Human MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB11687

Conjugate
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Human
Applications
Simple Western, Western Blot
Label
Unconjugated
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Mouse IgG2B Clone # 1099506
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived human MAG/Siglec-4a
Gly20-Pro516
Gly20-Pro516
Specificity
Detects recombinant human MAG protein in Direct ELISA.
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Mouse
Isotype
IgG2B
Scientific Data Images for Human MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
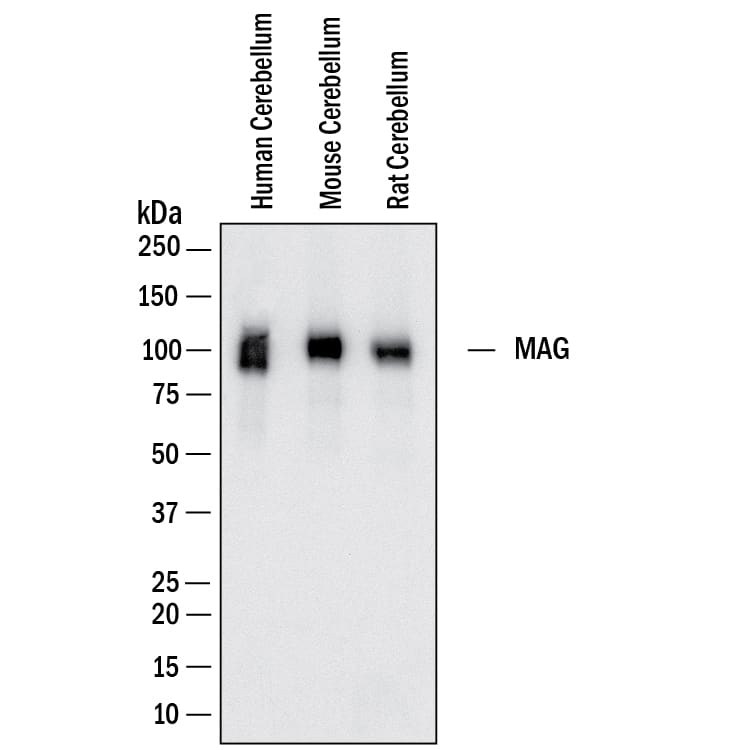
Detection of Human, Mouse and Rat MAG/Siglec-4a by Western Blot.
Western Blot shows lysates of human cerebellum, mouse cerebellum and rat cerebellum. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.1 µg/ml of Mouse Anti-Human MAG/Siglec-4a Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB11687) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for MAG/Siglec-4a at approximately 100 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Western Blot Buffer Group 1.Detection of Human, Mouse and Rat MAG/Siglec-4a by Simple WesternTM.
Simple Western lane view shows lysates of human hippocampus, mouse hippocampus and rat hippocampus, loaded at 0.5 mg/ml. A specific band was detected for MAG/Siglec-4a at approximately 110-130 kDa (as indicated) using 10 µg/ml of Mouse Anti-Human MAG/Siglec-4a Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB11687) followed by HRP-conjugated Goat Anti-Mouse Secondary Antibody (Catalog # 042-205). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230kDa separation system.Applications for Human MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
Application
Recommended Usage
Simple Western
10 µg/mL
Sample: Human hippocampus, mouse hippocampus and rat hippocampus
Sample: Human hippocampus, mouse hippocampus and rat hippocampus
Western Blot
0.1 µg/mL
Sample: Human cerebellum, mouse cerebellum and rat cerebellum
Sample: Human cerebellum, mouse cerebellum and rat cerebellum
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein A or G purified from hybridoma culture supernatant
Reconstitution
Reconstitute lyophilized material at 0.2 mg/ml in sterile PBS. For liquid material, refer to CoA for concentration.
Formulation
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose.
Shipping
Lyophilized product is shipped at ambient temperature. Liquid small pack size (-SP) is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: MAG/Siglec-4a
References
- Lopez, P.H. (2014) Adv. Neurobiol. 9:245.
- Salzer, J.L. et al. (1987) J. Cell Biol. 104:957.
- Tang, S. et al. (1997) Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 9:333.
- Schnaar, R.L. and P.H. Lopez (2009) J. Neurosci. Res. 87:3267.
- Schnaar, R.L. (2010) FEBS Lett. 584:1741.
- Akbik, F. et al. (2012) Exp. Neurol. 235:43.
- Lopez, P.H. et al. (2011) J. Neurochem. 116:900.
- Atwal, J.K. et al. (2008) Science 322:967.
- Goh, E.L. et al. (2008) Mol. Brain 1:10.
Long Name
Myelin-associated Glycoprotein
Alternate Names
Siglec-4a, Siglec4a
Gene Symbol
MAG
Additional MAG/Siglec-4a Products
Product Documents for Human MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human MAG/Siglec-4a Antibody
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
