Mouse SCF/c-kit Ligand Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AB-455-NA

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Lys26-Ala189
Accession # Q78ED8
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Mouse SCF/c-kit Ligand Antibody
Cell Proliferation Induced by SCF/c-kit Ligand and Neutralization by Mouse SCF/c-kit Ligand Antibody.
Recombinant Mouse SCF/ c-kit Ligand (Catalog # 455-MC) stimulates proliferation in the TF-1 human erythro-leukemic cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Mouse SCF/c-kit Ligand (25 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Mouse SCF/ c-kit Ligand Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AB-455-NA). The ND50 is typically 4-20 µg/mL.Detection of Mouse SCF/c-kit Ligand by Immunohistochemistry
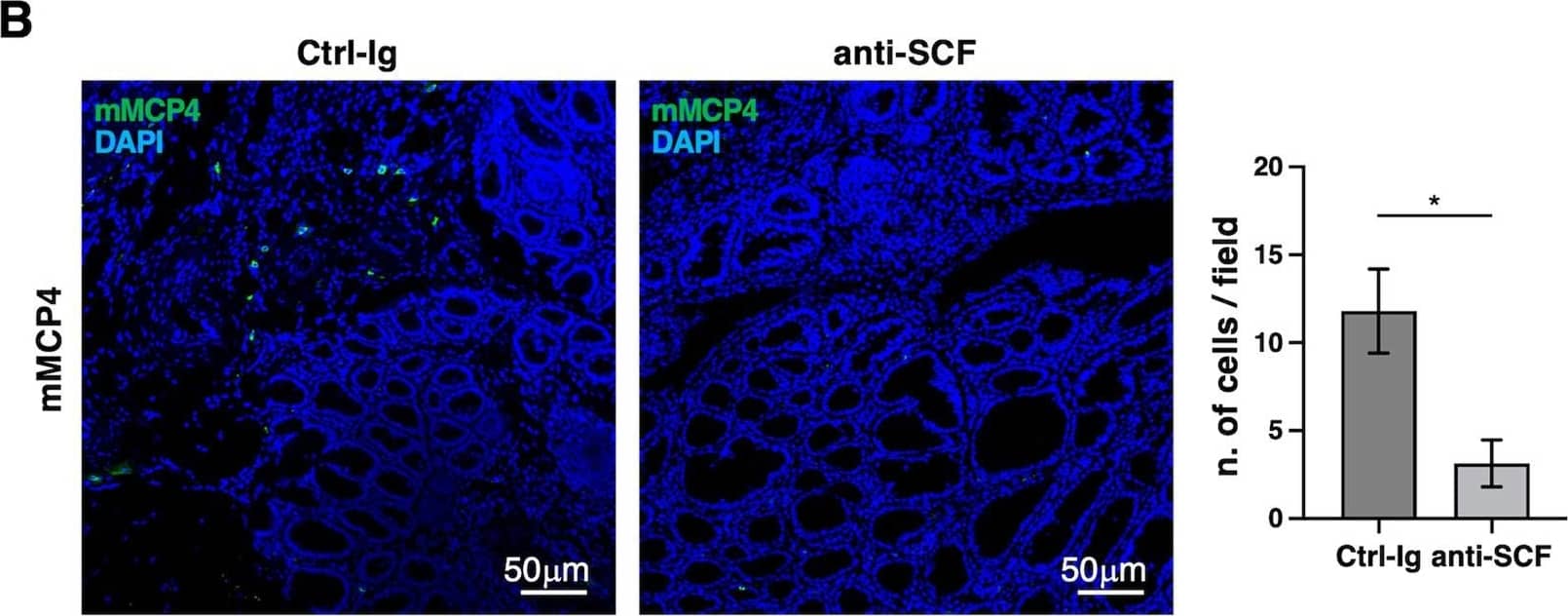
SCF controls connective tissue-like MC accumulation in tumor lesions. A Schematic representation of anti-SCF neutralizing Ab administration in vivo. AOM/DSS-treated mice were i.p. injected three times with anti-SCF or control Ab (100 μg/mouse) starting from the fourth DSS cycle. Treated and control mice were sacrificed at 13 weeks from AOM administration. B Colon paraffin-embedded sections from AOM/DSS mice treated with Ctrl-Ig or anti-SCF neutralizing antibodies as described in (A) were stained with anti-MCP4 Ab followed by Alexa Fluor 488 secondary Abs (green). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue) and images were acquired with a Zeiss LSM980 confocal microscopy using a 20× objective. The frequencies of MCs positive for mMCP4 protease were analyzed in 20 fields randomly acquired from tumor lesions and shown as mean ± SD cells/field. Paired Student’s t test: *p < 0.05. Number of adenomas and colon lengths are shown in (C). Paired Student’s t test: *p < 0.05. Graphs are representative of two independent experiments with a total of 5 mice/group. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37730723), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse SCF/c-kit Ligand Antibody
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse SCF/c-kit Ligand (Catalog # 455-MC)
Neutralization
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: SCF/c-kit Ligand
Stem cell factor (SCF), also known as c-kit ligand (KL), mast cell growth factor (MGF), and steel factor (SLF), is a widely expressed 28-40 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein (1). It promotes the survival, differentiation, and mobilization of multiple cell types including myeloid, erythroid, megakaryocytic, lymphoid, germ cell, and melanocyte progenitors (1-7). SCF is a primary growth and activation factor for mast cells and eosinophils (8). Mature mouse SCF consists of a 189 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD), a 23 aa transmembrane segment, and a 36 aa cytoplasmic tail (9). The ECD shows both N-linked and O-linked glycosylation (10). Proteolytic cleavage at two alternate sites in the extracellular juxtamembrane region releases a 25 kDa soluble molecule which is comparable to the only form produced by Steel-dickie mutant mice (11, 12). An alternately spliced isoform of mouse SCF lacks 28 aa that encompasses the primary proteolytic recognition site (13). Within the ECD of the short isoform (corresponding to this recombinant protein), mouse SCF shares 93% aa sequence identity with rat SCF and 72-75% with canine, feline, and human SCF. Rat SCF is active on mouse and human cells, but human SCF is only weakly active on mouse cells (14). Non-covalent dimers of transmembrane or soluble SCF interact with the receptor tyrosine kinase SCF R/c-kit to trigger receptor dimerization and signaling (15). SCF assists in the recovery of cardiac function following myocardial infarction by increasing the number of cardiomyocytes and vascular channels (16).
References
- Ashman, L.K. (1999) Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 31:1037.
- Sette, C. et al. (2000) Int. J. Dev. Biol. 44:599.
- Yoshida, H. et al. (2001) J. Invest. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 6:1.
- Erlandsson, A. et al. (2004) Exp. Cell Res. 301:201.
- Kapur, R. et al. (2002) Blood 100:1287.
- Wang, C.-H. et al. (2007) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 27:540.
- Bashamboo, A. et al. (2006) J. Cell Sci. 119:3039.
- Reber, L. et al. (2006) Eur. J. Pharmacol. 533:327.
- Huang, E. et al. (1990) Cell 63:225.
- Arakawa, T. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:18942.
- Majumdar, M.K. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:1237.
- Brannan, C.I. et al. (1991) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:4671.
- Flanagan, J.G. et al. (1991) Cell 64:1025.
- Martin, F.H. et al. (1990) Cell 63:203.
- Lemmon, M.A. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272:6311.
- Kanellakis, P. et al. (2006) Cardiovasc. Res. 70:117.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional SCF/c-kit Ligand Products
Product Documents for Mouse SCF/c-kit Ligand Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse SCF/c-kit Ligand Antibody
For research use only