Recombinant Human CD160 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 11575-CD

Key Product Details
- R&D Systems CHO-derived Recombinant Human CD160 Fc Chimera Protein (11575-CD)
- Quality control testing to verify active proteins with lot specific assays by in-house scientists
- All R&D Systems proteins are covered with a 100% guarantee
Source
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
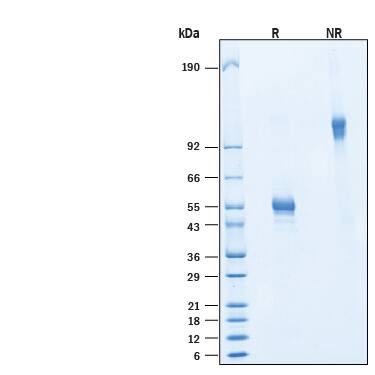
SDS-PAGE
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human CD160 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
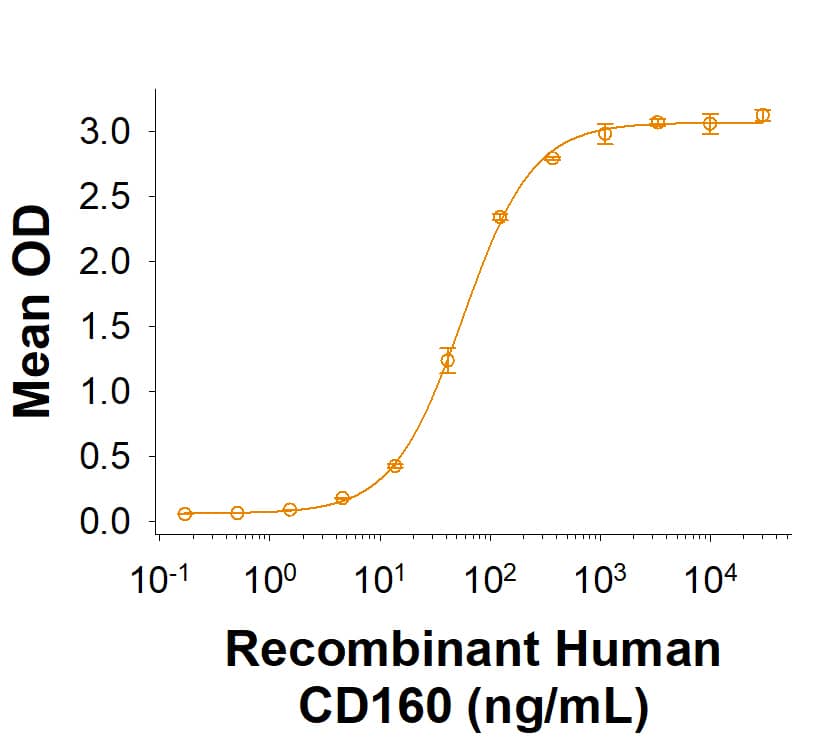
Recombinant Human CD160 Fc Chimera Protein Binding Activity.
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Recombinant Human CD160 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 11575-CD) binds to Recombinant Human HVEM/TNFRSF14 Fc Chimera Protein (11177-HV) with an ED50 of 30.0-300 ng/mL.Recombinant Human CD160 Fc Chimera Protein SDS-PAGE.
2 μg/lane of Recombinant Human CD160 Fc Chimera Protein (Catalog # 11575-CD) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) and non-reducing (NR) conditions and visualized by Coomassie® Blue staining, showing bands at SDS-PAGE 39-59 kDa and 80-120 kDa, respectively.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
11575-CD
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 250 μg/mL in sterile water. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Store the unopened product at -20 to -70 °C. Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Do not use past expiration date. |
Background: CD160
CD160 (also Natural killer cell receptor BY55) is a 27 ‑ 30 kDa member of the Ig superfamily (1 ‑ 4). In human, it is expressed principally on nonmyeloid hematopoietic cells. These include CD56DIMCD16+ cytolytic NK cells, CD8+CD28- T cells, CD8+CD101+ IELs, NKT cells, gamma delta TCR T cells, activated CD4+ T cells, and vascular endothelial cells (1, 5 ‑ 7). CD160 was initially identified as a GPI‑linked glycoprotein (3). It is synthesized as a preproprotein that is 181 amino acids (aa) in length. The precursor contains a 26 aa signal sequence, a 133 aa mature molecule that shows one 96 aa V‑type Ig‑like domain (aa 27 ‑ 122), and a 22 aa prosegment that is cleaved to generate a GPI‑linkage at Ser159. GPI‑linked CD160 is known to be cleaved by phospholipases and these generate an 80 kDa (presumably trimeric) band in SDS‑PAGE (1, 8). Alternative splice forms for CD160 are reported to exist on activated NK cells. The principal variant is an extended type I transmembrane (TM) protein that shows a 55 aa substitution for the C‑terminal two amino acids. It contains a 23 aa TM segment (aa 160 ‑ 182) and a 52 aa cytoplasmic region. Two other variants show deletions of the Ig‑like domain in both the GPI‑linked and TM form (9). Mature human CD160 shares 62% aa identity with mouse CD160.
CD160 is known to bind to HLA-G1, HLA-C, and HVEM (6, 9, 10). And upon engagement, it is reported to associate with CD2 in cis under certain conditions (11, 12). The effects of CD160 ligation appear to be context dependent. When expressed on endothelial cells, CD160 binding to HLA-G1 initiates apoptosis, and thus impacts angiogenesis (6). When expressed on CD56DIM NK cells, CD160 signaling in response to HLA-C binding promotes IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 secretion (10). And when up‑regulated on CD4+ T cells following activation, CD160 engagement by HVEM (expressed by APC) serves to block a simultaneous LIGHT stimulation of HVEM that promotes receptor expression and cytokine release (1, 2, 7, 13).
References
- Cai, G. & G.J. Freeman (2009) Immunol. Rev. 229:244.
- del Rio, M.L. et al. (2010) J. Leukoc. Biol. 87:223.
- Maiza, H. et al. (1993) J. Exp. Med. 178:1121.
- Anumanthan, A. et al. (1998) J. Immunol. 161:2780.
- Abecassis, S. et al. (2007) J. Invest. Dermatol. 127:1161.
- Fons, P. et al. (2006) Blood 108:2608.
- Kaye, J. et al. (2008) Nat. Immunol. 9:122.
- Giustiniani, J. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 178:1293.
- Giustinani, J. et al. (2009) J. Immunol. 182:63.
- Barakonyi, A. et al. (2004) J. Immunol. 173:5349.
- Nikolova, M. et al. (2002) Int. Immunol. 14:445.
- Rabot, M. et al. (2006) Transpl. Immunol. 17:36.
- Cai, G. et al. (2008) Nat. Immunol. 9:176.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
Additional CD160 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human CD160 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human CD160 Fc Chimera Protein, CF
For research use only