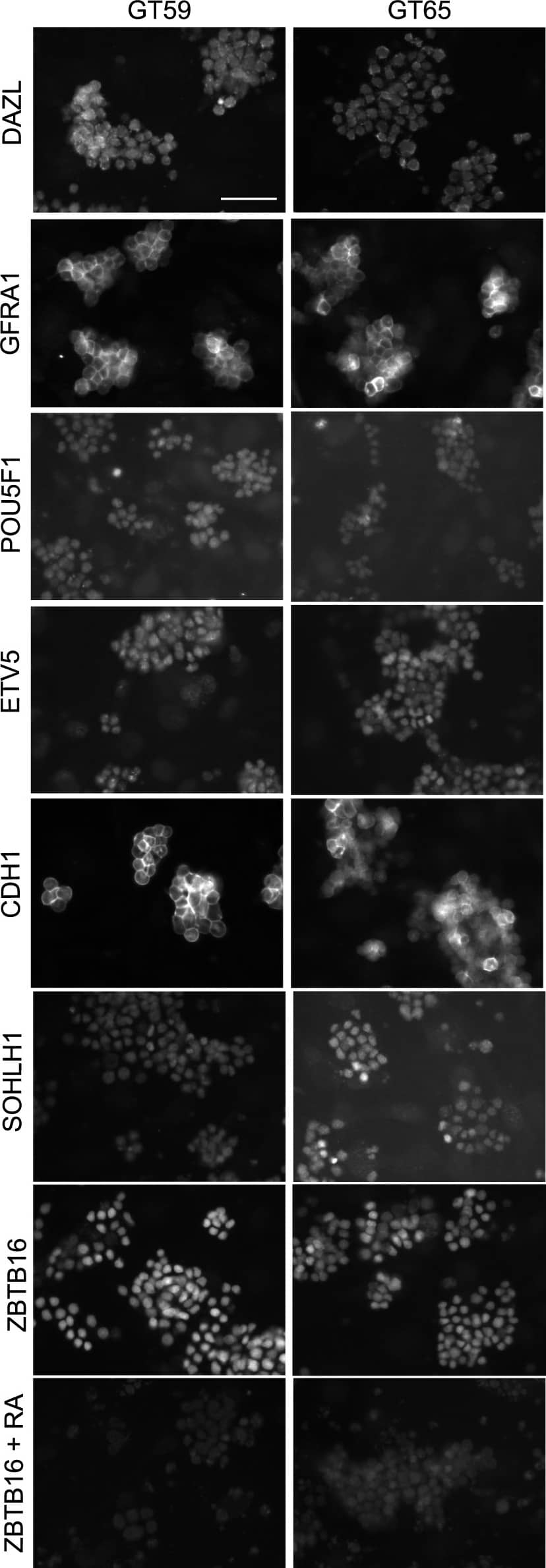
Retention of the spermatogonial phenotype following gene correction.Immunostaining was performed on gene-corrected GT59 (left) and GT65 cells (right): DAZL, a germ cell specific marker; GFRA1, POU5F1, ETV5, CDH1, and SOHLH1, markers of undifferentiated spermatogonia. Additionally, GT59 and GT65 cells were treated with the differentiation factor, retinoic acid (1 µM) or a vehicle control and then immunostained to examine levels of ZBTB16, a marker of undifferentiated spermatogonia. Bar represents 50 microns. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25409432), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse E-Cadherin by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
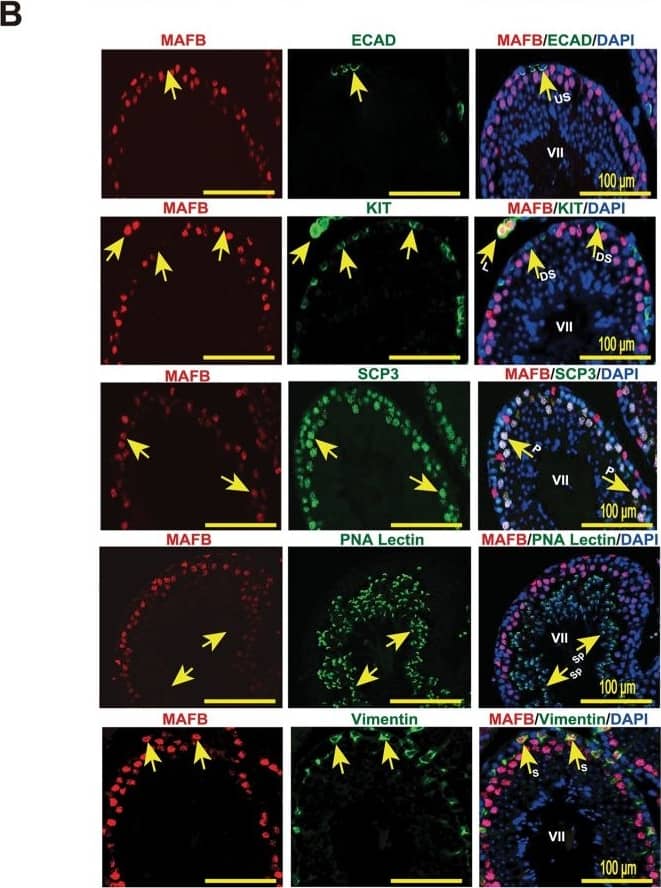
Localization of MAFB in mouse testes.(A) Localization of MAFB in E18.5 mouse testes. Double immunostaining of MAFB with E-cadherin (ECAD), GATA4, or STAR is shown. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The color of each marker is indicated above the images. G; germ cells. S; Sertoli cells. L; Leydig cells. MAFB was specifically detected in Leydig cells and Sertoli cells. (B) Localization of MAFB in adult mouse testes. Double immunostaining of MAFB with E-cadherin (ECAD), KIT, SCP3, PNA Lectin, or vimentin is shown. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The color of each marker is indicated above the images. All seminiferous tubules shown represent stage VII. US; undifferentiated spermatogonia. DS; differentiated spermatogonia. P; pachytene spermatocytes. Sp; spermatids. S; Sertoli cells. L; Leydig cells. MAFB was specifically detected in Leydig cells, Sertoli cells, and pachytene spermatocytes. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190800), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse E-Cadherin by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
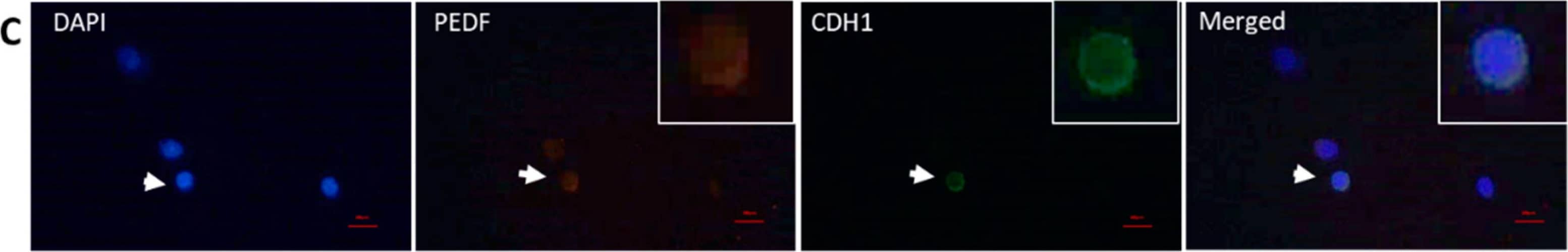
Cellular localization of PEDF in testicular spermatogenic cells. Methanol-fixed cells were used to stain premeiotic and meiotic/postmeiotic cells as described in Figure 2. (A) alpha6-integrin, (B) GFR-alpha, (C) CDH1, (D) and NC—IF staining without the presence of primary antibody. (E) CREM, (F) Boule, (G) Acrosin and (H) NC—IF staining without the presence of primary antibody. Scale bar: 100 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33498962), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse E-Cadherin by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
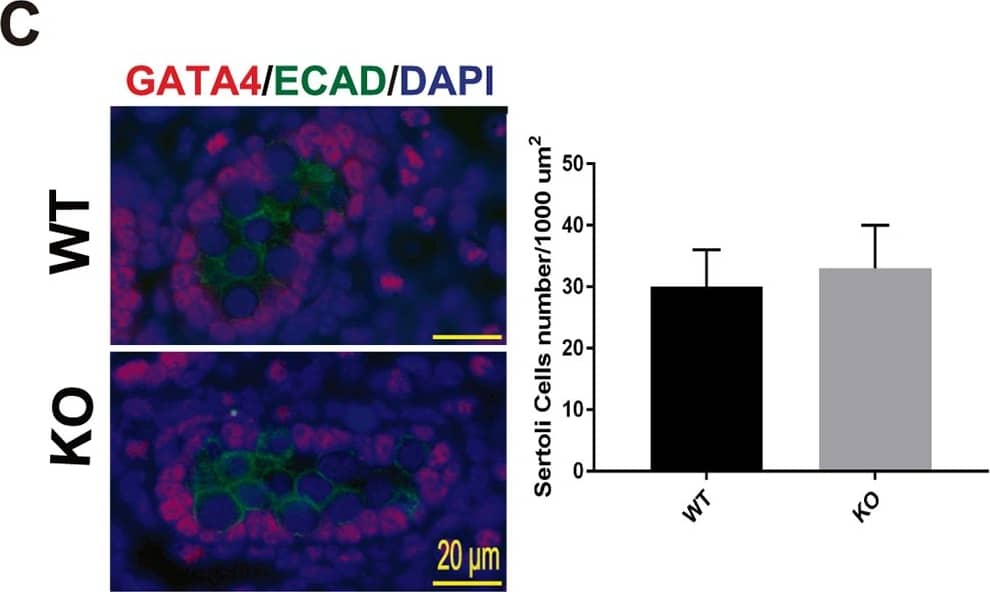
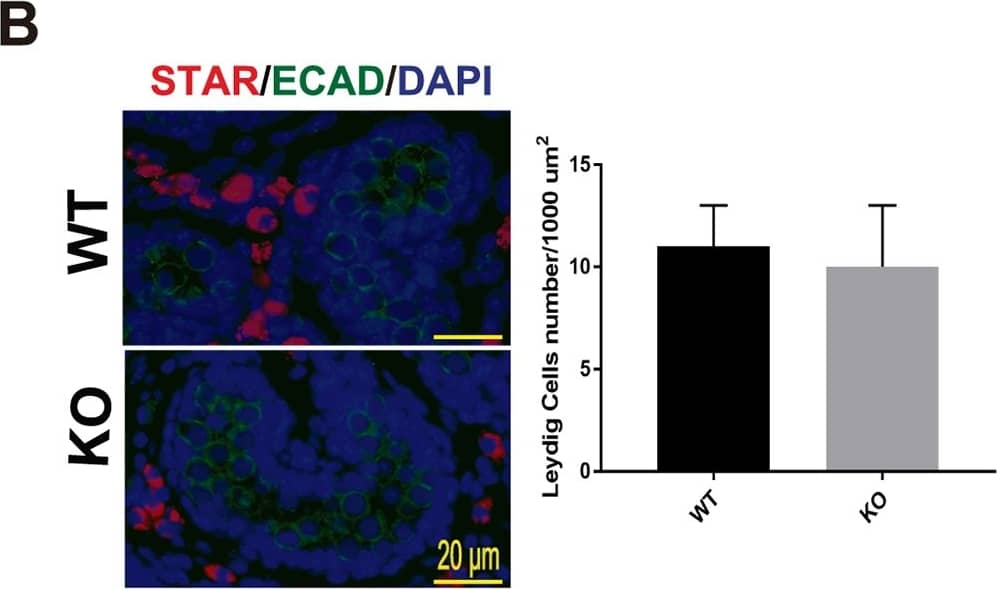
Testis morphogenesis of Mafb KO embryos developed normally.(A) Histological section of WT and KO E18.5 testes stained with HE. No morphological alteration or distribution was detectable. (B and C) Counts of Leydig and Sertoli cells from E18.5 WT and KO testes. Embryonic testes (n = 3 per genotype) were sectioned, and 4 sections for each gonad were randomly selected and stained with the germ cell marker E-cadherin (green) together with either STAR (red) or GATA4 (red). Numbers of STAR-positive cells outside seminiferous tubules (Leydig cells) or GATA4-positive cells inside the tubules (Sertoli cells) were counted per unit area. The values are the mean±S.D. *P<0.05. There was no significant difference between WT and KO cell counts. (D) The expression of genes involved in testes development and function. mRNA expression of the gene markers encoding for PGCs (Oct4), Leydig cells (Cyp17a1, StAR, Insl3, Hsd3b1, and Cyp11a1), and Sertoli cells (Amh, Sox9, and WT1) was determined by qRT-PCR in E18.5 WT and Mafb KO testes. Gene expression levels were normalized to Hprt. The bars represent the mean±SEM of five individuals. *P<0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190800), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse E-Cadherin by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Localization of MAFB in mouse testes.(A) Localization of MAFB in E18.5 mouse testes. Double immunostaining of MAFB with E-cadherin (ECAD), GATA4, or STAR is shown. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The color of each marker is indicated above the images. G; germ cells. S; Sertoli cells. L; Leydig cells. MAFB was specifically detected in Leydig cells and Sertoli cells. (B) Localization of MAFB in adult mouse testes. Double immunostaining of MAFB with E-cadherin (ECAD), KIT, SCP3, PNA Lectin, or vimentin is shown. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. The color of each marker is indicated above the images. All seminiferous tubules shown represent stage VII. US; undifferentiated spermatogonia. DS; differentiated spermatogonia. P; pachytene spermatocytes. Sp; spermatids. S; Sertoli cells. L; Leydig cells. MAFB was specifically detected in Leydig cells, Sertoli cells, and pachytene spermatocytes. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190800), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Detection of Mouse E-Cadherin by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
Testis morphogenesis of Mafb KO embryos developed normally.(A) Histological section of WT and KO E18.5 testes stained with HE. No morphological alteration or distribution was detectable. (B and C) Counts of Leydig and Sertoli cells from E18.5 WT and KO testes. Embryonic testes (n = 3 per genotype) were sectioned, and 4 sections for each gonad were randomly selected and stained with the germ cell marker E-cadherin (green) together with either STAR (red) or GATA4 (red). Numbers of STAR-positive cells outside seminiferous tubules (Leydig cells) or GATA4-positive cells inside the tubules (Sertoli cells) were counted per unit area. The values are the mean±S.D. *P<0.05. There was no significant difference between WT and KO cell counts. (D) The expression of genes involved in testes development and function. mRNA expression of the gene markers encoding for PGCs (Oct4), Leydig cells (Cyp17a1, StAR, Insl3, Hsd3b1, and Cyp11a1), and Sertoli cells (Amh, Sox9, and WT1) was determined by qRT-PCR in E18.5 WT and Mafb KO testes. Gene expression levels were normalized to Hprt. The bars represent the mean±SEM of five individuals. *P<0.05. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190800), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
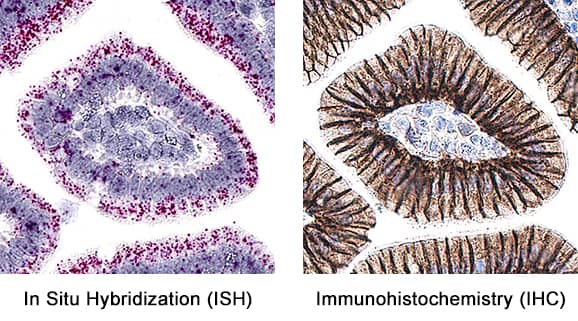
Detection of E-Cadherin in mouse intestine.
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections of mouse intestine were probed for E-Cadherin mRNA (ACD RNAScope Probe, catalog # 408651; Fast Red chromogen, ACD catalog # 322360). Adjacent tissue section was processed for immunohistochemistry using goat anti-mouse E-Cadherin polyclonal antibody (R&D Systems catalog #
AF748) at 0.5ug/mL with overnight incubation at 4 degrees Celsius followed by incubation with anti-goat IgG VisUCyte HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog #
VC004) and DAB chromogen (yellow-brown). Tissue was counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to glandular cells.
Detection of Mouse E-Cadherin by Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin
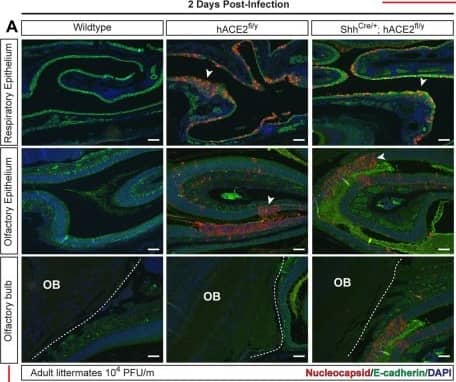
SARS-CoV-2 infection of the OE and brain in hACE2fl mice.(A, B) Immunohistochemistry of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid and epithelial cell E-cadherin in the RE, OE, and OB 2 and 5–6 days after infection of hACE2fl/y and ShhCre/+; hACE2fl/y mice. Arrowheads indicate sites of viral nucleocapsid detection. Representative of N = 4 animals per genotype and time point. Scale bars 100 μm. (C, D) Immunohistochemistry of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid, neuronal NeuN, and glial cell GFAP in the cerebral cortex (Co) 2 and 5–6 days after infection. Arrowheads indicate sites of GFAP+ reactive gliosis. Arrows indicate nucleocapsid colocalization with NeuN staining. Representative of N = 4 animals per genotype and time point. Scale bars 100 μm top, 50 μm bottom. (E) Diagram of the mouse nasal cavity and cranial anatomy. (F) In situ hybridization detection of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA 5 days postinfection reveals virus in the OB and cerebral cortex of the brain, but not the OE of the nose. Scale bar 250 μm. Note: Images in each panel were taken at lower or higher magnification from the same tissue section respective to genotype and highlight different anatomical regions. OB, olfactory bulb of the brain; OE, olfactory epithelium; RE, respiratory epithelium; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36745682), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.
Immunofluorescent Staining of Adult Stem Cell-derived Human Descending Colon Organoids.
Adult stem cells isolated from human descending colon were cultured following the steps detailed in the human intestinal organoid culture protocol. (A) The organoids were fixed and stained with a Mouse Anti-Human MUC2 Monoclonal Antibody (Novus Biologicals; Catalog # NBP2-44431; green) to visualize intestinal goblet cells and counterstained with a Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E-Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF748; red) and DAPI (Catalog # 5748; blue). The image shown was taken at 10x magnification. (B) The organoids were fixed and stained with a Mouse Anti-Human Chromogranin A Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB90981; green) to visualize enteroendocrine cells and counterstained with a Goat Anti-Human/Mouse E-Cadherin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF748; red) and DAPI (Catalog # 5748; blue). The image shown was taken at 20x magnification.
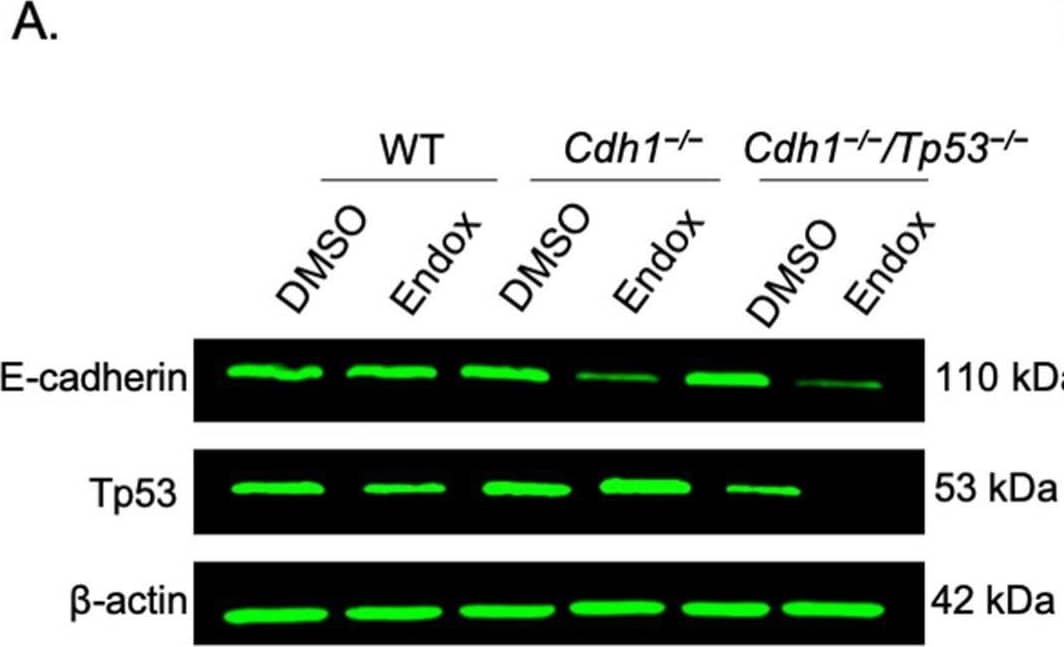
Detection of E-Cadherin by Western Blot
Characterisation of mammary organoids. (A) Endoxifen (endox) mediated knockout of E-cadherin and/or Tp53 in mammary organoids was detected utilizing western blotting. (B) Relative expression of E-cadherin and Tp53 protein in WT, Cdh1−/− and Cdh1−/−Tp53−/− mammary organoids. (C) 20× Brightfield and RFP channel images of mammary organoids induced with endoxifen. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35406381), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.