Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AVI1506

Key Product Details
- R&D Systems CHO-derived Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag Protein (AVI1506)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Source
CHO
Accession #
Structure / Form
Biotinylated via Avi-tag
Conjugate
Biotin
Applications
Bioactivity
Product Specifications
Source
Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line, CHO-derived human DLL4 protein
| Human DLL4 (Ser27-Pro524) Accession # Q9NR61.1 |
Avi-tag | 6-His tag |
| N-terminus | C-terminus |
Purity
>90%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Ser27
Predicted Molecular Mass
58 kDa
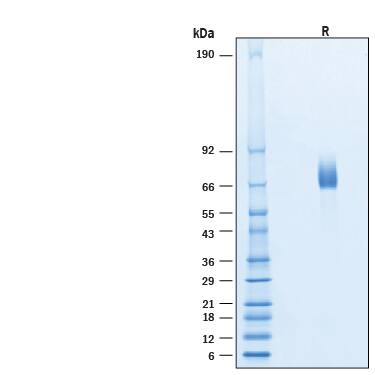
SDS-PAGE
63-75 kDa, under reducing conditions.
Activity
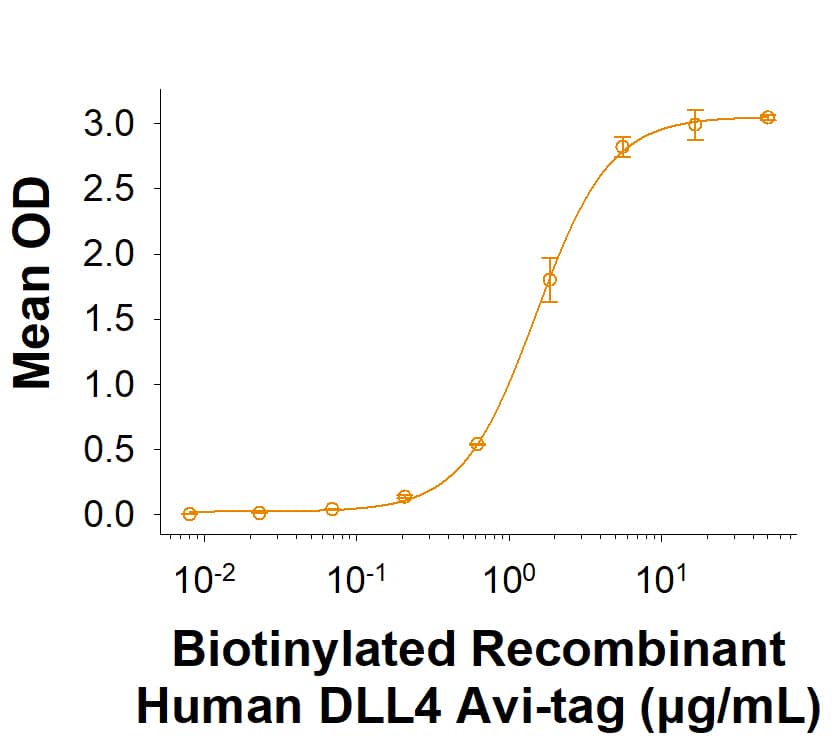
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
Biotinylated Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag (Catalog # AVI1506) binds to Recombinant Human Notch-1 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 3647-TK) with an ED50 of 0.600-7.20 μg/mL.
Biotinylated Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag (Catalog # AVI1506) binds to Recombinant Human Notch-1 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 3647-TK) with an ED50 of 0.600-7.20 μg/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag Protein, CF
Biotinylated Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag Protein Binding Activity.
In a functional ELISA, Biotinylated Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI1506) binds to Recombinant Human Notch‑1 Fc Chimera (3647-TK) with an ED50 of 0.600-7.20 μg/mL.Biotinylated Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Biotinylated Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag Protein (Catalog # AVI1506) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 63-75 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
AVI1506
| Formulation | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped with dry ice or equivalent. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: DLL4
References
- Shutter, J.R. et al. (2000) Genes Dev. 14:1313.
- Iso, Tatsuya et al. (2002) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23:543.
- Walker, L. et al. (2001) Stem Cells 19:543.
- Baron, M. (2002) Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 14:113.
- Ikeuchi, T. and S.S. Sisodia (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:7751.
- Bland, C.E. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:13607.
Long Name
Delta-like 4
Alternate Names
delta 4, Delta 4 precursor, delta ligand 4, delta4, delta-like 4 (Drosophila), delta-like 4 homolog, delta-like 4 homolog (Drosophila), delta-like 4 protein, delta-like protein 4, Drosophila Delta homolog 4, hdelta2, MGC126344, notch ligand delta-2, notch ligand DLL4
Gene Symbol
DLL4
UniProt
Additional DLL4 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human DLL4 Avi-tag His-tag Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...