alpha-Synuclein: Small Molecules and Peptides
alpha -Synuclein is a member of a family of small, soluble proteins that also include beta -, and gamma -Synuclein. alpha -Synuclein is one of the most highly expressed proteins in the human brain. It is predominantly expressed in neurons while lower levels are found in glial cells. alpha -Synuclein protein accumulates in the presynaptic region of nerve terminals where it is thought to play a role in synaptic vesicle biology, but its exact function remains largely unknown. The protein structure cycles between a free, partially unfolded form and a helical, membrane-bound form.
In alpha-Synucleinopathies, protein aggregates containing alpha-Synuclein protein form called Lewy Bodies, glial inclusions, or axonal spheroids depending on the disease. Lewy Bodies are associated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease dimentia. Post-secondary modifications and solubility of alpha -Synuclein are thought to affect Lewy body formation. Phosphorylation level increases before Lewy body formation and increased lipid association of alpha-Synuclein promotes formation as well. alpha -Synuclein protein aggregates have also been found associated with amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease. In vitro, alpha -Synuclein oligomers cause neuronal inflammation, degeneration, and cell death. Recombinant alpha -Synuclein protein can be used to study aggregation and toxicity in a controlled environment.
Products:
4 results for "alpha-Synuclein Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
4 results for "alpha-Synuclein Small Molecules and Peptides" in Products
alpha-Synuclein: Small Molecules and Peptides
alpha -Synuclein is a member of a family of small, soluble proteins that also include beta -, and gamma -Synuclein. alpha -Synuclein is one of the most highly expressed proteins in the human brain. It is predominantly expressed in neurons while lower levels are found in glial cells. alpha -Synuclein protein accumulates in the presynaptic region of nerve terminals where it is thought to play a role in synaptic vesicle biology, but its exact function remains largely unknown. The protein structure cycles between a free, partially unfolded form and a helical, membrane-bound form.
In alpha-Synucleinopathies, protein aggregates containing alpha-Synuclein protein form called Lewy Bodies, glial inclusions, or axonal spheroids depending on the disease. Lewy Bodies are associated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease dimentia. Post-secondary modifications and solubility of alpha -Synuclein are thought to affect Lewy body formation. Phosphorylation level increases before Lewy body formation and increased lipid association of alpha-Synuclein promotes formation as well. alpha -Synuclein protein aggregates have also been found associated with amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease. In vitro, alpha -Synuclein oligomers cause neuronal inflammation, degeneration, and cell death. Recombinant alpha -Synuclein protein can be used to study aggregation and toxicity in a controlled environment.
Products:
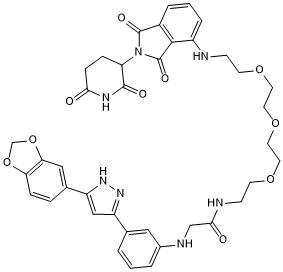
α-synuclein Degrader (PROTAC®)
| Chemical Name: | 2-[[3-[5-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]phenyl]amino]-N-[2-[2-[2-[2-[[2-(2,6-dioxo-3-piperidinyl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3-dioxo-1H-isoindol-4-yl]amino]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl]acetamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
β-secretase (BACE) inhibitor; inhibits amyloid assembly
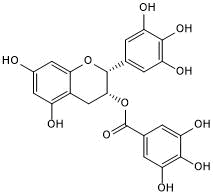
| Alternate Names: | Epigallocatechin gallate |
| Chemical Name: | 3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoic acid (2R,3R)-3,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-3-yl ester |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Potent COMT inhibitor; blocks α-synuclein aggregation
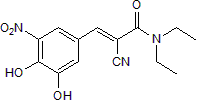
| Chemical Name: | (2E)-2-Cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-N,N-diethyl-2-propenamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
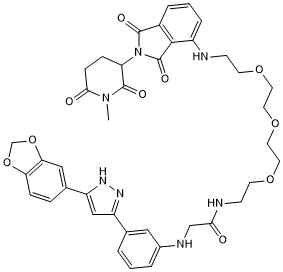
Negative control for α Synuclein Degrader 2b (Cat. No. 8040)
| Chemical Name: | 2-[[3-[5-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]phenyl]amino]-N-[2-[2-[2-[2-[[2-(1-methyl-2,6-dioxo-3-piperidinyl)-2,3-dihydro-1,3-dioxo-1H-isoindol-4-yl]amino]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl]acetamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |