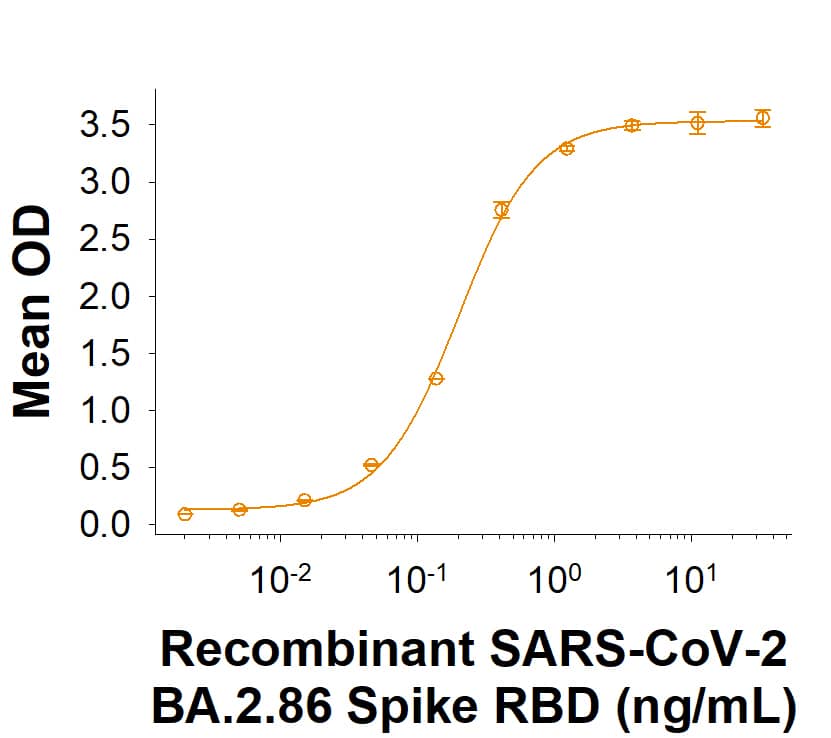
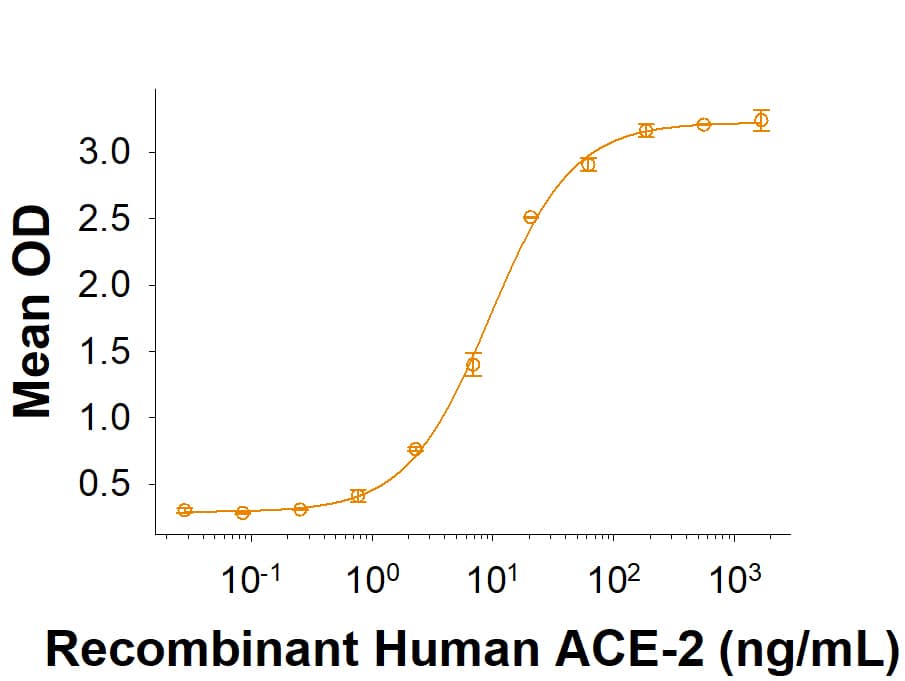
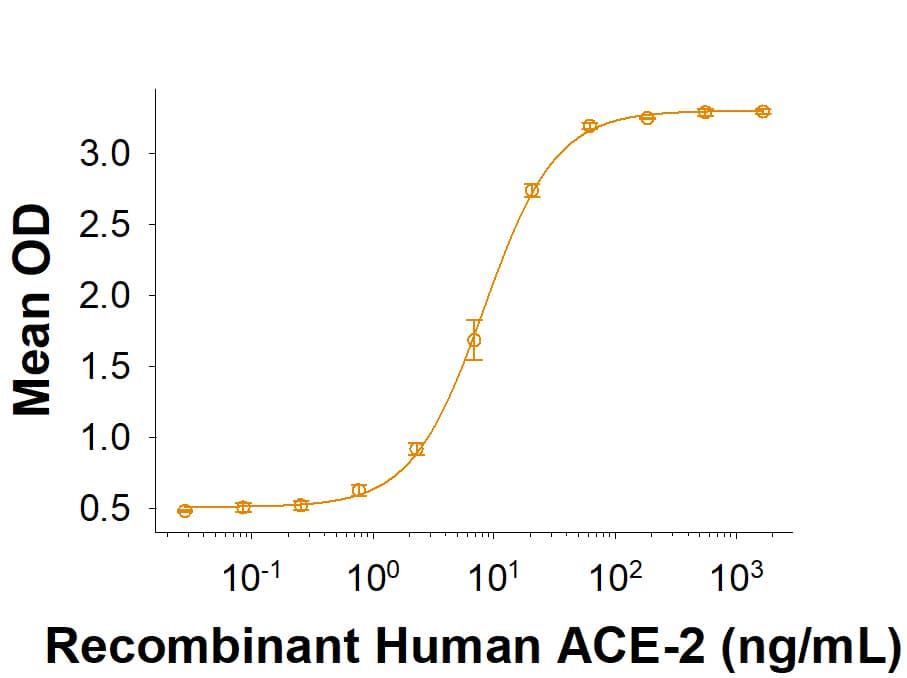
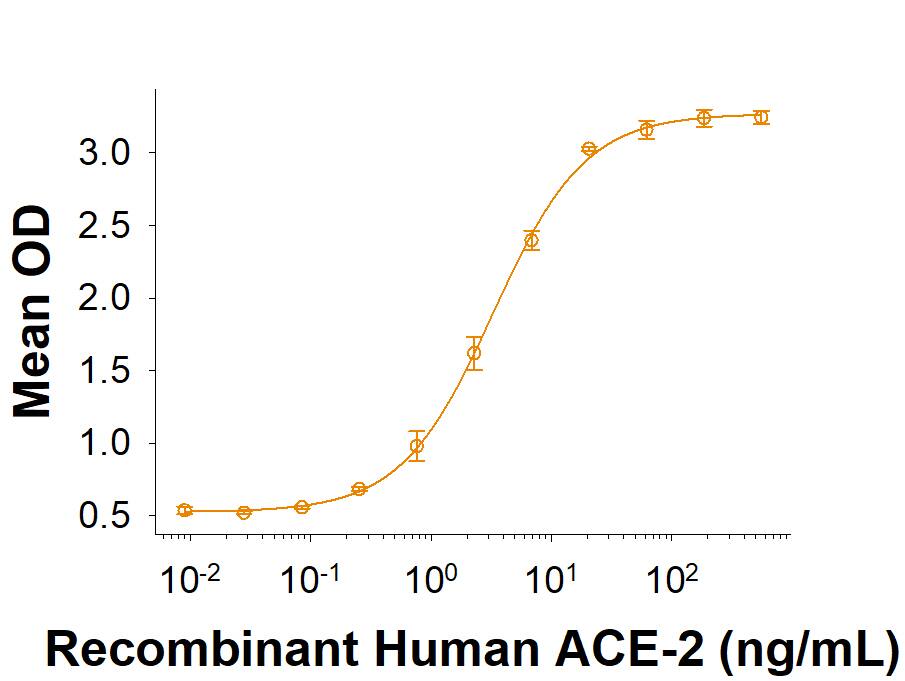
Spike RBD: Proteins and Enzymes
The coronavirus Spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD) resides within the S1 subunit and is responsible for binding to host cell receptors and initiating viral infection. Past coronaviruses SARS and MERS along with the global pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 have sparked great interest and scientific discovery leading to new vaccines and drug development. At the heart of coronavirus biology lies the Spike protein and its receptor-binding domain.
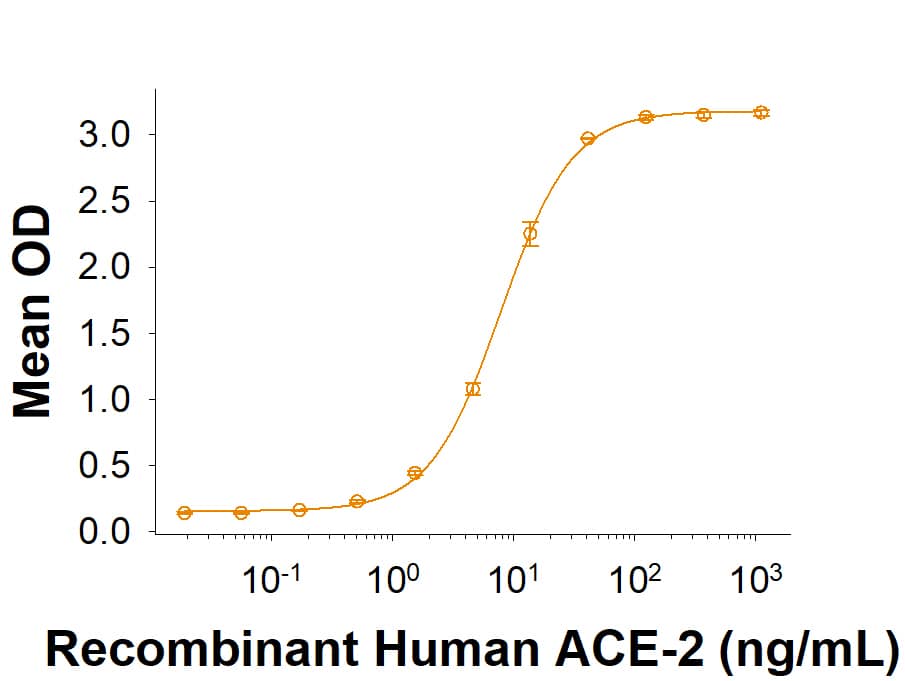
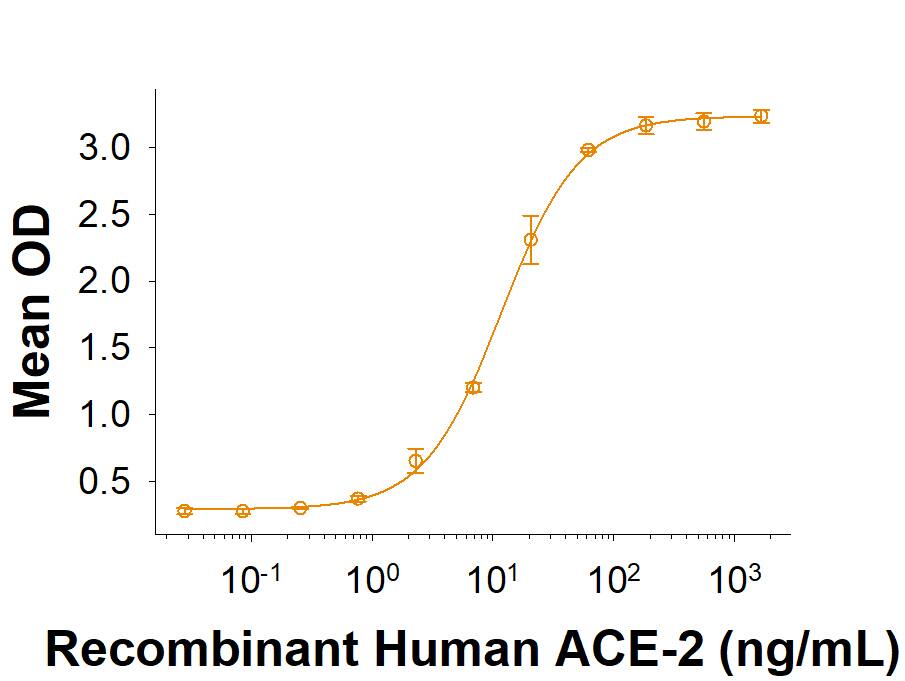
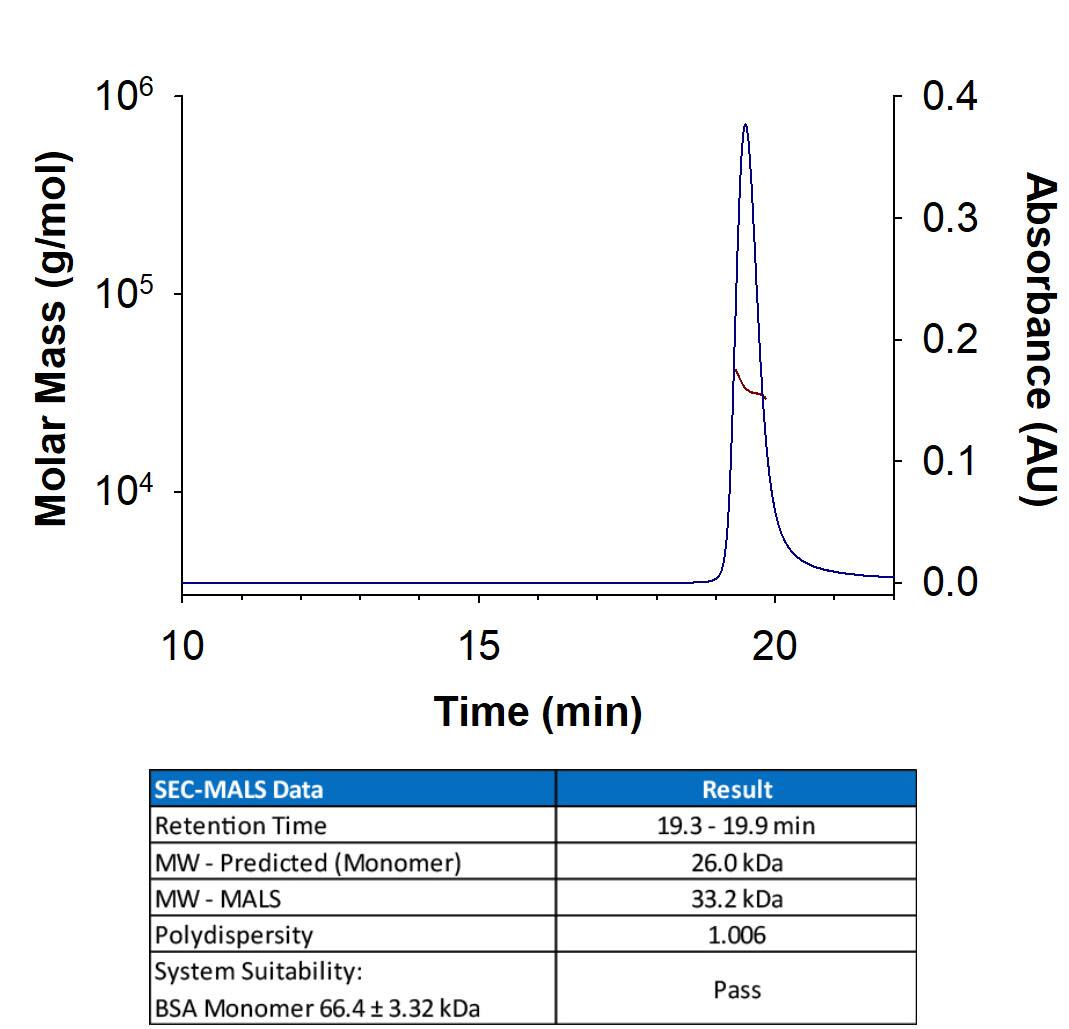
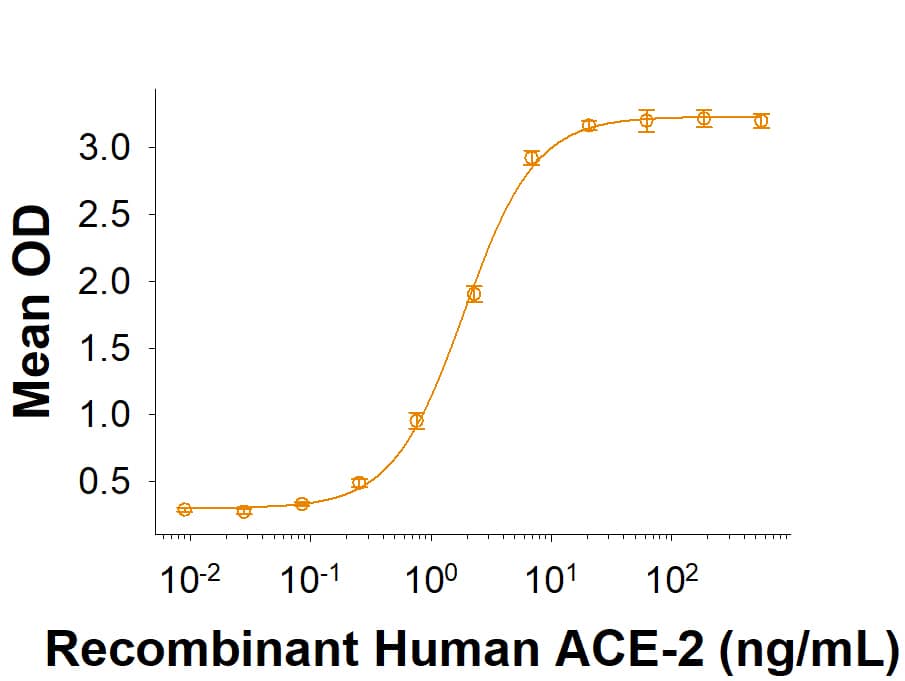
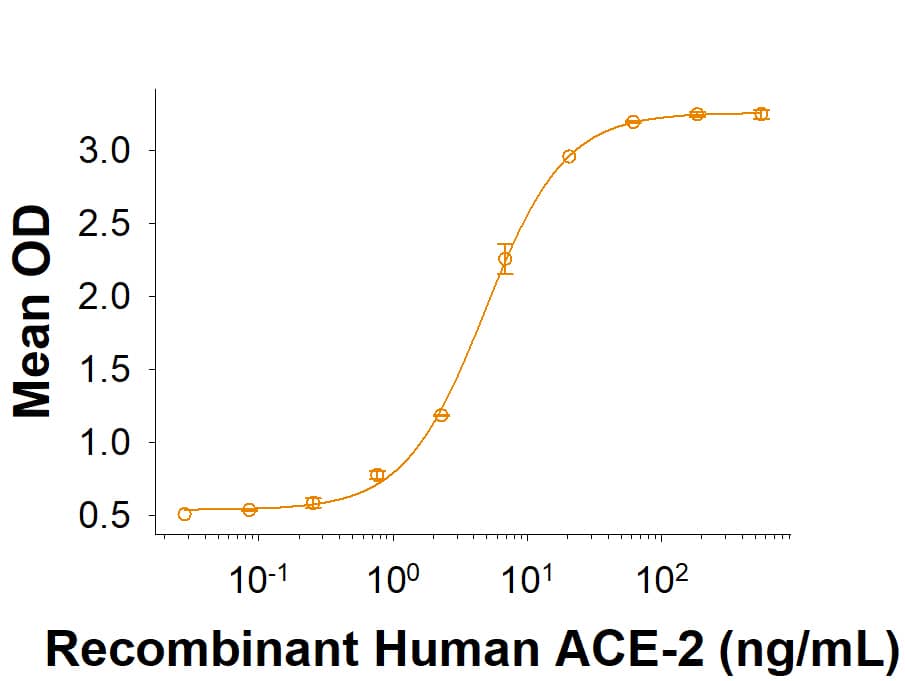
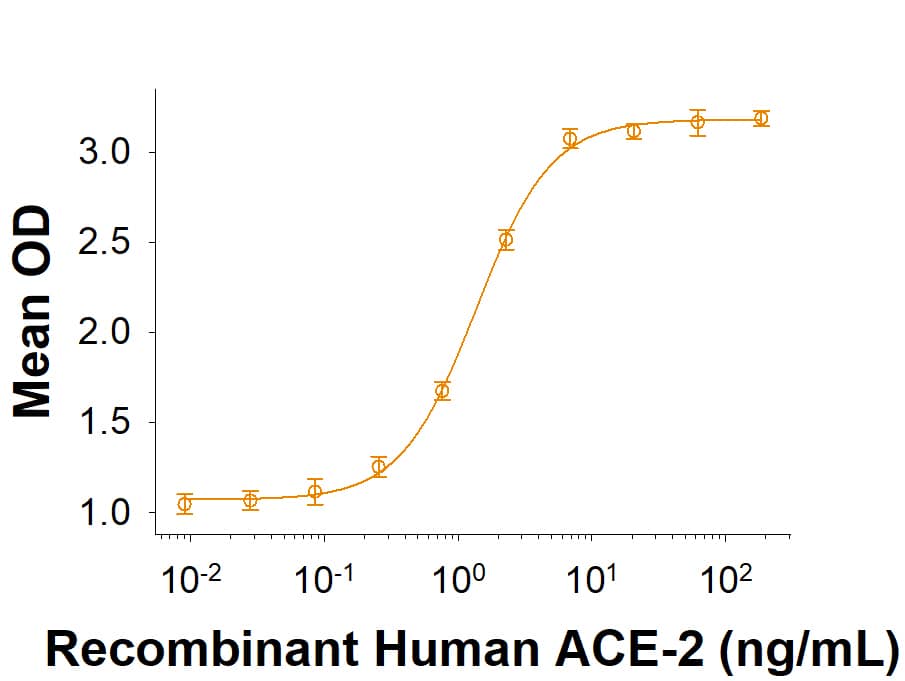
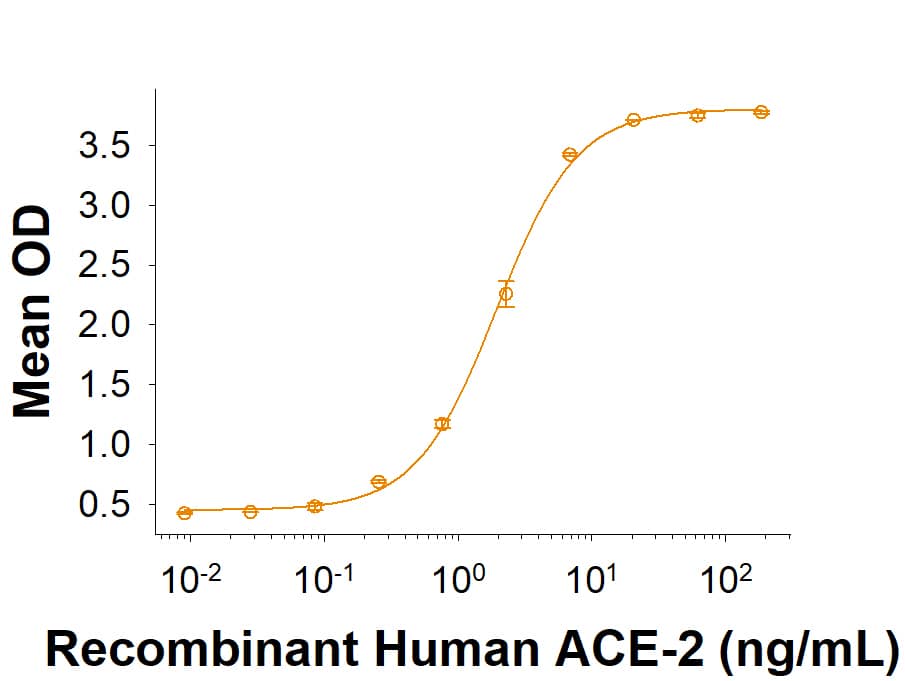
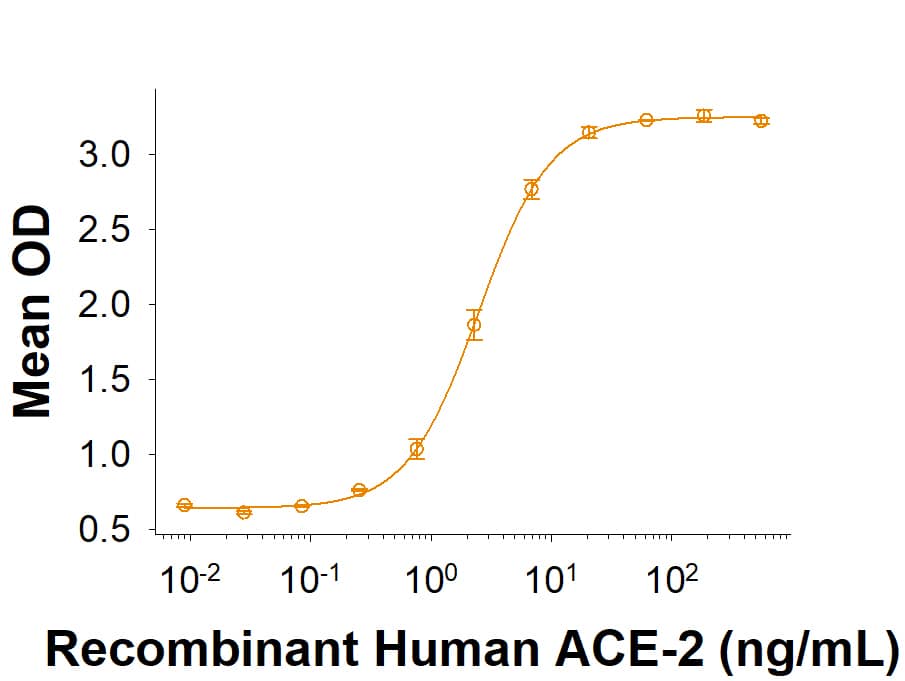
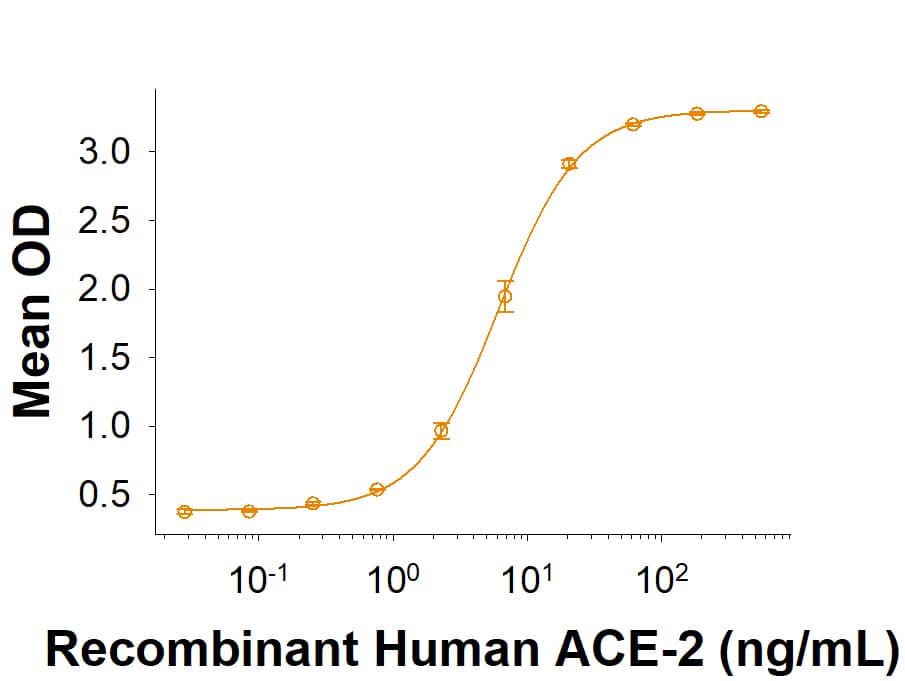
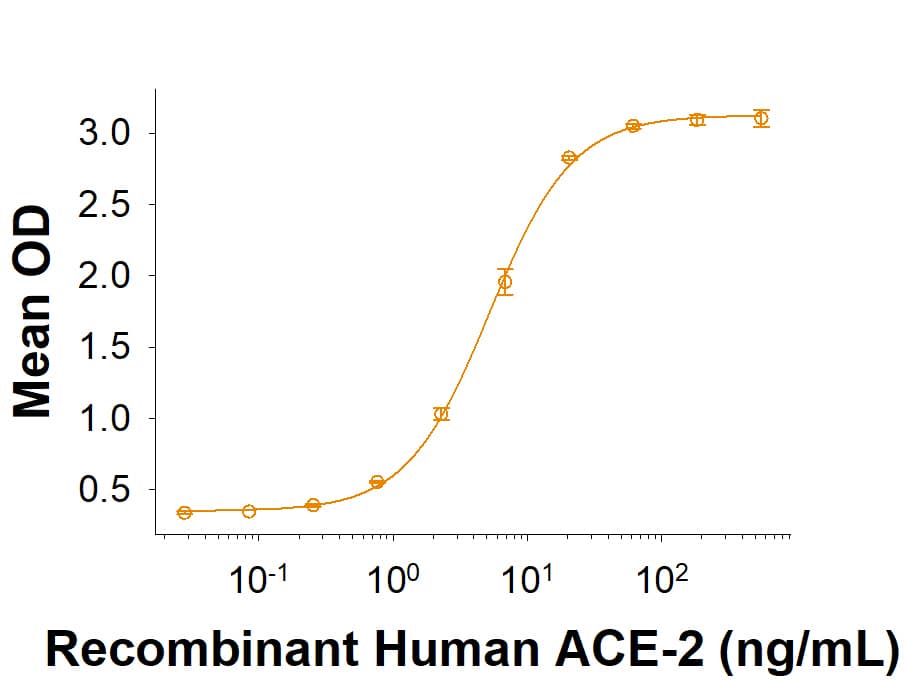
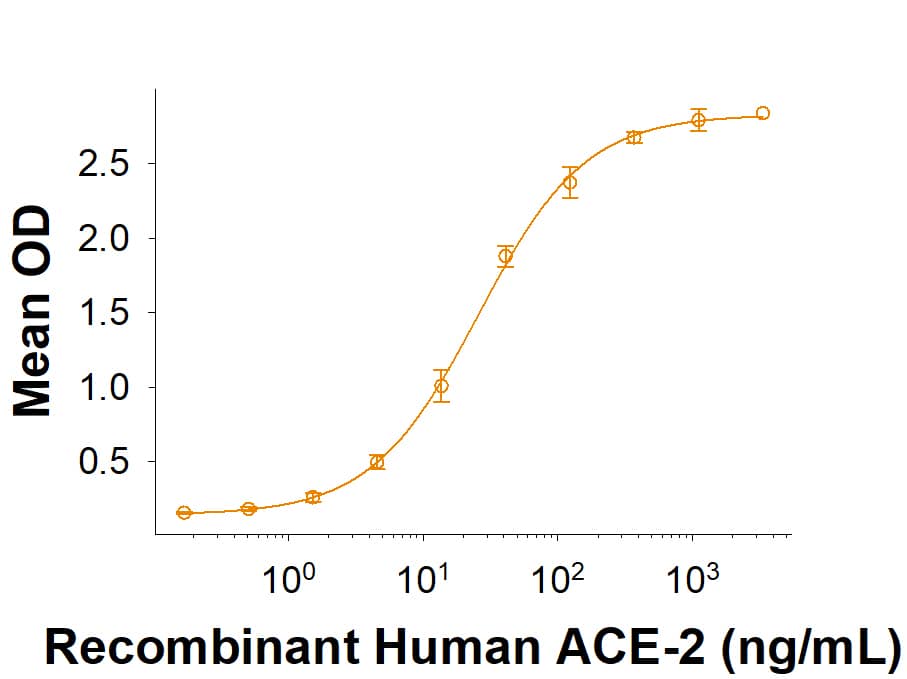
The Spike RBD is a 26 kDa domain consisting of a twisted five-stranded antiparallel beta sheet and sits at the apex of each Spike protein monomer. The Spike RBD is flexible thanks to a hinge region that allows for conformational changes that expose (up or open conformation) or hide (down or closed conformation) its receptor contacts. For SARS-CoV-2, the Spike RBD recognizes and tightly binds to the human receptor ACE-2. In the closely related MERS coronavirus, human DPPIV/CD26 acts as the receptor.
Products:
117 results for "Spike RBD Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
117 results for "Spike RBD Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
Spike RBD: Proteins and Enzymes
The coronavirus Spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD) resides within the S1 subunit and is responsible for binding to host cell receptors and initiating viral infection. Past coronaviruses SARS and MERS along with the global pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 have sparked great interest and scientific discovery leading to new vaccines and drug development. At the heart of coronavirus biology lies the Spike protein and its receptor-binding domain.
The Spike RBD is a 26 kDa domain consisting of a twisted five-stranded antiparallel beta sheet and sits at the apex of each Spike protein monomer. The Spike RBD is flexible thanks to a hinge region that allows for conformational changes that expose (up or open conformation) or hide (down or closed conformation) its receptor contacts. For SARS-CoV-2, the Spike RBD recognizes and tightly binds to the human receptor ACE-2. In the closely related MERS coronavirus, human DPPIV/CD26 acts as the receptor.
Products:
HEK293 Expressed, High ACE-2 Binding
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
HEK293 Expressed, High ACE-2 Binding
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA, BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated via Amines
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
E484K, S494P, N501Y
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Delta Variant (India) L452R T478K
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Applications: | BA |
Mammalian CHO Cell Expressed
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | NP_828851.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Kappa Variant L452R E484Q
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Tn5 Insect Cell Expressed, High ACE-2 Binding Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | T. ni (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
N501Y Mutation found in Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Variants
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
His-tag
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
N439K, E484K
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Beta Variant (South Africa), K417N, E484K, N501Y
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA, BA |
Mammalian CHO Cell Expressed, High ACE-2 Binding
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Sf21 Expressed, High ACE-2 Binding
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Mouse IgG2a Fc Chimera
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
A.23.1 Variant
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
N501Y Mutation found in UK, South African, and Brazilian Variants
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Gly476Ser Point Mutation
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
HEK293 Expressed
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | P59594.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Omicron Variant
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |