Human MICA PE-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB1300P

Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human MICA PE-conjugated Antibody
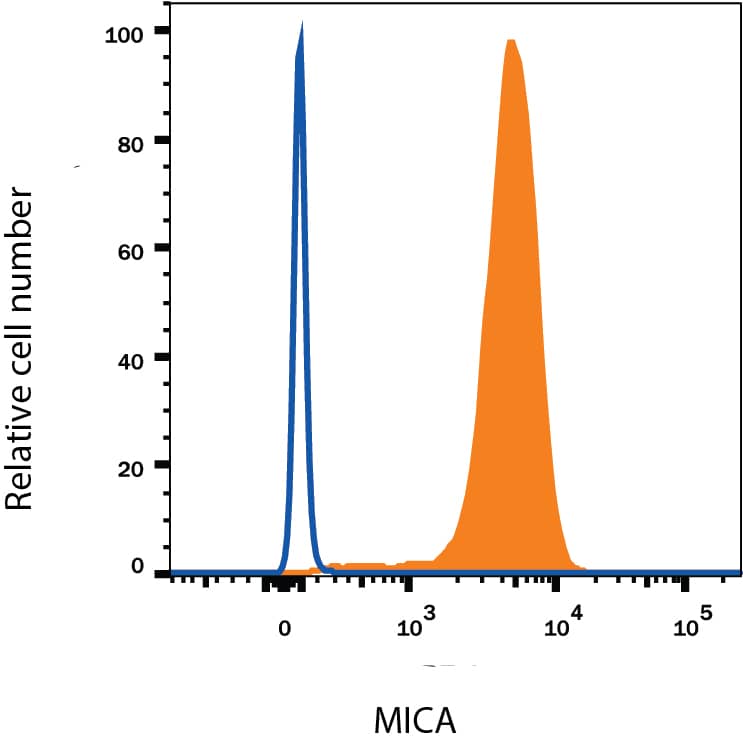
Detection of MICA in K562 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human MICA PE-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1300P, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC0041P, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.MICA Specificity is Shown by Flow Cytometry in Knockout Cell Line.
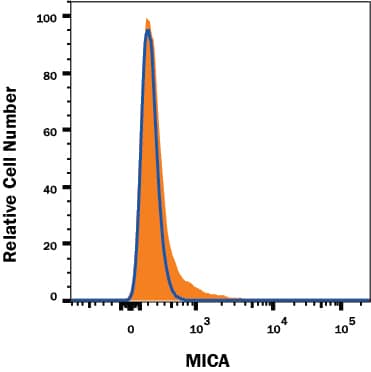
MICA knockout K562 human myelogenous leukemia cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human MICA PE-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB1300P, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC0041P, open histogram). No staining in the MICA knockout K562 cell line was observed. View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Detection of MICA by Flow Cytometry
Expression of the Sudan virus (SUDV)- or Makona-GP results in loss of surface staining of alphaMICA in HEK293T cells and JEG3 cells stably transfected with MICA. The figure shows representative flow cytometry analysis for steric shielding of the MICA antigen by SUDV-GP or Makona-GP. (A) HEK293T cells were transfected, harvested, and stained for SUDV-GP with a biotinylated 3C10 antibody, followed by allophycocyanin (APC)-conjugated streptavidin, and co-stained for MICA surface antigens with phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated alphaMICA antibody. Results are from one representative experiment of more than 10 performed (B) HEK293T cells were transfected, harvested, and stained for Makona-GP with survivor sera, followed by APC-labeled secondary antibody, and co-stained for MICA surface antigen using PE-conjugated alphaMICA antibody. Results are from one representative experiment of two performed. (C) SUDV-GP-transfected JEG3-MICA cells stained for SUDV-GP and co-stained for MICA surface antigens and NKG2D-Ig ligands. Results are from one representative experiment of more than four performed. (D–F) HEK293T cells were transfected with SUDV-GP or SUDV-GP-GFP, harvested shortly after they were treated with trypsin or left untreated, and finally stained for: (D) HLA-A, B, C, and SUDV-GP, (E) MICA and SUDV-GP, and (F) B7H6. Results are from one representative experiment of more than four performed. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30013549), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human MICA PE-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line
Knockout Validated
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: MICA
MICA (MHC class I chain-related gene A) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that functions as a ligand for human NKG2D. A closely related protein, MICB, shares 85% amino acid identity with MICA. These proteins are distantly related to the MHC class I proteins. They possess three extracellular Ig-like domains, but they have no capacity to bind peptide or interact with beta2-microglobulin. The genes encoding these proteins are found within the Major Histocompatibility Complex on human chromosome 6. The MICA locus is highly polymorphic with more than 50 recognized human alleles. MICA is absent from most cells but is frequently expressed in epithelial tumors and can be induced by bacterial and viral infections. MICA is a ligand for human NKG2D, an activating receptor expressed on NK cells, NKT cells, gamma delta T cells, and CD8+ alpha beta T cells. Recognition of MICA by NKG2D results in the activation of cytolytic activity and/or cytokine production by these effector cells. MICA recognition is involved in tumor surveillance, viral infections, and autoimmune diseases.
References
- Groh, V. et al. (2001) Nature Immunol. 2:255.
- Stephens, H. (2001) Trends Immunol. 22:378.
- Bauer, S. et al. (1999) Science 285:727.
- Groh, V. et al. (2002) Nature 419:734.
- Steinle, A. et al. (2001) Immunogenetics 53:279.
- Pende, D. et al. (2002) Cancer Res. 62:6178.
- NKG2D and its Ligands (2002) http://www.RnDSystems.com
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
Additional MICA Products
Product Documents for Human MICA PE-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human MICA PE-conjugated Antibody
For research use only