Recombinant Human IL-13 R alpha 2 His-tag, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 11562-IR

Key Product Details
- R&D Systems HEK293-derived Recombinant Human IL-13 R alpha 2 His-tag (11562-IR)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Product Specifications
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Pro 43
Predicted Molecular Mass
36 kDa
SDS-PAGE
53-58 kDa, under reducing conditions
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human IL-13 R alpha 2 His-tag, CF
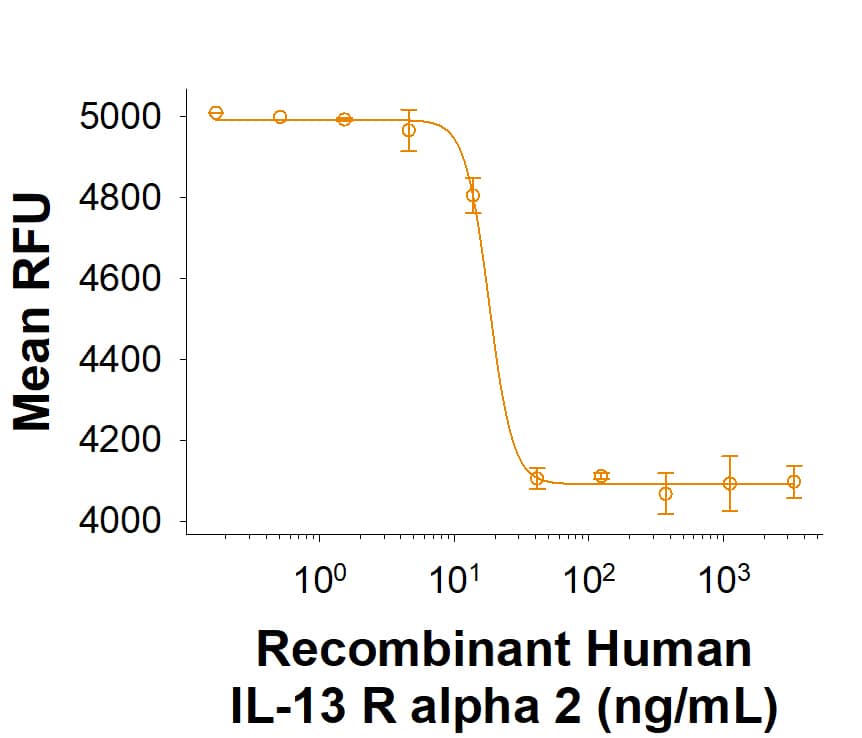
Recombinant Human IL-13 R alpha 2 His-tag Protein Bioactivity.
Recombinant Human IL-13 R alpha 2 His-tag Protein (Catalog # 11562-IR) inhibits Recombinant Human IL-13 (213-ILB) induced proliferation in the TF-1 human erythroleukemic cells. The ED50 for this effect is 4.00-60.0 ng/mL.Recombinant Human IL-13 R alpha 2 His-tag Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human IL-13 R alpha 2 His-tag Protein (Catalog # 11562-IR) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at 53-58 kDa, under reducing conditions.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
11562-IR
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 200 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Store the unopened product at -20 to -70 °C. Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Do not use past expiration date. |
Background: IL-13 R alpha 2
References
- Wynn, T.A. (2003) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21:425.
- Tabata, Y. et al. (2007) Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 7:338.
- Caput, D. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:16921.
- Chen, W. et al. (2008) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 122:625.
- O’Toole, M. et al. (2008) Clin. Exp. Allergy 38:594.
- Chen, W. et al. (2009) J. Immunol. 183:7870.
- Kasaian, M.T. et al. (2011) J. Immunol. 187:561.
- Andrews, A.-L. et al. (2006) J. Immunol. 176:7456.
- Zurawski, S.M. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270:13869.
- Donaldson, D.D. et al. (1998) J. Immunol. 161:2317.
- Andrews, A.-L. et al. (2006) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 118:858.
- Rahaman, S.O. et al. (2002) Cancer Res. 62:1103.
- Fichtner-Feigl, S. et al. (2006) Nat. Med. 12:99.
- Zhang, J.G. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:9474.
- Chiaramonte, M.G. et al. (2003) J. Exp. Med. 197:687.
- Morimoto, M. et al. (2009) J. Immunol. 183:1934.
- Zheng, T. et al. (2008) J. Immunol. 180:522.
Long Name
Interleukin 13 Receptor alpha 2
Alternate Names
CD213a2, IL-13Ra2, IL13R alpha 2, IL13RA2
Gene Symbol
IL13RA2
UniProt
Additional IL-13 R alpha 2 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human IL-13 R alpha 2 His-tag, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human IL-13 R alpha 2 His-tag, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...