Nurr1/NGFI-B beta/NR4A2: Small Molecules and Peptides
Nurr1 belongs to the nerve growth factor-induced clone B subfamily of nuclear receptor superfamily and is designated NR4A2 in the Unified Nomenclature System for NRs. Nurr1 can function as a ligand-independent transcription factor. Nurr1 also heterodimerizes with retinoid X receptors (RXRs) to function as ligand-regulated transcription factor. Nurr 1 is important for specification of dopaminergic neurons that degenerate in Parkinsons disease. Human and mouse Nurr1 share 99% amino acid sequence homology.
2 results for "Nurr1/NGFI-B beta/NR4A2 Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
2 results for "Nurr1/NGFI-B beta/NR4A2 Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
Nurr1/NGFI-B beta/NR4A2: Small Molecules and Peptides
Nurr1 belongs to the nerve growth factor-induced clone B subfamily of nuclear receptor superfamily and is designated NR4A2 in the Unified Nomenclature System for NRs. Nurr1 can function as a ligand-independent transcription factor. Nurr1 also heterodimerizes with retinoid X receptors (RXRs) to function as ligand-regulated transcription factor. Nurr 1 is important for specification of dopaminergic neurons that degenerate in Parkinsons disease. Human and mouse Nurr1 share 99% amino acid sequence homology.
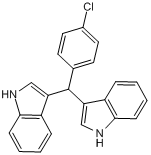
Nurr1 activator; inhibits NF-κB-dependent gene expression
| Chemical Name: | 3,3'-[(4-Chlorophenyl)methylene]bis[1H-indole] |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
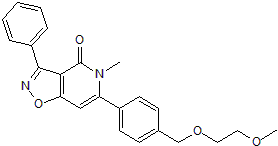
Potent Nurr1 activator
| Chemical Name: | 6-[4-[(2-Methoxyethoxy)methyl]phenyl]-5-methyl-3-phenyl-isoxazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-4(5H)-one |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |